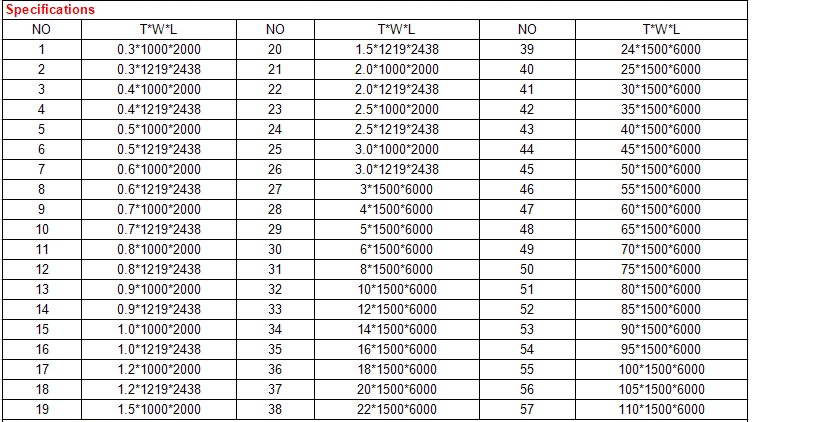
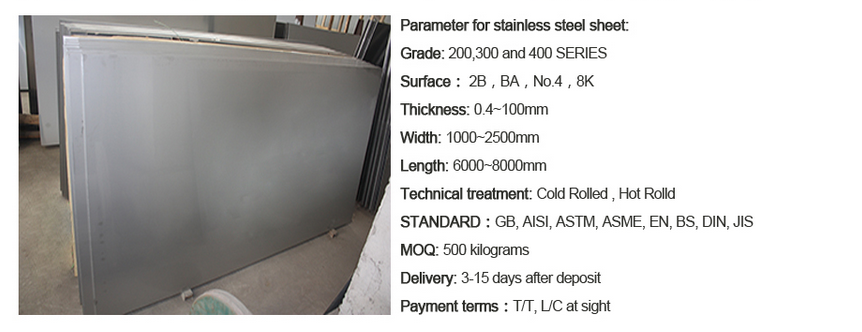
Gold supplier 201 304L 316 316L 304 stainless steel plate price
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
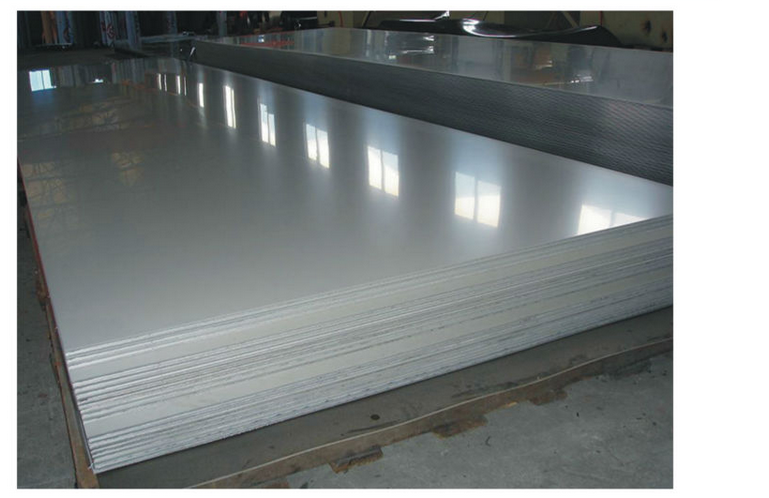
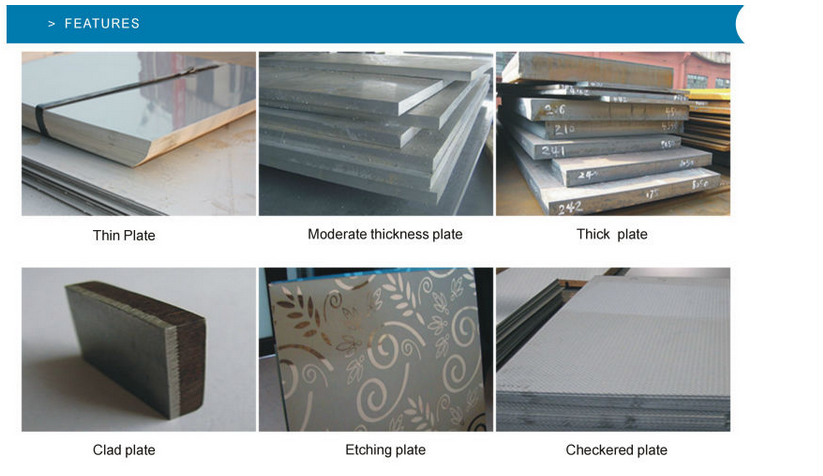







- Q:Can stainless steel pipes be used in drinking water systems?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be used in drinking water systems. Stainless steel is a highly durable and corrosion-resistant material that can withstand the harsh elements present in water systems. It does not leach any harmful substances into the water, making it a safe choice for drinking water applications. Additionally, stainless steel pipes are easy to clean and maintain, further ensuring the quality and safety of the drinking water.
- Q:What is the external protection used for stainless steel pipes?
- To safeguard stainless steel pipes from corrosion and maintain their integrity, various methods of external protection are employed. One approach involves the application of a protective coating or treatment to shield the pipes and prevent corrosion. Despite stainless steel's inherent resistance to corrosion, it remains vulnerable to certain environmental conditions. A commonly utilized method of external protection entails applying a corrosion-resistant coating, such as epoxy, polyethylene, or zinc. These coatings create a barrier between the stainless steel pipe and its surroundings, preventing direct contact and potential corrosion. Additionally, they serve to safeguard the pipe against physical damage, such as scratches or abrasions, which could lead to corrosion. Another method employed for external protection involves cathodic protection. This technique encompasses either the usage of sacrificial anodes or the application of an electric current to the stainless steel pipe. By sacrificing the anodes or inducing an electrochemical reaction, corrosion is redirected away from the pipe. Furthermore, external protection may include the utilization of insulation materials to prevent condensation and moisture accumulation on the pipe's surface. Moisture can expedite corrosion, and hence proper insulation aids in upholding the stainless steel pipes' integrity. Overall, the aim of external protection for stainless steel pipes is to avert corrosion and ensure their longevity and reliability. By employing various protective coatings, cathodic protection, and insulation, stainless steel pipes can be shielded from environmental factors, thereby guaranteeing optimal performance.
- Q:Can stainless steel pipes be used for wastewater treatment ponds?
- Indeed, wastewater treatment ponds can employ stainless steel pipes. Renowned for their resistance to corrosion, durability, and capacity to endure severe conditions, stainless steel pipes prove well-suited for such usage. These attributes render them appropriate for wastewater treatment ponds, which frequently encounter chemicals, moisture, and other corrosive elements. Moreover, stainless steel pipes facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance, essential factors for preserving the efficiency and efficacy of the wastewater treatment procedure.
- Q:What are the different grades of stainless steel used in pipes?
- Pipes commonly utilize various grades of stainless steel, each possessing distinct properties and characteristics. Notable grades include: 1. Stainless Steel Grade 304: Recognized as highly versatile and widely employed, Grade 304 exhibits non-magnetic qualities, exceptional resistance to corrosion, and ease of weldability. Its applications predominantly revolve around sectors emphasizing hygiene and cleanliness, such as food processing plants, hospitals, and the pharmaceutical industry. 2. Stainless Steel Grade 316: Renowned for its unparalleled resistance to corrosion, particularly in environments abundant in chloride or saltwater exposure, Grade 316 frequently finds utilization in marine settings, chemical processing facilities, and coastal areas necessitating robust corrosion resistance. 3. Stainless Steel Grade 321: Grade 321 boasts titanium stabilization, rendering it more impervious to sensitization and intergranular corrosion at elevated temperatures. It commonly serves in high-temperature scenarios, exemplified by exhaust systems, furnaces, and heat exchangers. 4. Stainless Steel Grade 409: Designed specifically for high-temperature applications like automotive exhaust systems, Grade 409 showcases remarkable heat resistance and exhibits low thermal expansion properties, making it an ideal choice for enduring extreme temperatures. 5. Stainless Steel Grade 904L: Grade 904L excels in corrosion resistance, particularly combating pitting and crevice corrosion. Frequently employed in aggressive environments prevalent in chemical processing plants, offshore oil and gas platforms, and pulp and paper industries. These examples merely exemplify the array of stainless steel grades employed in pipe manufacturing. The selection of a particular grade hinges upon the specific application and desired attributes, encompassing corrosion resistance, temperature resistance, and mechanical strength.
- Q:What is the difference between nominal size and actual size in stainless steel pipes?
- The difference between nominal size and actual size in stainless steel pipes lies in how they are measured and labeled. Nominal size refers to the designation given to a pipe based on its approximate dimensions, typically in inches or millimeters. This designation is used for easy identification and standardization purposes. On the other hand, actual size refers to the precise measurements of the pipe, such as its outer diameter (OD) and wall thickness. These measurements are usually expressed in fractions of an inch or in millimeters. The actual size is crucial for determining the pipe's compatibility with fittings, valves, and other components, as well as for calculating flow rates and pressure ratings. It is important to note that the nominal size of a stainless steel pipe may not necessarily match its actual size. This discrepancy is due to historical reasons and manufacturing practices. In some cases, the nominal size is slightly larger or smaller than the actual size to accommodate variations in wall thickness or to align with industry standards. Therefore, when selecting stainless steel pipes, it is essential to consider both the nominal size and the actual size to ensure proper fitment and functionality. Consulting the manufacturer's specifications or seeking professional advice can help in determining the appropriate pipe size for a given application.
- Q:What is the difference between 321 and 347 stainless steel pipes?
- The composition of their alloys is the main distinction between 321 and 347 stainless steel pipes. Both grades of stainless steel are titanium-stabilized to prevent the formation of harmful chromium carbides when exposed to high temperatures. However, 347 stainless steel contains additional columbium (niobium), which enhances its resistance to intergranular corrosion. This makes 347 stainless steel pipes suitable for applications that involve exposure to high temperatures and corrosive environments, such as in the petrochemical industry or exhaust systems. On the contrary, 321 stainless steel pipes exhibit excellent resistance to oxidation and scaling at elevated temperatures, making them ideal for applications that require continuous exposure to high heat, like in aircraft exhaust systems or furnace parts. Ultimately, the choice between 321 and 347 stainless steel pipes depends on the specific requirements of the application, with 347 offering superior intergranular corrosion resistance and 321 providing better oxidation resistance.
- Q:How do stainless steel pipes compare to PVC-coated steel pipes?
- Stainless steel pipes and PVC-coated steel pipes have distinct differences in terms of material composition, durability, corrosion resistance, cost, and specific applications. Firstly, stainless steel pipes are made from a combination of iron and chromium, which provides excellent corrosion resistance and durability. This makes them suitable for applications in harsh environments, such as industrial settings or marine applications. On the other hand, PVC-coated steel pipes are made from steel coated with a layer of polyvinyl chloride (PVC). While PVC provides some level of corrosion resistance, it is not as durable as stainless steel and may degrade over time, especially in high-temperature or corrosive environments. In terms of durability, stainless steel pipes have a longer lifespan compared to PVC-coated steel pipes. Stainless steel is highly resistant to rust, corrosion, and chemical damage, ensuring long-term reliability. PVC-coated steel pipes, although corrosion-resistant to some extent, are more prone to damage from exposure to sunlight, extreme temperatures, or chemicals. When it comes to cost, PVC-coated steel pipes are generally more affordable compared to stainless steel pipes. This makes them a cost-effective option for applications that do not require high levels of durability or corrosion resistance. Stainless steel pipes, while more expensive upfront, offer a better return on investment due to their longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. The specific application also plays a crucial role in determining which type of pipe is most suitable. Stainless steel pipes are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, food processing, and water treatment, where high strength, corrosion resistance, and hygiene are essential. PVC-coated steel pipes find application in areas such as underground drainage, irrigation systems, and electrical conduit, where cost-effectiveness and moderate durability are more important than extreme corrosion resistance. In summary, stainless steel pipes outperform PVC-coated steel pipes in terms of durability, corrosion resistance, and lifespan. However, PVC-coated steel pipes offer a more cost-effective solution for applications that do not require the same level of durability or corrosion resistance. Ultimately, the choice between these two types of pipes depends on the specific needs of the project, including its intended application, budget, and environmental conditions.
- Q:What is the difference between 347 and 321 stainless steel pipes?
- The main difference between 347 and 321 stainless steel pipes lies in their composition and intended use. 347 stainless steel contains a higher amount of niobium, which enhances its resistance to intergranular corrosion, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. On the other hand, 321 stainless steel has titanium as a stabilizing element, providing improved resistance against sensitization during welding.
- Q:How can the inner walls of stainless steel tubes be polished?
- 1) (used in polishing the inner surface polishing machine): rod is thrown into the tube to drive the impeller 1000 or homemade abrasive wheel rotating speed, and with the rotation of the polishing pipe itself, while rotating slowly forward throwing rod. Generally speaking, first use the 60#-80# wheel of Chiba or abrasive belt wheel for rough throwing, and then gradually fine throwing with high precision according to the requirement of smoothness. Large size pipe 6, more than the general use of thousands of impeller, small size of the pipe can be made with homemade abrasive belt wheel, you can reduce costs.
- Q:304L stainless steel pipe can withstand 0.1MPA?
- If you want to know how much pressure the steel pipe is under, you need to know the type of the stainless steel pipe.Pressure calculation formula of stainless steel management: pressure MPA=, tensile strength X40%X2X, wall thickness / outer diameterBut from my experience, generally speaking, stainless steel tubes can withstand 0. 1MPA. Unless it is used very thin stainless steel tube wall decoration.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Gold supplier 201 304L 316 316L 304 stainless steel plate price
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords