HOT ROLLED STEEL ANGLE BAR EAL QUAL ANGLE BAR Q235 JIS
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Specifications of Structure Steel Angle Bar
1.Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
2.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS3.Material:GBQ235B,Q345BorEquivalent;ASTMA36;EN10025,S235JR,S355JR;JISG3192,SS400;SS540.
4.Sizes:
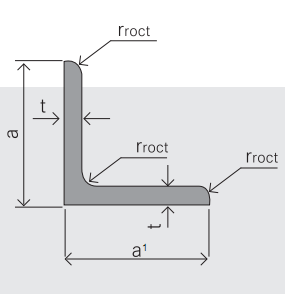
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
25 | 25 | 2.5---3.0 | 6M/12M |
30 | 30 | 2.5---4.0 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 2.5 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 3.0---5.0 | 6M/12M |
40 | 40 | 3.0---6.0 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3.7---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
60 | 60 | 5.0---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
63 | 63 | 6.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
65 | 65 | 5.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
70 | 70 | 6.0---7.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
75 | 75 | 5.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
80 | 80 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
90 | 90 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
5. Material details:
Alloy No | Grade | Element (%) | |||||
C | Mn | S | P | Si | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Q235 | B | 0.12—0.20 | 0.3—0.7 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.3 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Alloy No | Grade | Yielding strength point( Mpa) | |||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | ||||
≥ | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Q235 | B | 235 | 225 | 215 | 205 | ||
Alloy No | Grade | Tensile strength (Mpa) | Elongation after fracture (%) | ||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
| ≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | |||
≥ | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Q235 | B | 375--500 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | |
Usage & Applications of Structure Steel Angle Bar
According to the needs of different structures, Angle can compose to different force support component, and also can be the connections between components. It is widely used in various building structures and engineering structures such as roof beams, bridges, transmission towers, hoisting machinery and transport machinery, ships, industrial furnaces, reaction tower, container frame and warehouse etc.
- Q: How do steel angles contribute to the overall stability of a structure?
- Steel angles contribute to the overall stability of a structure in several ways. First and foremost, steel angles are commonly used as structural members in various applications such as building frames, bridges, and towers. Their L-shaped profile provides excellent strength and load-bearing capabilities, making them ideal for supporting heavy loads and resisting bending or buckling. One of the primary functions of steel angles is to provide structural support and stability by distributing the load evenly across different components of the structure. By connecting various elements together, such as beams, columns, and girders, steel angles ensure that the weight and forces acting on the structure are effectively transferred and resisted, preventing any potential collapse or failure. Moreover, steel angles enhance the overall rigidity and stiffness of a structure. By adding diagonal bracing elements made of steel angles, the structure becomes more resistant to lateral forces such as wind or earthquakes. These diagonal braces create a triangular configuration, which is known for its stability and ability to withstand horizontal loads. This increased stability and resistance to lateral forces significantly contribute to the overall safety and durability of the structure. Additionally, steel angles play a crucial role in mitigating torsional forces in a structure. Torsion occurs when one end of a structural member is twisted while the other end remains fixed, resulting in a twisting moment being applied to the structure. Steel angles can be strategically placed and connected to resist these torsional forces, preventing any excessive twisting or deformation that could compromise the stability of the structure. In summary, steel angles are essential components that contribute to the overall stability of a structure in multiple ways. They provide structural support, distribute loads efficiently, enhance rigidity, resist lateral forces, and mitigate torsional forces. By incorporating steel angles into the design and construction of a structure, engineers can ensure its long-term stability, safety, and durability.
- Q: What are the different connections used with steel angles?
- There are several different connections that can be used with steel angles, including bolted connections, welded connections, and clip connections. Bolted connections involve using bolts and nuts to connect the angles to other structural members. Welded connections involve fusing the angles to the other members using a welding process. Clip connections involve using clips or brackets to secure the angles to the other members. The choice of connection depends on factors such as the load requirements, design specifications, and fabrication capabilities.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in the construction of staircases?
- Indeed, staircases can be constructed using steel angles. Due to their strength and versatility, steel angles are frequently employed as structural elements in construction. In the context of staircases, steel angles serve to offer support and stability to the entire structure. They can establish the framework for the stairs, providing support for the treads and risers. Moreover, steel angles can serve as handrails or guardrails, ensuring a firm and safe grip for users. All in all, steel angles are a favored option for staircase construction due to their durability, capacity to bear loads, and aesthetic attractiveness.
- Q: Can iron angle steel be welded with stainless steel angle steel?
- If the angle, in a cross-sectional angle welding of carbon steel plate, stainless steel angle welding a stainless steel cross sectional iron. Two cross cutting iron plate punching, 8.8 high strength screw fastening piece.Carbon steel and stainless steel welding, belong to dissimilar metal welding. Higher requirements for welding technology. Screw connections are the most economical,
- Q: Are steel angles suitable for rooftop installations?
- Yes, steel angles are suitable for rooftop installations. They are commonly used in construction for their strength and durability. Steel angles provide structural support and can be easily attached to rooftops to secure various installations such as solar panels, antennas, or HVAC equipment.
- Q: What are the different types of connections for steel angles?
- Depending on the specific application and load requirements, there are various connection types available for steel angles. Some commonly used connections for steel angles include: 1. Welded connections: The most frequently employed connection type for steel angles involves welding the angle to the supporting structure or to another angle, creating a strong and rigid connection. Welded connections are typically utilized in applications where high load capacity and stability are essential. 2. Bolted connections: Bolts are used to connect the steel angles to the supporting structure or to other angles in bolted connections. This connection type allows for easy assembly and disassembly, making it suitable for applications where flexibility and adjustability are important. 3. Riveted connections: In riveted connections, rivets are used instead of bolts to secure the steel angles. This type of connection offers a robust and durable connection and is commonly found in structural applications. 4. Clip connections: Clip connections involve the use of steel clips to connect the angles to the supporting structure. This connection type is often employed in applications where ease of installation and flexibility are prioritized. 5. Moment connections: Moment connections are utilized to transfer bending moments between steel angles and the supporting structure. These connections are specifically designed to provide rigidity and stability in applications where high load capacity and resistance to lateral forces are required. 6. Gusset plate connections: Gusset plate connections involve the use of steel plates to connect the steel angles to the supporting structure. These connections provide additional strength and stability and are commonly employed in applications where heavy loads and high stresses are anticipated. It is important to consider various factors, such as the specific application, load requirements, and design considerations when selecting the appropriate connection type. Consulting with a structural engineer or a professional in steel construction is recommended to ensure the suitability of the chosen connection type for a specific project.
- Q: What is the minimum radius for a curved steel angle beam?
- Various factors, including material thickness, type of steel, and design requirements, contribute to determining the minimum radius for a curved steel angle beam. However, there are generally accepted guidelines that should be followed when considering this minimum radius. Typically, the minimum radius for a curved steel angle beam is determined by the bending capacity of the steel material being used. This bending capacity is influenced by the yield strength, tensile strength, and section properties of the steel angle beam. To calculate the minimum radius, the bending stress induced in the steel angle beam must be taken into account. This bending stress depends on the applied load, curvature radius, and section properties of the beam. By ensuring that the bending stress does not exceed the allowable stress limits of the steel material, a safe minimum radius can be established. Specific guidelines and requirements regarding minimum radii for curved steel angle beams can be found in relevant design codes and standards such as the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) Manual or the Eurocode. These codes provide detailed information on the design and fabrication of curved steel members, including any limitations on minimum radii. For accurate calculations and analyses based on the specific project requirements, it is advisable to consult a qualified structural engineer or a steel fabrication specialist. Their expertise can ensure that the necessary calculations are performed correctly.
- Q: What is the difference between galvanized steel angle and ordinary angle iron?
- Ordinary angle iron and hot galvanized steel angle per ton difference of about 2500 yuan.
- Q: Can steel angles be used as support beams?
- Indeed, it is possible to utilize steel angles as support beams. Due to their remarkable strength and durability, steel angles find widespread application in the construction industry. They frequently serve as support beams, contributing to the structural integrity and stability of various edifices, bridges, and other infrastructures. The ease of fabrication and installation of steel angles renders them a highly favored option in construction ventures. Their adaptability and capacity to withstand substantial loads render them exceptionally suitable for deployment as support beams.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in construction?
- Indeed, construction can utilize steel angles. Due to their versatility, strength, and cost-effectiveness, steel angles are frequently employed as structural elements in construction endeavors. Their primary purpose is to support and reinforce various structural components, including beams, columns, and walls. Various sizes and thicknesses of steel angles are available, allowing for a wide range of applications in construction. They can be easily joined together through welding, bolting, or fastening, facilitating convenient on-site installation and customization. A key advantage of incorporating steel angles in construction lies in their high strength-to-weight ratio. This attribute enables steel angles to possess outstanding load-bearing capacity while remaining relatively lightweight, rendering them highly suitable for structures that necessitate strength without excessive weight. Moreover, steel angles exhibit excellent durability and resistance against environmental factors such as corrosion, fire, and pests. Consequently, structures constructed with steel angles boast extended lifespans and require minimal maintenance over time. In summary, steel angles offer a versatile and dependable option for construction projects, regardless of whether they are residential, commercial, or industrial in nature. Architects, engineers, and contractors commonly favor steel angles due to their strength, durability, and ease of installation.
Send your message to us
HOT ROLLED STEEL ANGLE BAR EAL QUAL ANGLE BAR Q235 JIS
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























