Schedule 40 Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe 12Cr2Mo CNBM
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 30 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details
| Thickness: | 1.73 - 59.54 mm | Section Shape: | Round | Outer Diameter: | 10.3 - 914.4 mm |
| Secondary Or Not: | Non-secondary | Application: | Fluid Pipe | ||
| Technique: | Hot Rolled | Certification: | API | Surface Treatment: | Galvanized,vanish covering, black painting, galvenized ect. |
| Special Pipe: | API Pipe | Alloy Or Not: | Non-alloy | Length: | 5-12m as per customer's requirements |
| SCH: | SCH10~160, STD, XS & XXS | Payment Terms: | L/C T/T | Supply Ability: | 5000 Ton/Tons per Week |
| Product: | pipe prices | Grade: | 10#,20#,45#,A106(B,C),A53(A,B),12Cr1MoV,12Cr1MoVG,12Cr2Mo,13CrMo44,13CrMo45,15CrMo,15CrMoG,St52,St52.4,10#-45#,A53-A369,Cr-Mo alloy,ST35-ST52 | Standard: | API 5CT,API 5L,ASTM A106-2006,ASTM A53-2007,DIN 17175,GB 3087-1999,GB 5130,GB 6479-2000,GB 9948-2006,GB/T 17396-1998,GB/T 5312-1999,GB/T 8162-1999,GB/T 8163-1999,API,ASTM,DIN,GB |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Detail: | By bundles, seaworthy wooden cases, steel framed cases, and simple packaging or according to the demand of the customers. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 5-15 days |
Specifications
1.pipe prices
2.Supply Ability:5000 Tons per Week
3.Payment Terms:L/C T/T
High quality Carbon steel pipe, Best pipe prices
1) Application: Overheat pipe for low and mediumpressure boiler,boiling water pipe, locomotive smoke pipe(big and small),Carry gas ,water or oil in the industries of petroleum and natural gas etc
2) Materials: 10#, 20#, 45#, 15CrMo, 12Cr1MoV, 13CrMo44, 12Cr2Mo, 13CrMo45, 12Cr1MoVG, 15CrMoG, API J55, API K55, API N80, API L80, API P110
3)Pipe according to standard: GB 3087-1999, GB/T 8163-1999, GB/T 8162-1999, GB 9948-2006, GB/T 17396-1998, GB/T 5312-1999, GB 6479-2000, GB 5130, DIN 17175, API 5CT, API 5L .
4)Packing: By bundles, seaworthy wooden cases, steel framed cases, and simple packaging or according to the demand of the customers.
Technical Parameters of Seamless Steel Pipe
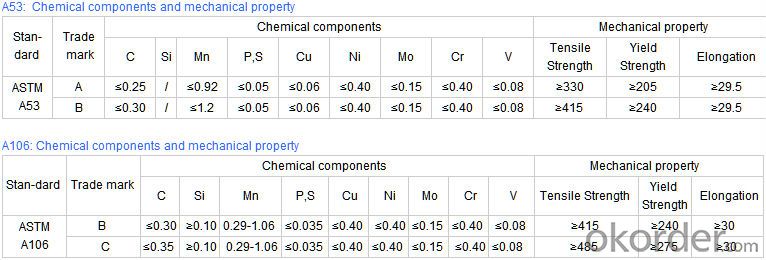
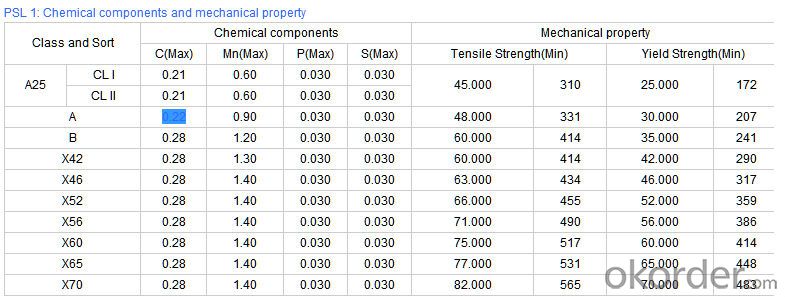
- Q: How do you inspect steel pipes for defects?
- The inspection of steel pipes for defects requires a methodical approach that combines visual examination, non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques, and specialized equipment. The following are the typical steps undertaken to inspect steel pipes for defects: 1. Visual Examination: Commence by visually inspecting the external surface of the pipe, searching for any visible indications of defects, including cracks, dents, or corrosion. Particular attention should be given to welds, joints, and areas prone to stress or damage. 2. Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Ultrasonic testing is commonly employed to identify internal defects in steel pipes. This technique involves transmitting ultrasonic waves into the pipe and then interpreting the echoes received. Any irregularities in the internal structure, such as cracks or voids, can be identified and analyzed. 3. Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI): MPI is a widely utilized technique for detecting defects on or near the surface, such as cracks, seams, or other discontinuities. This method involves applying a magnetic field to the pipe and subsequently applying ferromagnetic particles (usually iron-based) to the surface. These particles accumulate and form visible indications at areas where magnetic flux leakage is caused by defects. 4. Eddy Current Testing (ECT): Eddy current testing is suitable for detecting surface and near-surface defects in conductive materials like steel. This technique involves inducing an alternating current into the pipe and monitoring changes in the electrical currents induced by any present defects. These changes are then analyzed to identify and evaluate the defects. 5. Radiographic Testing (RT): Radiographic testing is conducted by exposing the steel pipe to X-rays or gamma rays and capturing radiographic images of the pipe. This technique allows for the detection of internal defects, such as cracks, porosity, inclusions, or variations in wall thickness. The radiographic images are subsequently examined for any indications of defects. 6. Dye Penetrant Inspection (DPI): DPI is a method used to identify defects on the surface of steel pipes. It involves applying a liquid dye to the surface, which penetrates into any surface cracks or flaws. After sufficient time for the dye to seep in and react, excess dye is removed, and a developer is applied to draw out the dye from the defects, rendering them visible. 7. Pressure Testing: Pressure testing entails pressurizing the steel pipe to a predetermined level and monitoring for any pressure drops or leaks. This test ensures that the pipe can withstand the required pressure without any structural defects. It is worth noting that the choice of inspection technique depends on various factors, such as the type of defect being sought, the size and characteristics of the pipe, and the specific industry standards and regulations. Inspection professionals with expertise in NDT methods and equipment are typically employed to ensure precise and dependable results.
- Q: What are the environmental benefits of using steel pipes?
- There are several environmental benefits of using steel pipes: 1. Durability: Steel pipes have a long lifespan, which reduces the need for frequent replacements. This helps to conserve resources and reduces the amount of waste generated. 2. Recyclability: Steel is one of the most recycled materials in the world. When steel pipes reach the end of their life, they can be easily recycled and used to manufacture new steel products. This reduces the demand for raw materials and saves energy that would otherwise be required for the production of new materials. 3. Reduced carbon emissions: Steel pipes have a low carbon footprint compared to other materials like concrete or plastic. The manufacturing process for steel pipes produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a lower carbon footprint overall. 4. Resistance to corrosion: Steel pipes have high resistance to corrosion, which means they require less maintenance and repair compared to other materials. This reduces the use of chemical coatings and treatments that can have negative environmental impacts. 5. Water conservation: Steel pipes are commonly used for water supply and distribution systems. They have smooth interiors that minimize friction, reducing the amount of energy required to pump water through the pipes. This helps to conserve energy and decrease the carbon emissions associated with water transportation. 6. Fire resistance: Steel pipes are inherently fire-resistant, which makes them a safer choice for many applications. In the event of a fire, steel pipes can help to contain the spread of flames and minimize damage to the environment. Overall, the use of steel pipes offers numerous environmental benefits such as durability, recyclability, reduced carbon emissions, water conservation, and fire resistance. These factors make steel pipes a sustainable choice for various infrastructure projects.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in the agricultural sector?
- Steel pipes are commonly used in the agricultural sector for various purposes such as irrigation systems, drainage systems, and construction of structures like greenhouses and barns. They are durable, strong, and can withstand harsh weather conditions, making them ideal for these applications in the agricultural industry.
- Q: Are steel pipes resistant to corrosion?
- Yes, steel pipes are generally resistant to corrosion due to their composition, which includes a protective layer of zinc or other anti-corrosion coatings. However, factors such as exposure to harsh environments or chemicals can affect the level of corrosion resistance.
- Q: What material is RHS in the steel tube?
- The CHS structure represents thin-walled round steel tubes, in which materials are referred to Taiwan CHS's steel and are used to indicate the series of anti rust paints used in metal materials.
- Q: What is the fatigue strength of steel pipes?
- The fatigue strength of steel pipes refers to the maximum stress level that the pipes can endure without experiencing fatigue failure or damage over a given number of stress cycles. It varies depending on factors such as the steel composition, manufacturing process, pipe dimensions, and environmental conditions.
- Q: What does "SC50" steel pipe mean in civil engineering?
- Welded steel pipe refers to the use of steel or steel plate bending deformation into a round, square and other shapes after welding into the surface of the joint of the steel pipe. The blank used in welded steel pipe is steel or strip steel.
- Q: What are the different methods of pipe joining for steel pipes?
- The different methods of pipe joining for steel pipes include welding, threaded connections, flanged connections, and grooved connections. Welding involves melting the two ends of the pipes together to form a strong bond. Threaded connections involve screwing the pipes together using thread tape or sealants to create a tight seal. Flanged connections use flanges and bolts to join the pipes together, providing a secure and leak-proof connection. Grooved connections involve using grooved couplings and gaskets to connect the pipes, allowing for quick and easy installation.
- Q: Can steel pipes be used for hydraulic systems?
- Yes, steel pipes can be used for hydraulic systems. Steel pipes are commonly used in hydraulic systems due to their high strength, durability, and ability to handle high pressure. They provide excellent resistance to corrosion and can effectively transport hydraulic fluids, making them a suitable choice for various hydraulic applications.
- Q: How are steel pipes protected against internal corrosion?
- Steel pipes are protected against internal corrosion primarily through the use of protective coatings such as epoxy or polyethylene. These coatings act as a barrier, preventing contact between the steel surface and corrosive substances present in the transported fluids. Additionally, corrosion inhibitors are often added to the transported fluids to further reduce the likelihood of internal corrosion. Regular inspections and maintenance are also carried out to identify any potential corrosion issues and address them promptly.
Send your message to us
Schedule 40 Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe 12Cr2Mo CNBM
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 30 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























