High Quality GB Standard Steel Square Bar 32mm-36mm
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
We offer Square Steel Bar with grade Q195 / Q235
Specifications of Square Steel Bar:
-Standard: GB,
-Grade: Q195/Q235 or equivalent.
Chemical Composition:
-Chemical Composition. Q195
Standard | Grade | Element (%) | ||||
GB | Q195 | C | Mn | S | P | Si |
0.06~0.12 | 0.25~0.50 | ≤0.050 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.30 | ||
-Chemical Composition. Q235
Standard | Grade | Element (%) | ||||
GB | Q235B | C | Mn | S | P | Si |
0.12~0.20 | 0.30~0.70 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.30 | ||
Measures and Tolerances of Square Steel Bar:
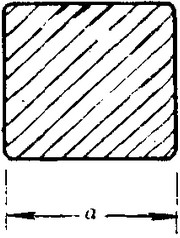
(The section of Square Steel Bar)
-The length of a side and the theoretical weight of Square Steel.
Length of a side(a, mm) | Theoretical weight(kg/m) | Length of a side(a, mm) | Theoretical weight(kg/m) |
6 | 0.283 | 32 | 8.04 |
7 | 0.385 | *33 | 8.55 |
8 | 0.502 | 34 | 9.07 |
9 | 0.636 | *35 | 9.62 |
10 | 0.785 | 36 | 10.17 |
11 | 0.950 | 38 | 11.24 |
12 | 1.13 | 40 | 12.56 |
13 | 1.33 | 42 | 13.85 |
14 | 1.54 | 45 | 15.90 |
15 | 1.77 | 48 | 18.09 |
16 | 2.01 | 50 | 19.63 |
17 | 2.27 | 53 | 22.05 |
18 | 2.54 | *55 | 23.6 |
19 | 2.82 | 56 | 24.61 |
20 | 3.14 | *58 | 26.4 |
21 | 3.46 | 60 | 28.26 |
22 | 3.80 | 63 | 31.16 |
*23 | 4.15 | *65 | 33.17 |
24 | 4.52 | *68 | 36.3 |
25 | 4.91 | 79 | 38.49 |
26 | 5.30 | 75 | 44.16 |
*27 | 5.72 | 80 | 50.24 |
28 | 6.15 | 85 | 56.72 |
*29 | 6.60 | 90 | 63.59 |
30 | 7.06 | 95 | 70.85 |
*31 | 7.54 | 100 | 78.50 |
Notes:
1, The theoretical weights in the list, base on the density of 7.85 g/cm3.
2, The numbers with *mean that they are not regulars or we don’t offer them.
-The allowed tolerance of Square Steel:
Length of a side(mm) | Allowed Tolerance | ||
Group1 | Group2 | Group3 | |
5.5~7 | ±0.20 | ±0.30 | ±0.40 |
7~20 | ±0.25 | ±0.35 | ±0.40 |
20~30 | ±0.30 | ±0.40 | ±0.50 |
30~50 | ±0.40 | ±0.50 | ±0.60 |
60~80 | ±0.60 | ±0.70 | ±0.80 |
80~110 | ±0.90 | ±1.0 | ±1.1 |
110~150 | ±1.2 | ±1.3 | ±1.1 |
150~190 | ―― | ―― | ±2.0 |
190~250 | ―― | ―― | ±2.5 |
Usage/Applications of Steel Square Bar:
-The Square Steel is normally used as structure steel.
-Row material for other structure steel like steel angles, channels, I-beams, H-beams, etc…
Packaging & Delivery of Steel Square Bar:
-Packing Detail: The products can be packed in bundles by steel wires.
-Marks:
1, Tag marks: the tag marks will be tied up to each bundle of the products. The information is usually including supplier’s logo and name, product name, made in China, products’ specifications, the painted color and other information requested by customers.
2, Color marks: we will paint both ends of the bundles of these products to make sure that they are more evident. It’s will be more convenient for the customers to distinguish them at the destination port.
-Delivery Detail: 30~45 working days after receive buyer’s T.T. or L/C.
Transportation:
-The products can be delivered by bulk vessel or by container. As for container, products with the length of 6m will be loaded in 20’ container, with 9m or 12m, in 40’ container.
-The maximum quantity of loading of container is 25 tons.
-The products usually are transported to the nearest port from the production place.
- Q: How do you use a steel square to measure and mark 157.5-degree angles?
- To use a steel square to measure and mark a 157.5-degree angle, you would first align one edge of the square with the reference line or surface. Then, rotate the square until the desired angle (157.5 degrees) is reached by aligning the protractor scale on the square with the line or surface. Once the angle is set, you can use the square to make accurate markings or measurements at that angle.
- Q: What are the different markings on a steel square used for?
- A steel square, also known as a framing square or carpenter's square, is an essential tool used in woodworking, construction, and other trades. It comprises two steel arms that meet at a 90-degree angle. These arms are engraved with different measurements and markings, each serving a specific purpose. 1. Degree Scale: One of the most noticeable markings on a steel square is the degree scale, enabling users to measure and mark angles other than 90 degrees. This scale proves valuable for tasks like cutting rafters, stair stringers, or other angled cuts. 2. Inch Scale: The inch scale, marked along one or both arms, allows for precise measurements in inches. This feature proves handy for measuring and marking lengths or widths of materials. 3. Rafter Tables: Some steel squares have rafter tables printed on one arm, providing measurements and angles for common rafter cuts, hip and valley rafter cuts, and other roofing-related calculations. Carpenters and roofers utilize these tables to determine the correct angles and lengths of rafters needed for a specific roof design. 4. Octagon Scale: Certain steel squares possess an octagon scale, facilitating the marking out of octagonal shapes. This scale provides the necessary angles and lengths required to construct an octagon, making it useful for projects such as building gazebos or other eight-sided structures. 5. Protractor: Many steel squares incorporate a protractor or angle finder into one arm. This enables users to accurately measure and mark angles, especially when attempting to replicate or transfer an existing angle. 6. Center Finding Scale: Several steel squares feature a center finding scale that assists users in locating the center point of a board or material. This scale proves beneficial for tasks like drilling holes or marking the midpoint for symmetrical cuts. In conclusion, the different markings on a steel square enhance its versatility and functionality. They enable users to measure angles accurately, mark dimensions precisely, and perform various calculations. As a result, the steel square becomes an indispensable tool for carpenters, woodworkers, and construction professionals.
- Q: Can a steel square be used for laying out a pergola?
- Yes, a steel square can be used for laying out a pergola. A steel square is a versatile tool commonly used in carpentry and construction to ensure accurate and precise measurements and angles. It can be employed to mark out and lay the foundation, posts, and beams of a pergola, helping to ensure its structural integrity and alignment.
- Q: Can a steel square be used for marking straight lines?
- Yes, a steel square can be used for marking straight lines. A steel square, also known as a framing square or a carpenter's square, is a versatile tool used in carpentry and other trades. It consists of a long metal blade with measurements and angles marked on it, and a shorter perpendicular metal tongue. One of the primary functions of a steel square is to ensure the accuracy of right angles, but it can also be used to draw or mark straight lines. To use a steel square for marking a straight line, you can position the blade or tongue against the edge of the material you want to mark, ensuring it is aligned properly. Then, using a pencil or a marking tool, you can trace along the edge of the steel square, creating a straight line. By utilizing the straight edges and precise measurements of a steel square, you can accurately mark straight lines on various materials, such as wood, metal, or plastic. However, it is important to note that while a steel square can be used for marking straight lines, it may not be as convenient or efficient as other tools specifically designed for this purpose, such as a ruler or a straightedge. The large size and weight of a steel square can make it cumbersome for small or intricate markings. Additionally, if the material you are working with is not flat or has irregular edges, it may be more challenging to achieve a perfectly straight line using a steel square alone. In conclusion, while a steel square can be used for marking straight lines, it is generally recommended to use it for checking right angles and utilizing specialized tools for precise and efficient marking of straight lines.
- Q: Can a steel square be used for checking the verticality of a wall?
- No, a steel square cannot be used for checking the verticality of a wall. A steel square, also known as a framing square, is a tool primarily used in carpentry for measuring angles and making straight cuts. It is not designed or calibrated to determine verticality. To check the verticality of a wall, a level or plumb bob is typically used. A level is a tool with a bubble vial that helps indicate if a surface is perfectly vertical or horizontal. Plumb bobs, on the other hand, consist of a weighted string that hangs from a fixed point. By observing the alignment of the string with a reference point, one can determine if the wall is perfectly vertical. These tools are specifically designed for vertical measurements and provide more accurate results compared to a steel square.
- Q: How do you use a steel square for creating precise spline joints?
- To use a steel square for creating precise spline joints, first, measure and mark the desired length on both pieces of wood. Then, align the steel square against the edge of the wood, ensuring it is perpendicular to the surface. Next, draw a line along the edge of the steel square using a pencil or a marking knife. Repeat this process on both pieces of wood. Finally, align the marked lines and cut along them to create precise spline joints.
- Q: Can a steel square be used for roof truss layout and construction?
- Yes, a steel square can be used for roof truss layout and construction. A steel square, also known as a framing square or carpenter's square, is a versatile tool that is commonly used in the construction industry for various tasks, including roof truss layout. A steel square consists of two arms that meet at a right angle, forming a 90-degree corner. One arm is longer than the other, typically 24 inches long, and is used for measuring and marking straight lines. The shorter arm, usually 16 inches long, is used for measuring and marking angles. When it comes to roof truss layout, a steel square can be used to determine and mark the angles for the truss members. It can be used to layout the pitch or slope of the roof, ensuring that the trusses are properly aligned and positioned. Additionally, a steel square can also be used for cutting and marking the truss members. It can be used to mark the angles for the cuts, ensuring that the truss members fit together accurately. The longer arm can be used to measure and mark the length of the truss members, ensuring that they are cut to the correct size. Overall, a steel square is a valuable tool for roof truss layout and construction. Its versatility and accuracy make it an essential tool for carpenters and construction professionals working on roof truss projects.
- Q: Can a steel square be used for precise woodworking?
- Yes, a steel square can be used for precise woodworking. Steel squares are typically made with precision and accuracy in mind, making them suitable for a variety of woodworking tasks. They are designed to be square and have precise angles, allowing woodworkers to accurately measure and mark out right angles and other angles required for precise woodworking. Steel squares are often used for tasks such as marking and checking for squareness, laying out joints, making accurate cuts, and ensuring the correct alignment of pieces. Additionally, steel squares are durable and can withstand the rigors of woodworking, making them a reliable tool for precise woodworking projects.
- Q: How does a steel square assist in checking the alignment of power tools?
- A steel square assists in checking the alignment of power tools by providing a straight and accurate reference edge or surface. It can be used to ensure that the tool's blade or fence is perfectly perpendicular or parallel to the reference edge, allowing for precise and accurate cuts or measurements.
- Q: How do you use a steel square to measure and mark 90-degree angles?
- To effectively measure and designate 90-degree angles using a steel square, commence by aligning one of the square's edges with the corresponding edge of the material you intend to mark or cut. It is crucial to firmly secure the square in its position. Following that, ascertain that the elongated side or blade of the square stands perpendicular to the aforementioned edge of the material. This guarantees the measurement and marking of a flawless 90-degree angle. At this point, employ either a marking knife or a pencil to trace along the inner edge of the square's blade. This action will result in an exact mark on the material, serving as an indicator of the 90-degree angle. Should you require measuring and marking multiple 90-degree angles, you can effortlessly repeat the aforementioned steps, ensuring the square is suitably aligned on each occasion. Always bear in mind the importance of double-checking your measurements and marks prior to proceeding with any cutting or construction work to ensure utmost accuracy.
Send your message to us
High Quality GB Standard Steel Square Bar 32mm-36mm
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























