Hot Rolled Structure Steel Angle Bar Angle Steel JIS Standard GB Standard
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 30000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Specifications of Hot Rolled Angle Steel
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request3.Material:GBQ235B,Q345BorEquivalent;ASTMA36;EN10025,S235JR,S355JR;JISG3192,SS400;SS540.
4. Payment terms:
1).100% irrevocable L/C at sight.
2).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against the copy of B/L.
3).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against L/C
5.Sizes:
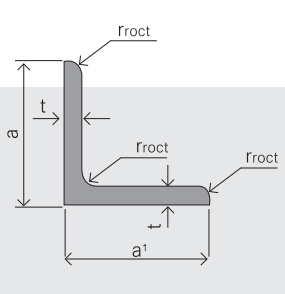
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES | |||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
25 | 25 | 2.5---3.0 | 6M/12M |
30 | 30 | 2.5---4.0 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 2.5 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 3.0---5.0 | 6M/12M |
40 | 40 | 3.0---6.0 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3.7---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
60 | 60 | 5.0---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
63 | 63 | 6.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
65 | 65 | 5.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
70 | 70 | 6.0---7.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
75 | 75 | 5.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
80 | 80 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
90 | 90 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
5. Material details:
Alloy No | Grade | Element (%) | |||||
C | Mn | S | P | Si | |||
Q235 | B | 0.12—0.20 | 0.3—0.7 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.3 | |
Alloy No | Grade | Yielding strength point( Mpa) | |||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | ||||
≥ | |||||||
Q235 | B | 235 | 225 | 215 | 205 | ||
Alloy No | Grade | Tensile strength (Mpa) | Elongation after fracture (%) | ||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | ||||
≥ | |||||||
Q235 | B | 375--500 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | |
Packaging & Delivery of Equal Steel Angle
1.Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2.With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: There will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.


- Q: Can steel angles be used as supports for HVAC systems or ductwork?
- Certainly! Steel angles have the ability to function as supports for HVAC systems or ductwork. Given their robustness and endurance, these angles are frequently employed in construction and engineering ventures. By serving as a stable and dependable framework, they guarantee the proper installation and resilience of HVAC systems or ductwork against the weight and vibrations generated during operation. Moreover, steel angles can be effortlessly fabricated and installed, rendering them a cost-efficient and effective choice for supporting HVAC systems or ductwork.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for modular construction?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for modular construction. Steel angles provide structural support and can be easily fabricated and assembled to create modular components in construction projects. They are commonly used for framing, bracing, and connecting modular units, providing strength and stability to the overall structure.
- Q: Do steel angles have a smooth or textured surface?
- Steel angles generally possess a textured exterior, which is formed when the steel is either hot-rolled or cold-formed into the angled shape during the manufacturing process. As a consequence, the steel angles acquire a slightly uneven or knobby surface, enhancing their ability to offer improved grip and stability in diverse applications. Furthermore, this texture serves to deter objects from slipping or sliding when they come into contact with the steel angles. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the degree of texture can differ based on the particular manufacturing technique employed and the intended purpose of the steel angles.
- Q: Do steel angles come with any warranties?
- Yes, steel angles typically come with warranties. The specific warranty terms may vary depending on the manufacturer or supplier. However, most reputable companies offer warranties to ensure the quality and performance of their steel angles. These warranties typically cover defects in materials or workmanship and may range from a few months to several years. It is advisable to check the warranty terms and conditions provided by the manufacturer or supplier before purchasing steel angles to understand the extent and duration of the warranty coverage.
- Q: Can steel angles be used as structural supports for bridges?
- Yes, steel angles can be used as structural supports for bridges. Steel angles, also known as angle irons, are commonly used in bridge construction as they provide stability and strength. They can be used as diagonal bracing or as reinforcement for beams and columns, enhancing the structural integrity of the bridge.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in HVAC ductwork?
- HVAC ductwork can indeed make use of steel angles. To ensure structural support and reinforcement, ductwork often incorporates steel angles. These angles are frequently employed at corners and joints, reinforcing the ductwork and preserving its shape. Thanks to their durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion, steel angles are highly suitable for use in HVAC ductwork systems. Moreover, their easy weldability and ability to be fastened together allow for effortless installation and customization. Consequently, steel angles serve as a dependable and frequently utilized element within HVAC ductwork systems.
- Q: How do you determine the appropriate thickness of a steel angle for a specific application?
- To determine the appropriate thickness of a steel angle for a specific application, several factors need to be considered. These factors include the load-bearing requirements, the length and span of the angle, and the structural design codes and standards applicable to the specific application. By evaluating these factors, engineers can calculate the required moment of inertia and bending capacity, allowing them to select the appropriate thickness of the steel angle that will provide sufficient strength and structural integrity for the intended use.
- Q: How do steel angles perform under high temperatures?
- Steel angles perform well under high temperatures due to their high melting point and excellent heat resistance. Steel is a widely used material in construction and engineering, known for its structural strength and durability. When exposed to high temperatures, steel angles retain their structural integrity and do not deform or weaken easily. This is because steel has a high melting point, typically around 1370 to 1530 degrees Celsius (2500 to 2800 degrees Fahrenheit), which allows it to withstand extreme heat without significant damage. Additionally, steel has excellent heat resistance, meaning it can dissipate heat efficiently and maintain its stability under high thermal loads. This makes steel angles suitable for applications where elevated temperatures are present, such as in industrial furnaces, power plants, or high-temperature environments. However, it is important to note that the specific performance of steel angles under high temperatures may vary depending on the grade and composition of the steel, as well as the duration and intensity of the heat exposure.
- Q: What are the different types of steel angles used in transmission towers?
- In transmission tower construction, there are three primary types of steel angles commonly employed: equal angles, unequal angles, and back-to-back angles. Equal angles, denoted as L-shaped sections, possess equal sides. They serve as cross-arms in transmission towers, providing structural stability and support. These angles are well-suited for bearing horizontal loads and are frequently utilized in the middle and upper regions of the tower. Unequal angles, as indicated by their name, possess unequal sides. They are utilized in transmission towers to enhance strength and stability in areas where load distribution is uneven. The longer side of the unequal angle is typically positioned on the side requiring greater strength. These angles are commonly used in the lower sections of transmission towers. Back-to-back angles are created by joining two equal angles together, forming a singular section. They are employed in transmission towers to augment strength and rigidity. Back-to-back angles find application in areas with non-uniform load distribution or where the tower must support heavier loads. These angles are commonly found in the base sections of transmission towers. The selection of steel angles for transmission towers depends on several factors, including tower height, load requirements, and specific design considerations. Engineers meticulously analyze these factors to determine the most suitable type of steel angle for each tower section, ensuring overall stability and strength of the transmission tower structure.
- Q: What is the maximum length for a steel angle bracket?
- The maximum length for a steel angle bracket can vary depending on the specific design and manufacturer, but it generally ranges from 6 to 12 inches.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Structure Steel Angle Bar Angle Steel JIS Standard GB Standard
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 30000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords
































