Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Corundum Castable for EAF Roof
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Corundum Castable for EAF Roof
Made as per international standards, FIREF corundum castable for EAF roof is known for its excellent corrosion and scouring resistance of iron steel, long operating life and easy execution and mending. Further, FIREF corundum castable for EAF roof can be provided in different specifications as required by the clients.
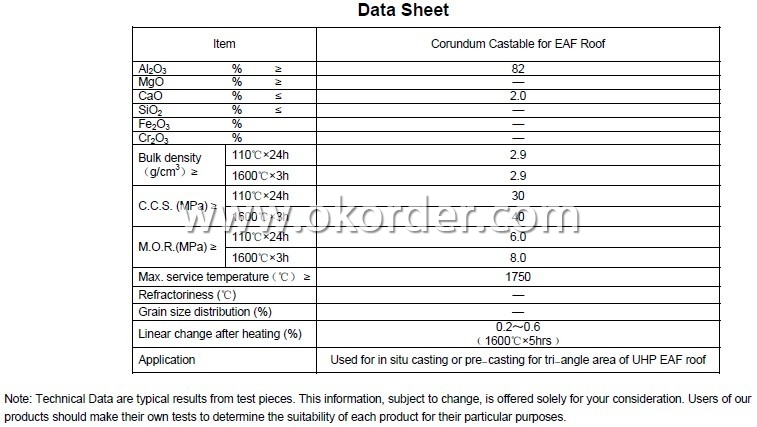
Technical data of Corundum Castable for EAF Roof
Production line and packing of Corundum Castable for EAF Roof


Feature of Corundum Castable for EAF Roof
Excellent corrosion and scouring resistance of iron steel
Long operating life
Easy execution and mending
Application of Corundum Castable for EAF Roof
FIREF corundum castable for EAF roof can be used widely for in situ casting or pre-casting for tri-angle area of UHP EAF roof.
Production Flow of Corundum Castable for EAF Roof
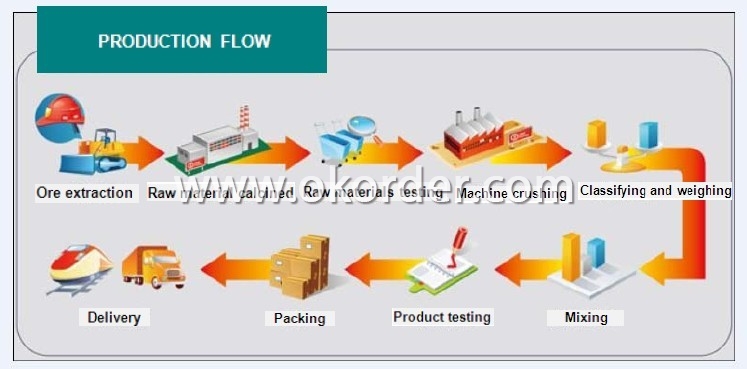
- Q: What are the recent developments in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry?
- Over the past few years, significant progress has been made in the field of monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry. These refractories are vital in the production of iron and steel, as they provide insulation and withstand high temperatures in furnaces and other equipment. One major advancement is the development of advanced alumina-based castables. These castables offer exceptional thermal shock resistance, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance, making them perfect for the iron and steel industry. They can endure extreme temperatures and mechanical stress, resulting in longer service life and less maintenance downtime. Another noteworthy development is the introduction of low-cement and ultra-low cement castables. Compared to traditional castables, these have reduced cement content, leading to improved refractory properties. They have higher hot strength, lower porosity, and increased resistance to slag and metal corrosion. This enhances productivity and efficiency in the iron and steel manufacturing processes. Moreover, insulating refractories have seen advancements in their usage. Insulating castables and bricks are now used to line ladles, tundishes, and other equipment, providing better insulation and energy efficiency. These materials help reduce heat loss and improve thermal efficiency, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Additionally, there have been significant improvements in the installation techniques of monolithic refractories. Traditional brick lining methods require skilled labor and a longer installation time. However, the introduction of gunning and shotcreting techniques has made the process faster and more efficient. These techniques involve spraying refractory materials onto the lining surface, ensuring better adherence and reducing the risk of lining failure. Overall, recent developments in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry have focused on enhancing thermal shock resistance, corrosion resistance, insulation properties, and installation techniques. These advancements have led to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved productivity in the iron and steel manufacturing processes.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to reducing emissions in iron and steel processes?
- The reduction of emissions in iron and steel processes is greatly aided by the use of monolithic refractories, which offer a more efficient and sustainable lining solution compared to traditional brick refractories. To begin with, monolithic refractories possess a homogeneous structure that allows for easier installation and repair. This characteristic reduces the amount of time needed for maintenance, ultimately leading to increased productivity and decreased emissions. In contrast, brick refractories require more labor-intensive and time-consuming procedures for installation and repair, resulting in longer shutdown periods and higher emissions. Additionally, monolithic refractories demonstrate superior thermal insulation properties. By minimizing heat loss from furnaces or kilns, they enhance energy efficiency and decrease the amount of fuel required to reach the desired temperature. This reduction in fuel consumption directly translates into lower emissions of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, which contributes to the overall environmental sustainability of iron and steel processes. Furthermore, monolithic refractories possess excellent resistance to both thermal and chemical wear, thereby enhancing the durability and lifespan of the lining. This increased durability reduces the frequency at which refractories need to be replaced, resulting in reduced waste generation and resource consumption. By extending the service life of the lining, monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of refractory materials. Moreover, monolithic refractories can be formulated with specialized compositions and additives to improve their resistance to corrosion and erosion, which are common challenges in iron and steel processes. By minimizing the wear and tear on the refractory lining, they help maintain the integrity of furnaces and kilns, preventing the leakage of harmful gases and pollutants that would otherwise contribute to emissions. In conclusion, monolithic refractories aid in the reduction of emissions in iron and steel processes through their ease of installation and repair, superior thermal insulation properties, increased durability, and resistance to corrosion and erosion. By optimizing energy efficiency, minimizing downtime, and reducing waste generation, monolithic refractories provide a sustainable solution for the industry, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change and promote environmental stewardship.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories withstand high temperatures in iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories, which are tailored for iron and steel production, have the capability to endure the formidable temperatures involved. Unlike traditional brick refractories that are built brick by brick, monolithic refractories are made from a single piece or material. The resilience of monolithic refractories against high temperatures is due to their distinctive composition and structure. They are crafted from top-notch raw materials, such as alumina, magnesia, silica, and carbon, which possess high melting points and exceptional heat resistance. To shape and strengthen the monolithic refractory, it is commonly mixed with a binder like clay or cement. This binder assists in binding the refractory particles together and provides the necessary structure to withstand thermal stresses. Moreover, the mixture can include various additives to further enhance the refractory properties. Throughout the iron and steel production process, monolithic refractories encounter extreme temperatures, rapid heating and cooling cycles, and chemical reactions with molten metals and slag. Nevertheless, the unique composition and structure of monolithic refractories enable them to withstand these harsh conditions. The high melting point materials utilized in monolithic refractories prevent them from melting or deforming under the intense heat of iron and steel production. These materials exhibit excellent thermal conductivity, effectively transferring heat away from hot surfaces and preventing overheating and damage. Furthermore, the binders and additives in monolithic refractories enhance their resistance to thermal shock, which arises from sudden temperature changes. This resistance is vital in iron and steel production since the refractories are frequently exposed to extreme temperature differentials. Lastly, the monolithic nature of these refractories eliminates the presence of joints and gaps commonly found in traditional brick refractories. The absence of joints minimizes the risk of heat leakage and infiltration of molten metal or slag, ensuring a more efficient and durable lining. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are specifically engineered to endure the high temperatures involved in iron and steel production. Their composition, structure, and unique properties enable them to withstand extreme heat, rapid temperature changes, chemical reactions, and thermal stresses, making them essential components in the manufacturing of iron and steel.
- Q: How are monolithic refractories installed and repaired in iron and steel plants?
- Monolithic refractories play a vital role in iron and steel plants, offering resistance to high temperatures and insulation. They are widely utilized in various applications, including lining furnaces, ladles, and equipment that comes into contact with molten metal. The process of installing monolithic refractories in iron and steel plants typically involves several sequential steps. Initially, the surface where the refractory material will be applied must be prepared, removing any existing refractories or contaminants. This can be accomplished through mechanical means, such as sandblasting, or through chemical cleaning processes. Following this, the monolithic refractory material is mixed with water or a suitable binder to achieve a workable consistency. The resulting mixture is then applied to the prepared surface using a variety of techniques, such as gunning, casting, or troweling. Gunning involves using a high-pressure gun to spray the refractory material onto the surface, while casting involves pouring the mixture into a mold. Troweling is a manual method that entails spreading the refractory material with a trowel. After the application of the refractory material, it must be appropriately cured or dried. This is usually accomplished by allowing the material to air dry or by employing controlled heating. The curing process is imperative to ensure that the refractory material develops the desired properties, including strength and resistance to thermal shock. Regarding repairs, monolithic refractories in iron and steel plants may deteriorate over time due to the harsh operating conditions. When repairs are necessary, damaged or worn-out sections of the refractory lining need to be identified. This can be achieved through visual inspection or non-destructive testing techniques. The repair procedure generally involves removing the damaged refractory material by chipping, drilling, or cutting. The surface is then prepared as previously mentioned, and a fresh batch of monolithic refractory material is applied to reinstate the lining. The repair material must be compatible with the existing lining and provide similar properties to ensure the overall integrity of the refractory structure. It is important to highlight that the installation and repair of monolithic refractories in iron and steel plants necessitate skilled personnel who possess knowledge of refractory materials and installation techniques. Additionally, proper safety precautions should be adhered to in order to safeguard workers from potential hazards, such as exposure to high temperatures, dust, and chemicals. Regular inspection and maintenance are also critical to identify any potential issues early on and prevent major failures that could affect production and safety.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories contribute to the overall safety of iron and steel operations?
- The overall safety of iron and steel operations is greatly ensured by the crucial role played by monolithic refractories, which provide various important benefits. Firstly, these refractories are renowned for their exceptional thermal insulation properties, enabling them to effectively withstand extreme temperatures and prevent heat loss. This is particularly crucial in iron and steel operations where high temperatures are involved in processes like melting, casting, and heat treatment. By minimizing heat loss, monolithic refractories help maintain a stable temperature environment, thereby reducing accident risks and ensuring personnel safety. Secondly, monolithic refractories offer outstanding resistance to chemical attacks. In iron and steel operations, the presence of different chemicals and gases can corrode and deteriorate the linings of furnaces, ladles, and other equipment. By serving as a protective barrier, monolithic refractories prevent the penetration of these corrosive substances, prolonging the equipment's lifespan and minimizing the chances of failures or leaks that could pose safety hazards. Moreover, monolithic refractories are known for their structural integrity and high mechanical strength. In iron and steel operations, heavy loads and stresses are common, especially during the handling and movement of molten metal and raw materials. Monolithic refractories can withstand these stresses without cracking or collapsing, ensuring the equipment's structural stability and minimizing accidents or equipment failures. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit excellent thermal shock resistance. In iron and steel operations, sudden temperature changes can occur due to the introduction of cold materials or liquids into hot equipment. This thermal shock can cause cracking and spalling of the refractory lining, compromising the operation's safety and efficiency. With their ability to withstand thermal shock, monolithic refractories help minimize the risk of unexpected failures and maintain the operation's overall safety. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly contribute to the overall safety of iron and steel operations through their high thermal insulation, chemical resistance, structural integrity, and thermal shock resistance. By ensuring a stable temperature environment, protecting against chemical attacks, withstanding heavy loads, and resisting thermal shock, monolithic refractories help prevent accidents, equipment failures, and potential hazards, creating a safer working environment for personnel in the iron and steel industry.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories perform in blast furnace taphole applications?
- Monolithic refractories perform excellently in blast furnace taphole applications due to their high thermal resistance, mechanical strength, and resistance to chemical attack. They are able to withstand the extreme temperatures and abrasive conditions of the blast furnace discharge, ensuring reliable and efficient operation of the taphole. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and maintenance, reducing downtime and improving overall productivity in the blast furnace.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories protect the lining of ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories protect the lining of ladles and tundishes by forming a strong and durable barrier against high temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses. These refractories are designed to be resistant to thermal shock and erosion, ensuring that the lining remains intact and unaffected by the molten metal or slag. They also provide insulation, minimizing heat loss and reducing energy consumption. Overall, monolithic refractories act as a reliable shield, extending the lifespan of the ladles and tundishes and preventing any detrimental effects on the lining.
- Q: What are the considerations for repairing and patching monolithic refractories?
- When it comes to the repair and patching of monolithic refractories, there are several key factors that must be taken into consideration. First and foremost, it is crucial to thoroughly evaluate the extent and severity of the damage or deterioration. This assessment will help determine the most appropriate repair method and materials required. Minor cracks or small damages may only necessitate a simple patch or seal, whereas larger or more serious damage may require a complete replacement or a more extensive repair process. Secondly, the type of monolithic refractory material being utilized is a critical factor to consider. Different types of monolithic refractories possess varying properties and characteristics, such as thermal conductivity, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Therefore, it is vital to select a repair material that is compatible with the existing refractory material, ensuring proper bonding and optimal performance. Another factor to take into account is the operating conditions and environment in which the monolithic refractory is exposed. Variables such as temperature, pressure, chemical exposure, and abrasion can significantly impact the durability and longevity of the refractory material. Understanding these conditions will assist in selecting the appropriate repair materials and techniques that can withstand and perform well under these specific circumstances. Furthermore, it is imperative that the repair process is carried out by experienced personnel who possess knowledge about refractory materials and their installation. Improper repairs can lead to further damage or diminished performance, so it is essential to have skilled professionals who can execute the repair work correctly. Lastly, regular inspection and maintenance of the monolithic refractories are crucial in order to detect any potential damage or deterioration early on. Timely repairs and patching can prevent further deterioration and prolong the service life of the refractory material. In summary, the considerations for repairing and patching monolithic refractories involve evaluating the extent of damage, selecting compatible repair materials, understanding the operating conditions, employing skilled personnel, and conducting regular inspections and maintenance. By taking these factors into account, one can ensure effective repairs and the continued performance of monolithic refractories.
- Q: How do monolithic refractories improve the thermal efficiency of iron and steel furnaces?
- The thermal efficiency of iron and steel furnaces greatly benefits from the use of monolithic refractories. These refractories, which are solid and unified, are essential for lining the furnaces and protecting them from the extreme temperatures involved in the metal production process. One way in which monolithic refractories enhance thermal efficiency is by minimizing heat loss. Due to their low thermal conductivity, these materials do not conduct heat well. By lining the furnace with monolithic refractories, the heat produced inside the chamber is effectively contained, resulting in less heat being lost to the surroundings. This allows for a more efficient use of energy, as less heat goes to waste and more is utilized for the purpose of heating and melting the metal. Moreover, monolithic refractories also contribute to the overall efficiency of iron and steel furnaces by offering a high level of heat resistance. The extreme temperatures experienced inside these furnaces can easily damage traditional refractory materials. However, monolithic refractories are specifically designed to withstand these harsh conditions, maintaining their integrity and performance over long periods of time. This durability ensures that the lining remains intact, preventing any potential leakage of heat and allowing the furnace to operate at its maximum efficiency. Furthermore, the installation process of monolithic refractories is flexible. They can be easily shaped and molded to fit the intricate designs and contours of the furnace, resulting in a seamless and continuous lining. This eliminates any gaps or weak points that could allow heat to escape or cold air to enter, further enhancing the thermal efficiency of the furnace. In conclusion, monolithic refractories significantly improve the thermal efficiency of iron and steel furnaces by reducing heat loss, providing high heat resistance, and ensuring a tight and continuous lining. By optimizing heat utilization and minimizing energy wastage, these refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the productivity and sustainability of the iron and steel industry.
- Q: What are the key properties of pumpable refractories used for monolithic refractory applications?
- The key properties of pumpable refractories used for monolithic refractory applications include high flowability, good workability, excellent bonding strength, and high resistance to thermal shock. These pumpable refractories should also possess good pumpability and be able to withstand the intense heat and mechanical stress in the application environment. Additionally, they should have low water demand, high chemical resistance, and the ability to maintain their properties even after exposure to high temperatures.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 60 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Eastern Europe; North America |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 31% - 50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 36,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 5 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Monolithic Refractories for Iron and Steel Industry:Corundum Castable for EAF Roof
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords