Cyanuric Acid 98.5% Granular High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 17 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1800 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Cyanuric Acid
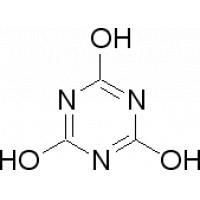
Structure of Cyanuric Aicd Descriptions:
Trade Name: Isocyanuric Acid
Other name: Cyanuric Acid; 1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triol
Uses: Bleaches and sanitisers.
Formula: C3H3N3O3
Molecular Weight: 129.07
CAS NO.: 108-80-7
Main Feautrues of Cyanuric Acid
White powder, granular or colored tablet form, non-toxic and odorless
Cyanuric Acid Image:

Cyanuric Acid Specification:
| ITEM | SPECIFICATION | RESULT | |||
| Content | ≥98.5% | 98.64% | |||
| Moisture | ≤0.5% | 0.11% | |||
| PH value | 4.0-4.5 | 4.26 | |||
| Fe2+ | ≤15ppm | 7.5ppm | |||
| NH4+ | ≤200ppm | 97ppm | |||
| Ash | ≤0.1% | 0.05% | |||
| Insoluble matter in DMF | ≤0.3% | 0.25% | |||
| Appearance | White crystalline power | White crystalline power | |||
| Mesh number | 95% pass 80 mesh | 95% pass 80 mesh | |||
| White degree | ≥89 | 90.5 | |||
| Conclusion: | The product complies with the standard above. | ||||
Packing:
in 25kg, 1000kg bag for powder
in 25kg plastic bag or 50kg PE drums for granular


Storage:
kept in a light-proof,well-colsed,dry and cool place.
- Q: A biological catalyst or a chemical reaction facilitator is know as a/an?
- A biological catalyst is an enzyme. Here are more details for you. Enzymes – biological catalysts Normally chemical reactions do not proceed spontaneously, but require the help of a catalyst. A catalyst accelerates a chemical reaction without itself being changed. For example, the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen to produce water requires the addition of the metal platinum. These days we encounter the concept of a catalyst most often in connection with technology for cleaning up the exhaust fumes from our automobiles, where platinum and rhodium catalyze the breakdown of polluting nitrogen oxides. Chemical reactions within living cells must also be catalyzed. Biological catalysts are called enzymes. There is, for instance, an enzyme in our saliva which converts starch to a simple sugar, which is used by the cell to produce energy, and another enzyme which degrades the excess lactic acid produced when we overexert ourselves. All green plants contain enzymes which convert carbon dioxide in the air to nutritious carbohydrates such as sugar and starch. Without enzymes life would not be possible! Enzymes are highly selective. Among the thousands of different compounds in a cell, an enzyme can recognize the right molecule (substrate) and transform it into a new product. This property arises from the special three-dimensional structure of each enzyme. One can compare an enzyme and its substrate with a lock and its key. Enzymes are very effective catalysts. A chemical reaction might require several months to reach completion without a catalyst, but only a few seconds with the help of an enzyme. Since the enzyme remains unchanged, one enzyme molecule can catalyze the transformation of millions of substrate molecules. Up until the beginning of the 1980's, all enzymes were thought to be proteins. We now know that proteins do not have a monopoly on biocatalysis. RNA molecules can also function as enzymes.
- Q: Before and after the reaction, the chemical properties and quality of the water did not change, and the water was the catalyst
- 3HIO + 3H2 = 3H2O + 3HI
- Q: No one knows the expression of the catalyst and the chemical expression of the acridine
- In organic reactions, the catalyst is complex and consists of several or more. Write Chinese characters directly.
- Q: Does a catalyst work for both reactants and products?From my understanding, organic catalyst or enzyme does not necessarily work for the product of the reaction because of the shape of the activation site. However I cannot speak for inorganic ones.
- Generally, catalysts participate and facilitate a reaction, but the catalyst is returned unchanged. For example, sulfuric acid may be used in a Fischer esterification, palladium in a Heck reaction, pyridine in an acylation reaction, hydroxide in an aldol condensation, cyanide in a benzoin condensation, etc. An enzyme can facilitate a reaction is a similar manner, by being an acid or base catalyst for example. We could say that generally, reactions are reversible. Practically, that is not true as the energy differences of the reactants and products may be so different to prevent the reverse, an explosion for example. If a reaction is reversible, that may not mean the reverse reaction will take place. Le Chatelier's Principle can apply to determine the products.
- Q: Why is the catalyst in the chemical balance, the rate of change and balance?
- But the positive reaction rate is accelerated, but also speed up the reverse reaction rate, the two increase the same multiple, so the system is still in a stable state, the same balance.
- Q: Who knows hydrogen and nitrogen in the high temperature, high pressure and catalyst conditions for the synthesis of ammonia chemical equation ah? Urgent! The SOS
- 3H2 + N2 ===== 2NH3 conditional catalyst
- Q: explain how a catalyst can affect the rate of reaction but not be in the overall equation.?
- a catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of reactions that would already happen (the reactions are spontaneous) but would take a long long time to occur. Every reaction proceeds from a level of high energy to a lower level of energy, but in order to start going downhill you need to get up, in affect getting more energy than the reactants have now. This is because the transition state, or what the reactnat/product is in the middle of the reaction, is less stable and requires more energy than the reactants. Catalysts lower the extra energy needed (called activation energy) to a level that the reactants already have, and the reaction occurs.
- Q: What is the difference between an enzyme catalyst in a living body and a catalyst in chemistry?
- (Such as: high temperature, high pressure, strong acid, alkali, etc.), but the enzyme catalyzed reaction (enzymatic reaction) is generally at room temperature, atmospheric pressure (normal reaction), the reaction temperature of the chemical reaction, , Neutral pH, etc. under mild reaction conditions.
- Q: In the chemical reaction, the rate of decomposition reaction is related to the quality of the catalyst?
- The catalyst can affect the reaction rate, the faster the amount of reaction or slower. Of course there are limits,
- Q: Can you describe at least 4 ways a catalyst can lower the activation energy of a reaction?
- To see how a catalyst accelerates the reaction, we need to look at the potential energy diagram shown below which compares the non-catalytic and the catalytic reaction. For the non-catalytic reaction, the figure is simply the familiar way to visualize the Arrhenius equation: the reaction proceeds when A and B collide with succificient energy to overcome the activation barrier. The change in Gibbs free energy between reactants, A + B, and the product P is delta G. The catalytic reaction starts by bonding of the reactants A and B to the catalyst, in a spontaneous reaction. Hence, the formation of this complex is exothermic and the free energy is lowered. There then follows the reaction between A and B while they are bound to the catalyst. This step is associated with an activation energy; however, it is significantly lower than that for the uncatalyzed reaction. Finally, the product P seperates from the catalyst in an endothermic step. The energy diagram illustrates 4 ways the catalyst works : The catalyst offers an alternative path for the reaction that is energetically more favorable The activation energy of the catalytic reaction is significantly smaller than that of the uncatalyzed reaction; hence the rate of the catalytic reaction is much larger The overall change in free energy for the catalytic reaction equals that of the uncatalyzed reaction. Hence, the catalyst does not affect the equilibrium constant for the overall reaction. A catalyst cannot change the thermodynamics of a reaction but it can change the kinetics. The catalyst accelerates both the forward and the reverse reaction to the same extent. In other words, if a catalyst accelerates the formation of product P from A and B, it will do the same for the decomposition of P into A and B.
Send your message to us
Cyanuric Acid 98.5% Granular High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 17 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1800 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches