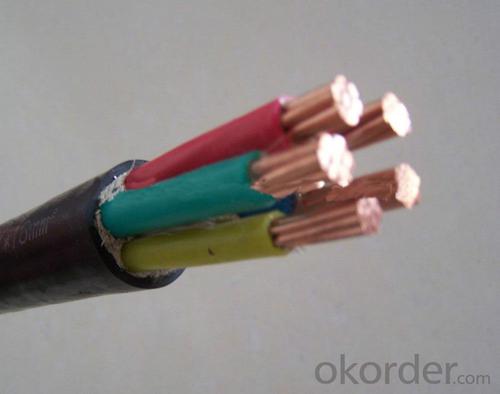
Factory Price High Quality PVC sheathed insulated power cable
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Factory Price High Quality PVC sheathed XLPE insulated power cable
1. The cable is made of copper line with PVC insulated, and PVC/XLPE sheathed, the cable of the wire is strand. The voltage is 600/1000V; the color of the cable can be any color as your need. The cable is widely used in construction, industry and other sites, the cable can be used overhead, underground.
2. Certificates of the cable: ISO, CE, RoHS, CCC.
3. More related products:
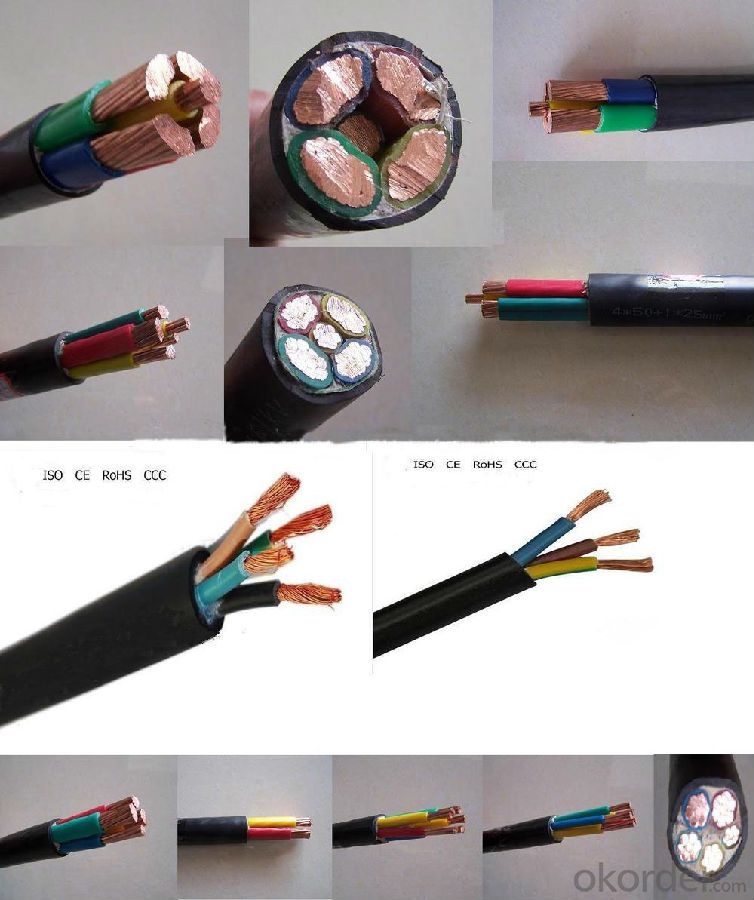

4. Products list and parameter
No. | Size | Specification | Length per roll |
PVC insulated non-sheathed copper wires BV (450-750 Voltage) | |||
1 | 1.5 mm2 | 1×1.38 mm2 | 100 m |
2 | 2.5 mm2 | 1×1.78 mm2 | 100 m |
3 | 4 mm2 | 1×2.25 mm2 | 100 m |
4 | 6 mm2 | 1×2.76 mm2 | 100 m |
5 | 10 mm2 | 7×1.35 mm2 | 100 m |
6 | 16 mm2 | 7×1.70 mm2 | 100 m |
7 | 25 mm2 | 7×2.14 mm2 | 100 m |
PVC insulated PVC/XLPE sheathed Twin cables with/without earth BVVB (300-500 Voltage) | |||
8 | 2×1 +1 mm2 | 2×1.13 +1.13 mm2 | 100 m |
9 | 2×1.5 +1 mm2 | 2×1.38 +1.13 mm2 | 100 m |
10 | 2×2.5 +1.5 mm2 | 2×1.78 +1.38 mm2 | 100 m |
11 | 2×4 +2.5 mm2 | 2×2.25 +1.78 mm2 | 100 m |
12 | 2×6 +4 mm2 | 2×2.76 +2.25 mm2 | 100 m |
13 | 2×10+4 mm2 | 2×7×1.35 +2.25 mm2 | 100 m |
14 | 2×16+6 mm2 | 2×7×1.70 +2.76 mm2 | 100 m |
PVC insulated non-sheathed Multi flexible wires BVR (450-750 Voltage) | |||
15 | 1.5 mm2 | 7×0.52 mm2 | 100 m |
16 | 2.5 mm2 | 19×0.41 mm2 | 100 m |
17 | 4 mm2 | 19×0.52 mm2 | 100 m |
18 | 6 mm2 | 19×0.63 mm2 | 100 m |
19 | 10 mm2 | 49×0.52 mm2 | 100 m |
20 | 16 mm2 | 49×0.63 mm2 | 100 m |
PVC insulated PVC/XLPE sheathed copper cables (Lower than 1000 Voltage) | |||
No. | Size | Specification | |
21 | 3×2.5 mm2 | 3×1.78 mm2 | |
22 | 3×4 mm2 | 3×2.25 mm2 | |
23 | 3×4+1×2.5 mm2 | 3×2.25+1×1.78 mm2 | |
24 | 3×4+2×2.5 mm2 | 3×2.25+2×1.78 mm2 | |
25 | 3×6 mm2 | 3×2.76 mm2 | |
26 | 3×6+1×4 mm2 | 3×2.76+1×2.25 mm2 | |
27 | 3×6+2×4 mm2 | 3×2.76+2×2.25 mm2 | |
28 | 3×10 mm2 | 3×7×1.35 mm2 | |
29 | 3×10+1×6 mm2 | 3×7×1.35+1×2.76 mm2 | |
30 | 3×10+2×6 mm2 | 3×7×1.35+2×2.76 mm2 | |
31 | 3×16 mm2 | 3×7×1.70 mm2 | |
32 | 3×16+1×10 mm2 | 3×7×1.70+1×7×1.35 mm2 | |
33 | 3×16+2×10 mm2 | 3×7×1.70+2×7×1.35 mm2 | |
34 | 3×25+1×16 mm2 | 3×7×2.14+1×7×1.70 mm2 | |
35 | 3×25+2×16 mm2 | 3×7×2.14+2×7×1.70 mm2 | |
36 | 3×35+1×16 mm2 | 3×7×2.52+1×7×1.70 mm2 | |
37 | 3×35+2×16 mm2 | 3×7×2.52+2×7×1.70 mm2 | |
38 | 3×50+1×25 mm2 | 3×10×2.52+1×7×2.14 mm2 | |
39 | 3×50+2×25 mm2 | 3×10×2.52+2×7×2.14 mm2 | |
40 | 3×70+1×35 mm2 | 3×14×2.52+1×7×2.52 mm2 | |
41 | 3×70+2×35 mm2 | 3×14×2.52+2×7×2.52 mm2 | |
42 | 3×95+1×50 mm2 | 3×19×2.52+1×10×2.52 mm2 | |
43 | 3×95+2×50 mm2 | 3×19×2.52+2×10×2.52 mm2 | |
44 | 3×120+1×70 mm2 | 3×24×2.52+1×14×2.52 mm2 | |
45 | 3×120+2×70 mm2 | 3×24×2.52+2×14×2.52 mm2 | |
46 | 3×150+1×70 mm2 | 3×30×2.52+1×14×2.52 mm2 | |
47 | 3×150+2×70 mm2 | 3×30×2.52+2×14×2.52 mm2 | |
48 | 3×185+1×95 mm2 | 3×37×2.52+1×19×2.52 mm2 | |
49 | 3×185+2×95 mm2 | 3×37×2.52+2×19×2.52 mm2 | |
50 | 4×2.5 mm2 | 4×1.78 mm2 | |
51 | 4×4 mm2 | 4×2.25 mm2 | |
52 | 4×4+1×2.5 mm2 | 4×2.25+1×1.78 mm2 | |
53 | 4×6 mm2 | 4×2.76 mm2 | |
54 | 4×6+1×4 mm2 | 4×2.76+1×2.25 mm2 | |
55 | 4×10 mm2 | 4×7×1.35 mm2 | |
56 | 4×10+1×6 mm2 | 4×7×1.35+1×2.76 mm2 | |
57 | 4×16 mm2 | 4×7×1.70 mm2 | |
58 | 4×16+1×10 mm2 | 4×7×1.70+1×7×1.35 mm2 | |
59 | 4×25 mm2 | 4×7×2.14 mm2 | |
60 | 4×25+1×16 mm2 | 4×7×2.14+1×7×1.70 mm2 | |
61 | 4×35 mm2 | 4×7×2.52 mm2 | |
62 | 4×35+1×16 mm2 | 4×7×2.52+1×7×1.70 mm2 | |
63 | 4×50 mm2 | 4×10×2.52 mm2 | |
64 | 4×50+1×25 mm2 | 4×10×2.52+1×7×2.14 mm2 | |
65 | 4×70 mm2 | 4×14×2.52 mm2 | |
66 | 4×70+1×35 mm2 | 4×14×2.52+1×7×2.52 mm2 | |
67 | 4×95 mm2 | 4×19×2.52 mm2 | |
68 | 4×95+1×50 mm2 | 4×19×2.52+1×10×2.52 mm2 | |
69 | 4×120 mm2 | 4×24×2.52 mm2 | |
70 | 4×120+1×70 mm2 | 4×24×2.52+1×14×2.52 mm2 | |
71 | 4×150 mm2 | 4×30×2.52 mm2 | |
72 | 4×150+1×70 mm2 | 4×30×2.52+1×14×2.52 mm2 | |
73 | 4×185 mm2 | 4×37×2.52 mm2 | |
74 | 4×185+1×95 mm2 | 4×37×2.52+1×19×2.52 mm2 | |
75 | 5×2.5 mm2 | 5×1.78 mm2 | |
76 | 5×4 mm2 | 5×2.25 mm2 | |
77 | 5×6 mm2 | 5×2.76 mm2 | |
78 | 5×10 mm2 | 5×7×1.35 mm2 | |
79 | 5×16 mm2 | 5×7×1.70 mm2 | |
80 | 5×25 mm2 | 5×7×2.14 mm2 | |
81 | 5×35 mm2 | 5×7×2.52 mm2 | |
82 | 5×50 mm2 | 5×10×2.52 mm2 | |
83 | 5×70 mm2 | 5×14×2.52 mm2 | |
84 | 5×95 mm2 | 5×19×2.52 mm2 | |
85 | 5×120 mm2 | 5×24×2.52 mm2 | |
86 | 5×150 mm2 | 5×30×2.52 mm2 | |
87 | 5×185 mm2 | 5×37×2.52 mm2 | |
5. Package: mainly the cables are packed in steel-wooden drum, the length is on the size and weight, but also the cables can be packed as your demand.
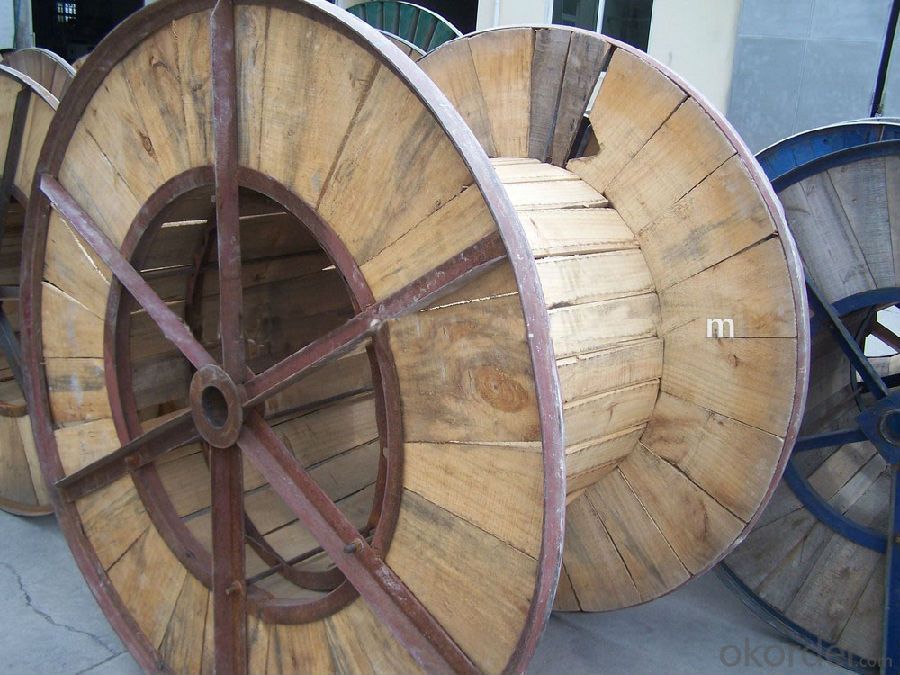
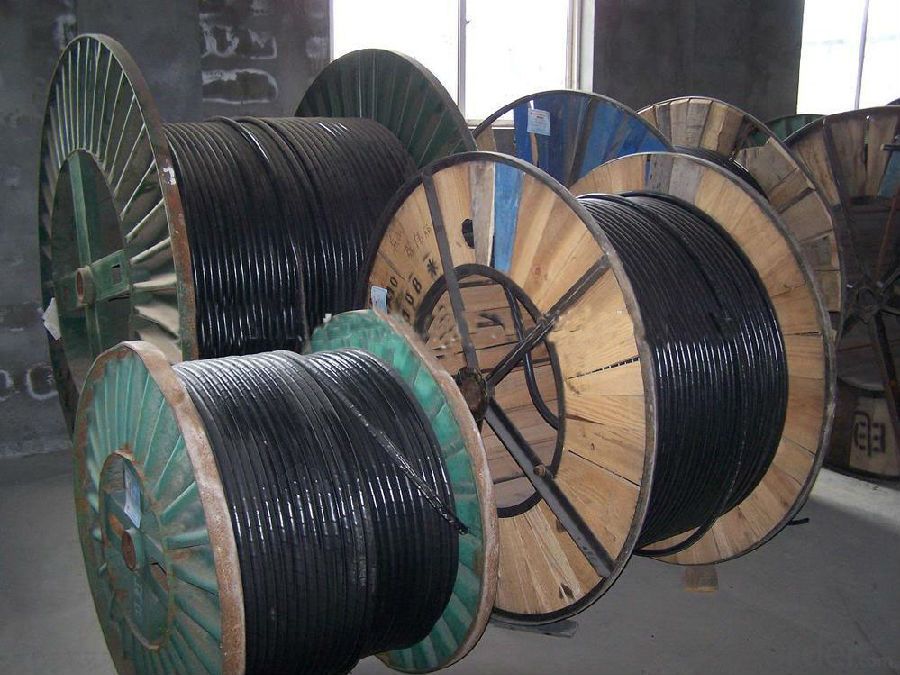
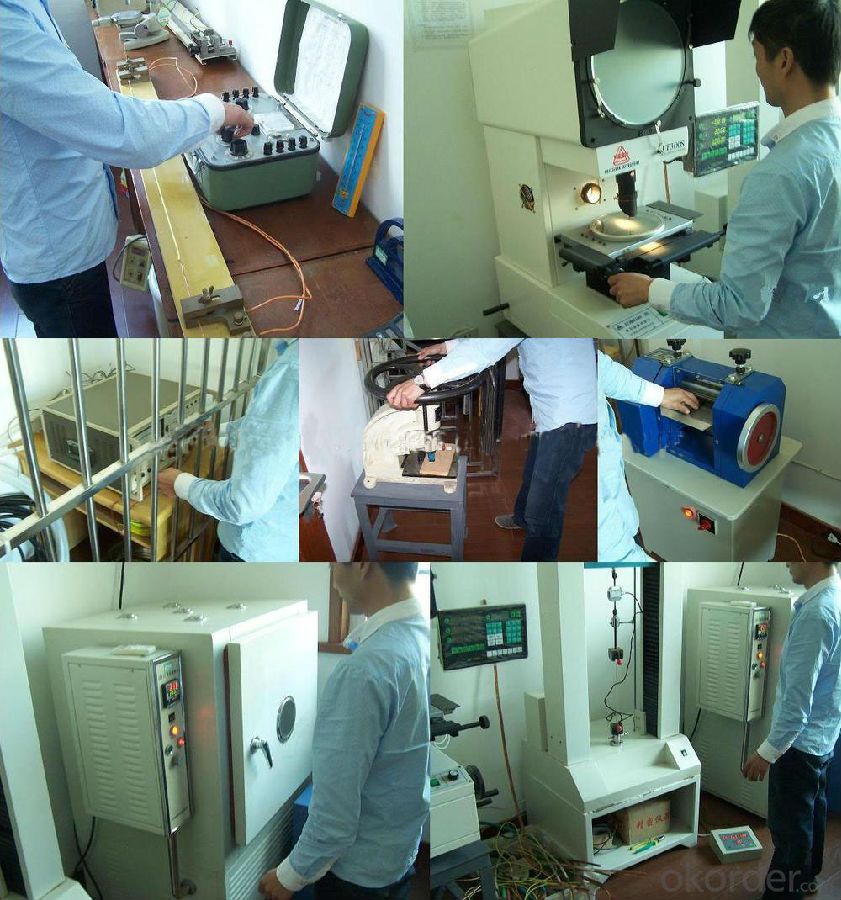



7. The workshop
Looking forward to co-operate with you!
- Q: Why medium voltage power cable sometimes write 8.7 / 10kv sometimes written in 8.7 / 15kv where the difference
- 1 audio and video line of the problem (red and white) to connect the TV box set-top box that line to the cable or radio equipment store to buy a definite muscle wings can be Jiu sad snow on the line 2 TV bad to find TV manufacturers
- Q: What I really just want to know is the equation and basic concept on how to determine the optimal length of power cable needed to connect two poles while knowing only the linear density of the cable.It does not matter how much sag is produced because of limitations due to the strength of the power cable.
- The web page provides very thorough information and rigorous mathematical treatment relevant to the answer you seek. But it is just too much all at once to digest. So take it piecemeal, one bit at a time! First, you must realize that the sag of the cable is the single most important design parameter and strict attention to cable weight determines the optimal length. The equation of the catenary is the precise model but a parabolic approximation may work. (parabolic approx.) ymax = (3wl?) / ?√(64EA) P = wl?/(8ymax) Where ymax is the maximum sag l is the unstretched length w is the weight/unit length E Youngs modulus A Wire area P axial tension the curve is a parabola, which is a good approximation if the depth of sag is no greater than 1/8th of the span. Use the second equation to derive the induced tension P. H:=WL?/8S S:=WL?/8H L: distance between support S: Sag at mid-span H: tension (horizontal component of tension) The tension depends purely on the loaded geometry and the weight per unit length.
- Q: does anyone know a website that has like a chart with pictures of the different power supply connectors and where in the desktop computer they go all I know is the 24 pin goes to the motherboard and the 6 pin goes to my graphics card
- Its on your motherboard factory web site. usually there is a 4 or 8 pin for the mobo PCI bridge, sata, pata, power connectors for drives. smaller for floppy, blue wire for PSU fan speed report. just find out what FORM you need, most are ATX.
- Q: How can i fix it and how much would it cost?
- its possible (unless you're sure) that its not the socket. It could be the surge adapter(the plug itself). possible it can be the outlet itself, have you checked a different outlet? Anyway, fortunately, that's not too big of a problem, especially for a laptop. To get it fixed, if its still under warranty, you have to call the manufacturer and ask for technical support. They will most likely send you a box to put the computer in, have you send it to them(prepaid), and they will send it back repaired, IF ITS UNDER WARRENTY. If its not under warranty, you will have to go to a computer technician. usually a place like Best Buy has fast and cheap computer repairs, or you may find a local computer repair shop that suits your needs better. Or you can even send it back to the manufacturer to fix it, be warned however, they usually overcharge on expired warranty repairs. As far as the cost, it can range from fifty to a couple hundred dollars, depending on the problem. Hope i helped
- Q: I am getting a new 160 amp high output alternator for my 2005 Mazda 3 2.3L. I am running a 1000w amp with two subs. I have the stock alternator in it right now. There are two power cable kits available for me to get. One that has 4 gauge wire with a 100 amp fuse and the other, 1 gauge with 150 amp fuse. Which kit should I get? Can I just add 4 gauge wire along with my stock wire instead of the 1 gauge kit? What are the fuses for and which one would work better? I know nothing about this. Thanks.
- A fuse is a necessary circuit protection device, if there becomes a short in the circuit, it can cause a fire, the fuse is a precise conductor which will break if too much current (energy) is being drawn. A 4 gauge wire will work fine, and you need a least a 160 amp fuse, any less and it will blow if your alternator is at full load.
- Q: I just purchased and mounted my 52lcd and I cut holes to run the HDMI cables behind the wall. As I was snaking the power cable, I realized this might not be the best way. Is there anything I need to do (I only have basic 'contracting' skills) to keep my install fire code safe?
- Sorry dude you have me there... Running the power cable behind the wall is clear and ok but what has your install fire code got to do with running a cable behind a wall...??
- Q: I want to know if the dell vostro 260 has it
- Even okorder /
- Q: we have one control cable 120 VAC contains 7 conductors and another power cable of 480 VAC each contains 7conductors. can be installed in one conduit
- Physically yes, but it is definitely not good practice. Normal practice is to segregate power and control cables. Local regulations may also prevent installing systems of 2 different voltage levels in the same conduit
- Q: I'm new to PCs and I recently bought a Dell Optiplex 745 desktop PC but it came without cables. I thought I had the correct power cord but it turns out I gave it away to friends. I have the power cable that you plug into the wall which has the standard PC kettle plug (the correct one for PCs not an actual kettle plug) that you'd usually plug into an adapter then into your PC but I'm not sure if you can just plug it in without the correct adapter. I have Googled but cant make head nor tail of it all. And by adapter I mean the cable with the little box that you usually plug into a device such as a PC, laptop or Xbox 360 before you connect the cable to the mains.Thanks.
- It all comes down to the amount of output that the pc is set to take. I would think that you would be fine without the adapter, assuming it already works. If you do decide to do this make sure you set up a surge protector, dont just plug it into the wall. A power surge could fry the internals and brick the pc.
- Q: Is a graphics card power cable needed because not all graphics cards come with one? And if it isn't needed, what is the benefit?
- The more powerful graphics cards require the 6-pin power connector to a PCI-E slot. The benefits of NOT requiring one are: 1) The card uses less power, which might save the expense of having to upgrade the power supply. 2) The card works with power supplies that don't have the PCI-E cable, without having to buy an adapter. The best card which doesn't need a power cable is the ATI Radeon 4670. The card models above that (like the GeForce 9800GT, Radeon 4830 etc) all require the cable.
Send your message to us
Factory Price High Quality PVC sheathed insulated power cable
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches