HONGRI -stainless steel sheet 304/316/321/309S/310S/904L/202/201
- Loading Port:
- Guangzhou
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
stainless steel plate/sheet detailed information:
Type | Wuxi boro-304/304L/316/316L/321/309S/310S/904L/202/201/430 stainless steel sheet |
Thinckness | 0.3mm-60mm |
Widthness | 50mm~2000mm or customized |
Length | 1000mm~8000mm or customized |
Brand name | FO SHAN HONG RI |
Standard | JIS, AISI, ASTM, GB, DIN, EN |
Material | 201/201/304/304L/316/316L/321/309S/310S/904L stainless steel sheet |
Surface | 2B,BA,HL,BK,NO.1,NO.4,8K,SB,etc |
Certificate | We accept the third inspections--SGS-BV etc. |
Application | Bridge, Shipbuilding,roofing,Car, etc |
Standard sheet sizes | 1000mm*2000mm,1250mm*2500mm,1219mm*2438mm,1500mm*3000mm We can produce other standard as customized |
Certification | BV,SGS ,CE |
Stainless steel maintenance:
(1) Regular cleaning and maintenance
(2) Pay attention to prevent the occurrence of the phenomenon of surface scratches
(3) Use soap, weak detergent or warm water to remove surface dust, dirt
(4) In addition to the surface of the binder with alcohol or an organic solvent (ether, benzene)
(5) Use neutral detergent or ammonia solution in addition to surface oil
(6) With 10% nitric acid or abrasive detergent in addition to the surface of the embroider caused by the dirt.
stainless steel plate/sheet detailed apllication:
| Finish | Thickness | Characteristics | Applications |
| No. 1 | 3.0mm~50.0mm | Finished by hot-rolling, annealing and pickling, characterized by white pickled surface | Chemical industry equipment, Industrial tanks |
| No. 2B | 0.3mm~6.0mm | Finished by heat treatment, pickling after cold rolling, followed by skin pass line to be more brighter and smooth surface | General Application Medical Instruments,Tableware |
| No. BA (Bright Annealed) | 0.5mm~2.0mm | Bright heat treatment after cold rolling | Kitchen utensil, kitchen ware,architectural purpose |
| No. 4 | 0.4mm~3.0mm | Polishing with No. 150 to No.180 mesh abrasivesThe most popular finishes | Milk & Food processing acilities, Hospital Equipment, Bath-tub |
| HL(Hair Line) | 0.4mm~3.0mm | Finished by continuous linear polishing | Architectural purposes, escalators, kitchen ware vehicles |
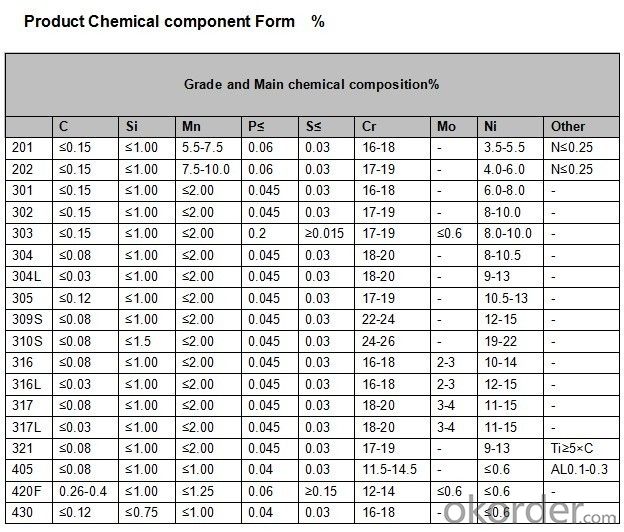
Chemical Composition:stainless steel sheet
Processing:stainless steel sheet
There are high-tech equipments to processing stainless coils and sheets/plates with skilled workers.
Cut to length
Decoiling and slitting
Grinding and brushing
Film protection
Plasma and water jet cutting
Folding and embossing
- Q: Can stainless steel strips be used in HVAC applications?
- Certainly, HVAC applications can indeed utilize stainless steel strips. Stainless steel, known for its high durability and resistance to corrosion, proves to be an ideal material for HVAC systems that are exposed to moisture, chemicals, and fluctuating temperatures. In fact, fabricating HVAC components like ducts, pipes, fittings, and heat exchangers frequently involves the use of stainless steel strips. These strips offer exceptional strength, longevity, and resistance to rust and corrosion, ensuring the HVAC system's reliability and efficiency in the long run. Furthermore, stainless steel's sanitary properties make it suitable for cleanroom environments or for handling delicate materials. All in all, stainless steel strips prove to be a versatile and dependable choice for various HVAC applications.
- Q: How do stainless steel strips perform in the presence of chlorine?
- Stainless steel strips generally perform well in the presence of chlorine. Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance properties, and it forms a passive chromium oxide layer on its surface that provides protection against oxidation and corrosion. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing chlorine from reaching the underlying steel and causing corrosion. However, in certain conditions, stainless steel can still be susceptible to localized corrosion, such as pitting and crevice corrosion, in the presence of high concentrations of chlorine or in the presence of other corrosive agents. It is important to consider the specific grade of stainless steel being used, as some grades may have better resistance to chlorine than others. Additionally, proper maintenance and cleaning procedures should be followed to ensure the longevity and performance of stainless steel strips in chlorine-rich environments.
- Q: How do stainless steel strips perform in the presence of sulfuric acid?
- Stainless steel strips generally exhibit good resistance to sulfuric acid under certain conditions. The performance of stainless steel in the presence of sulfuric acid depends on several factors including the concentration and temperature of the acid, the grade of stainless steel, and the duration of exposure. In general, stainless steel is resistant to dilute sulfuric acid solutions (up to 10%) at room temperature. The passive film that naturally forms on the surface of stainless steel provides excellent protection against corrosion in these conditions. The resistance can vary depending on the specific grade of stainless steel, with austenitic stainless steel (such as 304 and 316) offering better corrosion resistance than ferritic or martensitic grades. However, as the concentration of sulfuric acid increases or the temperature rises, the corrosion resistance of stainless steel can be compromised. At higher concentrations (above 10%) or elevated temperatures, stainless steel may experience localized corrosion, including pitting or crevice corrosion. Under such conditions, it is common to use higher alloyed stainless steels, such as duplex or super duplex grades, which offer enhanced resistance to sulfuric acid. It is important to note that prolonged exposure to sulfuric acid can eventually lead to corrosion even in stainless steel. Therefore, it is advisable to limit the exposure time and concentration of the acid to minimize the risk of corrosion. Additionally, proper maintenance and regular cleaning can help maintain the corrosion resistance of stainless steel in the presence of sulfuric acid.
- Q: Can stainless steel strips be used in electrical applications?
- Yes, stainless steel strips can be used in electrical applications. Stainless steel is known for its high resistance to corrosion and heat, making it suitable for various electrical components like connectors, terminals, and conductors. Additionally, stainless steel's excellent mechanical properties and conductivity make it a reliable choice for applications where electrical conductivity and durability are required.
- Q: What is the difference between austenitic and martensitic stainless steel strips?
- Austenitic stainless steel strips have a face-centered cubic crystal structure, which provides high corrosion resistance, excellent formability, and good weldability. On the other hand, martensitic stainless steel strips have a body-centered cubic crystal structure, making them harder and more brittle than austenitic steel. Martensitic steel is known for its high strength and hardness, but it sacrifices some of the corrosion resistance and formability found in austenitic steel.
- Q: How do stainless steel strips resist erosion?
- Stainless steel strips have the ability to resist erosion due to their unique composition and properties. Firstly, stainless steel is an alloy that contains a high percentage of chromium, which forms a protective layer of chromium oxide on the surface of the steel. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing oxygen and moisture from reaching the underlying metal and thus protecting it from corrosion and erosion. Additionally, stainless steel strips are also highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and various chemicals, which makes them suitable for applications in harsh environments. The presence of other alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum further enhances the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. Furthermore, the structure of stainless steel, particularly the austenitic stainless steel, provides excellent strength and toughness, making it more resistant to mechanical erosion. The combination of its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties makes stainless steel strips highly durable and able to withstand erosive forces. Moreover, stainless steel strips can be treated with various surface finishes like passivation or electro-polishing, which further improves their resistance to erosion. These treatments remove impurities and contaminants from the surface, creating a smoother and more corrosion-resistant finish. Overall, the ability of stainless steel strips to resist erosion can be attributed to their corrosion-resistant composition, surface treatments, and excellent mechanical properties. These factors make stainless steel an ideal material for various applications where erosion resistance is crucial, such as in the manufacturing of automotive components, kitchen appliances, and chemical processing equipment.
- Q: What are the limitations of using 111 stainless steel strips?
- When using 111 stainless steel strips, certain limitations should be taken into account: 1. Corrosion Resistance: While stainless steel is generally known for its resistance to corrosion, 111 stainless steel strips may not exhibit the same level of resistance as other grades. This can make them more prone to corrosion in environments with high chloride or sulfur levels. 2. Strength and Hardness: Compared to other stainless steel grades, 111 stainless steel strips may have lower strength and hardness properties. This can limit their suitability for applications that require high tensile strength or resistance to wear and abrasion. 3. Weldability: The higher carbon content of 111 stainless steel strips can pose challenges during welding. This can result in the formation of carbides during the welding process, reducing weldability and potentially causing brittleness in the heat-affected zone. 4. Magnetic Properties: Unlike some other stainless steel grades, 111 stainless steel strips are generally magnetic. This limits their usage in applications that require non-magnetic properties, such as electronic devices or sensitive equipment. 5. Availability and Cost: 111 stainless steel strips may be less readily available in the market compared to more commonly used grades. This can make them harder to source and potentially more expensive. 6. Temperature Limitations: When exposed to high temperatures, 111 stainless steel strips may have limitations. They may experience reduced strength and increased susceptibility to oxidation or scaling, which restricts their use in high-temperature applications. When selecting stainless steel strips for specific applications, it is crucial to consider these limitations as they can impact the material's performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Q: What are the maximum temperatures stainless steel strips can withstand?
- The maximum temperatures that stainless steel strips can endure are dependent on the particular grade of stainless steel utilized. In general, stainless steel is recognized for its ability to resist high temperatures, making it suitable for a wide array of applications. The commonly employed grades of stainless steel, like 304 and 316, typically possess the capacity to withstand temperatures of up to approximately 1500°F (815°C) without experiencing significant deformation or loss of mechanical properties. Nonetheless, there exist specialized grades of stainless steel, for instance, 310 and 330, which exhibit an even greater resistance to high temperatures, enduring temperatures of around 2100°F (1150°C). It is vital to consider the specific grade and intended application when establishing the maximum temperature that stainless steel strips can bear.
- Q: Can stainless steel strips be used in high-temperature applications?
- Certainly! High-temperature applications can indeed utilize stainless steel strips. Renowned for its impressive heat resistance, stainless steel is capable of enduring elevated temperatures while maintaining both its strength and structural integrity. With a high melting point and minimal thermal expansion, stainless steel proves to be an excellent choice for environments characterized by heightened temperatures. Moreover, its resistance to oxidation and corrosion further enhances its aptness for high-temperature applications. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, chemical, and power generation frequently employ stainless steel strips in order to withstand extreme temperatures and challenging conditions.
- Q: Are stainless steel strips suitable for electrical applications?
- Yes, stainless steel strips are suitable for electrical applications. Stainless steel is a highly versatile material that offers excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and electrical conductivity. These properties make it ideal for various electrical applications, including electrical enclosures, conduits, electrical connectors, and grounding equipment. Additionally, stainless steel strips can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for applications that involve heat, such as electric heating elements. Overall, stainless steel strips provide a reliable and long-lasting solution for electrical applications.
Send your message to us
HONGRI -stainless steel sheet 304/316/321/309S/310S/904L/202/201
- Loading Port:
- Guangzhou
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords
































