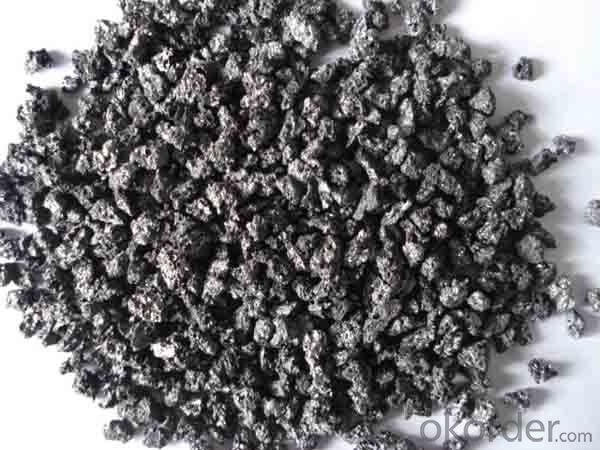
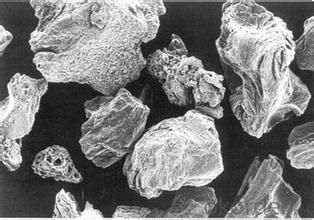
Low Sulfur Calcined Petroleum Coke of CNBM in China
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1.Structure of Calcined Petroleum Coke Description
Calcined Petroleum Coke is made from raw petroleum coke,which is calcined in furnace at a high temperature(1200-1300℃).CPC/Calcined Petroleum Coke is widely used in steelmaking,castings manufacture and other metallurgical industry as a kind of recarburizer because of its high fixed carbon content,low sulfur content and high absorb rate.Besides,it is also a best kind of raw materials for producing artifical graphite(GPC/Graphitized Petroleum Coke) under the graphitizing temperature(2800℃).
2.Main Features of the Calcined Petroleum Coke
High-purity graphitized petroleum coke is made from high quality petroleum coke under a temperature of 2,500-3,500°C. As a high-purity carbon material, it has characteristics of high fixed carbon content, low sulfur, low ash, low porosity etc.It can be used as carbon raiser (Recarburizer) to produce high quality steel,cast iron and alloy.It can also be used in plastic and rubber as an additive.
3. Calcined Petroleum Coke Images
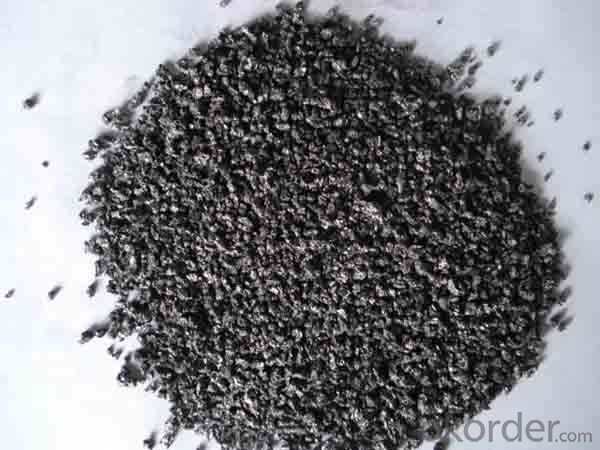
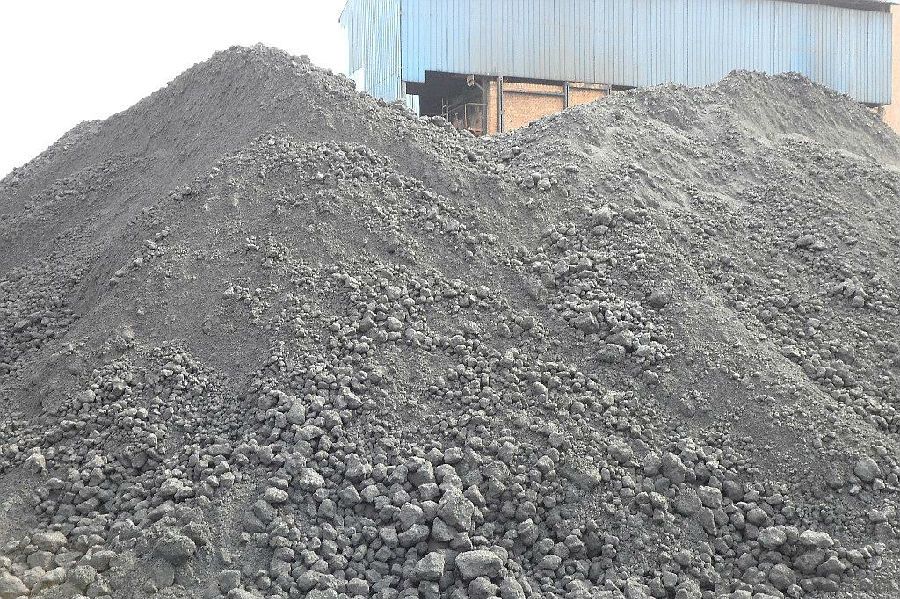


4. Calcined Petroleum Coke Specification
| Place of Origin: | Jiangsu, China (Mainland) | Type: | Petroleum Coke | Calory (J): | 7783 |
| Sulphur Content (%): | 4 | Ash Content (%): | 0.5 | Fixed Carbon (%): | 86 |
| Moisture (%): | 7.3 | Volatile Matter (%): | 10.12 | Abrasive Resistance: | 70 |
| Size: | Different sizes |
5.FAQ of Calcined Petroleum Coke
1). Q: Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are a factory.
2). Q: Where is your factory located? How can I visit there?
A: Our factory is located in ShanXi, HeNan, China. You are warmly welcomed to visit us!
3). Q: How can I get some samples?
A: Please connect me for samples
4). Q: Can the price be cheaper?
A: Of course, you will be offered a good discount for big amount.
- Q: What is carbon neutral certification?
- The process of carbon neutral certification involves evaluating and verifying organizations, products, or services to ensure they have a carbon footprint that equals zero. This requires taking significant measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and offsetting any remaining emissions through the purchase of carbon credits or investments in projects that remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. To achieve carbon neutrality, entities undergo a thorough assessment that measures their carbon emissions, sets reduction targets, implements initiatives to reduce their carbon footprint, and tracks progress. After reducing emissions as much as possible, any remaining emissions are offset by investing in verified projects such as reforestation, renewable energy, or energy efficiency projects that reduce greenhouse gases. Certification is conducted by an independent third-party organization to evaluate and verify carbon neutrality claims, ensuring transparency and credibility. Once certified, organizations or products can display the carbon neutral label to demonstrate their commitment to environmental sustainability and responsible carbon management. Carbon neutral certification is crucial as it offers a standardized and recognized method for organizations and products to showcase their dedication to combating climate change. It enables consumers and stakeholders to make informed choices by supporting entities that have taken concrete steps to reduce their carbon emissions and contribute to a more sustainable future. Moreover, carbon neutral certification encourages organizations to adopt sustainable practices and invest in environmentally positive projects, thus hastening the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Q: How do fossil fuels release carbon into the atmosphere?
- Fossil fuels release carbon into the atmosphere through the process of combustion. When fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are burned for energy production, carbon dioxide (CO2) is released as a byproduct. This CO2 is a greenhouse gas that traps heat in the Earth's atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
- Q: How about carbon content of coal ash?
- 3, burning(1) prepared burning specimen with constant weight in the outer side of the crucible crucible, only a few 10-18ml and drying on the only black ink written into the code, mother Eph furnace, baby 50+-25 degrees Celsius temperature burning 1 hours after cooling, weighing with analytical balance, write down the number of crucible weight again after burning, and then weighed to weight two times constant (weight <=0.0004 grams). Record crucible weight G1.(2) place about 1 grams of dry ash sample in a constant crucible, and accurately weigh (accurate to 0.0001 grams), record (crucible + sample) weight G2. (3) a crucible with soil sample is placed in a crucible cover, heated to 875 degrees Celsius in the Maffei furnace for ignition, keep the temperature of 850+-25 degrees Celsius, after 2 hours, take out, after cooling, cooling to room temperature to put in a drying box. 4 W T'o X7 I3 L) |% "Z (4) weighing burned (crucible + specimen), down under the weight of G3.4. Calculate ash carbon content C (%) = (G2-G3) / (G2-G1) *100 (%)
- Q: How does carbon pricing work?
- Carbon pricing is an approach that utilizes the market to decrease greenhouse gas emissions by placing a value on carbon emissions. This is achieved by assigning a financial cost to the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which greatly contribute to climate change. There exist two primary forms of carbon pricing mechanisms: carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems. Under a carbon tax, a fixed price per metric ton of carbon emissions is established, and emitters are obligated to pay this tax according to their emissions. The tax can be imposed at different points in the supply chain, such as during extraction, production, or consumption. The goal of a carbon tax is to create a economic deterrent for emitting carbon and motivate industries and individuals to reduce their emissions. On the other hand, cap-and-trade systems impose a limit or cap on the total amount of carbon emissions permitted within a specific jurisdiction. This cap is divided into allowances, which represent the right to emit a particular amount of carbon. These allowances are either distributed or auctioned to emitters in the form of permits. Emitters can then trade these permits amongst themselves in a market. If an emitter surpasses their allocated allowances, they must purchase additional permits from those who have surplus allowances. This establishes a market-based incentive for emission reduction, as those who can more cost-effectively decrease their emissions can sell their excess allowances to those who are unable to. Both carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems aim to incorporate the cost of carbon emissions into the economy, making pollution more expensive and encouraging the adoption of cleaner technologies and practices. By assigning a value to carbon, these mechanisms provide economic signals that urge businesses, industries, and individuals to invest in low-carbon alternatives, energy efficiency, and innovation. Additionally, they generate revenue for governments, which can be utilized to fund efforts in climate change mitigation and adaptation, renewable energy projects, or to reduce other taxes. Overall, carbon pricing mechanisms are designed to establish economic incentives for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, facilitating the transition to a low-carbon economy, and mitigating climate change. While they may not be a perfect solution, they are widely acknowledged as one of the most effective tools for driving emission reductions and combating climate change.
- Q: How do plants and trees absorb carbon dioxide?
- Through photosynthesis, plants and trees engage in a process known as carbon dioxide absorption. This process entails the conversion of sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. Within the plant cells, this transformation occurs in specialized structures called chloroplasts. During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere via small openings on their leaves called stomata. The carbon dioxide then infiltrates the plant's cells and travels to the chloroplasts. Within these chloroplasts, the energy from sunlight is utilized to convert the carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The glucose generated through photosynthesis serves as a vital energy source for the plant's growth, reproduction, and other metabolic activities. Some of this glucose is stored as starch within the plant, while the remainder is used to produce other crucial compounds. The oxygen produced during photosynthesis is subsequently released back into the atmosphere through the stomata. This oxygen is indispensable for the survival of various animals, including humans, as it is necessary for respiration. In essence, the absorption of carbon dioxide through photosynthesis is an essential function performed by plants and trees. They function as natural carbon sinks, playing a vital role in regulating the levels of this greenhouse gas and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
- Q: How is carbon used in the production of steel?
- The production of steel heavily relies on carbon as it directly impacts the characteristics and properties of the end product. Carbon is primarily used as an alloying element in the steelmaking process, where it is carefully added to modify the composition of the steel. The basic oxygen furnace (BOF) process is one of the most commonly employed methods for steel production. In this process, carbon is introduced to the molten iron to achieve the desired grade of steel. The quantity of carbon added determines the steel's mechanical properties, including hardness and strength. Generally, higher levels of carbon result in a harder and stronger steel. Another steelmaking process, known as the electric arc furnace (EAF) process, also utilizes carbon. In this process, recycled steel scrap is melted down using an electric arc to create new steel. Carbon is added during this stage to adjust the carbon content to meet the requirements of the desired steel grade. Moreover, carbon plays a critical role in the heat treatment of steel. Through techniques like carburizing and quenching, carbon is utilized to enhance the surface hardness and wear resistance of steel components. This is particularly vital in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, where the durability and strength of steel are of utmost importance. To summarize, carbon is indispensable in the production of steel as it directly influences the mechanical properties and overall quality of the final product. From regulating the carbon content to controlling heat treatment processes, carbon serves as an essential component in the steelmaking industry.
- Q: Consult the carbon content of austenite
- Pure iron carbon alloys, austenitic (A) carbon content in different grades, different temperature and different, in more than 727 degrees (727 degrees when the carbon content is 0.77%), 1148 degrees, 2.11% carbon content with see iron carbon phase diagram
- Q: What's the difference between an alkaline cell and a carbon cell?
- 3. Alkaline batteries, also called alkaline dry cells, are suitable for large capacity and long time use. The internal resistance of the battery is low, so the current produced is larger than that of the general zinc manganese battery, while the environmental protection type mercury content is only 0.025%, and no recycling is needed. Based on his environmental protection, and the current characteristics of large, so now alkaline battery more.4. In the final analysis, the essential difference between a carbon cell and an alkaline cell is the internal material. In short, carbon battery consists of carbon, zinc skin composition, but its internal cadmium and mercury, is not conducive to environmental protection, but it is cheap, so there is a space for one person in the market, and the alkaline battery no pollution of heavy metal ions, high current, conducive to environmental protection, is the future development direction of the battery!
- Q: What are the effects of carbon emissions on the stability of desertification?
- Carbon emissions have a significant impact on the stability of desertification. The release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere through human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, contribute to global warming. This increase in temperature leads to several adverse effects on desertification. One of the key consequences of carbon emissions is the alteration of precipitation patterns. As the planet warms, the evaporation rate increases, causing more water to be held in the atmosphere. This results in reduced rainfall in many regions, including arid and semi-arid areas already prone to desertification. The decrease in water availability exacerbates the dry conditions, making it easier for desertification to occur and intensify. Moreover, higher temperatures caused by carbon emissions contribute to the acceleration of soil erosion. As the land heats up, it becomes more prone to erosion through wind and water. This leads to the loss of topsoil, which is crucial for plant growth and stability. Without a stable layer of topsoil, vegetation struggles to establish and survive, ultimately contributing to the expansion of deserts. Furthermore, carbon emissions also impact the health and productivity of plant communities. Increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can stimulate plant growth in some cases, but this often leads to the proliferation of invasive species that are better adapted to the changing conditions. These invasive species outcompete native plants, reducing biodiversity and further destabilizing the ecosystem. Additionally, as desertification progresses, the loss of plant cover results in reduced carbon sequestration capacity, leading to even higher carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. In conclusion, carbon emissions have detrimental effects on the stability of desertification. They disrupt precipitation patterns, accelerate soil erosion, reduce plant productivity, and diminish the capacity to sequester carbon. It is crucial to reduce carbon emissions through sustainable practices and conservation efforts to mitigate the impacts on desertification and prevent its further progression.
- Q: The victory of the lightning 3361 material is full of carbon fiber, and the 3363 is made of carbon fiber and resin, which is better??
- All carbon fiber is good. The resin is only used for the badminton line, not for the racket.All carbon fiber material, is the most important material for badminton racket, all carbon fiber, good toughness, but also take into account the light performance.Carbon composite fiber, that is, in the carbon fiber added ordinary metal elements, such as aluminum, this material is relatively heavy, and toughness is not all carbon material.The best one is the carbon fiber material of racket frame which added to the rare metal, adding rare metal frame strong resilience, stability is better, and more suitable for double play.
Send your message to us
Low Sulfur Calcined Petroleum Coke of CNBM in China
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords