Galvanized Corrugated Steel Sheet in High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Hot-dip Zinc Coating Steel Building Roof Walls
1.Structure of Hot-Dip GI/GL Steel Sheet Description:
Hot-dip galvanized steel coils are available with a pure zinc coating through the hot-dip galvanizing process. It offers the economy, strength and formability of steel combined with the corrosion resistance of zinc. The hot-dip process is the process by which steel gets coated in layers of zinc to protect against rust. It is especially useful for countless outdoor and industrial applications. Production of cold formed corrugated sheets and profiles for roofing, cladding, decking, tiles, sandwich walls, rainwater protective systems, air conditioning duct as well as electrical appliances and engineering.
2.Main Features of the Hot-Dip GI/GL Steel Sheet:
• Excellent process capability
• Smooth and flat surface
• Workability, durability
• Excellent anticorrosive property
• High strength
• Good formability
• Good visual effect
3.Hot-Dip GI/GL Steel Sheet Images:


4.Hot-Dip GI/GL Steel Sheet Specification:
Standard: ASTM, JIS,EN
Grade: CS, DX51D+Z,SGCC, SS 230~550,S220GD+Z~S550GD+Z, SGC340~SGC570
Thickness: 0.1mm~5mm
Width: max 2000mm
Coil weight:3-12 MT
Coil ID:508/610mm
Surface structure: zero spangle, regular spangle or minimum spangle
Surface treatment: Chromate treatment, Oiled/dry, skinpassed/non-skinpassed
Packing: Standard seaworthy export package
Technology test results:
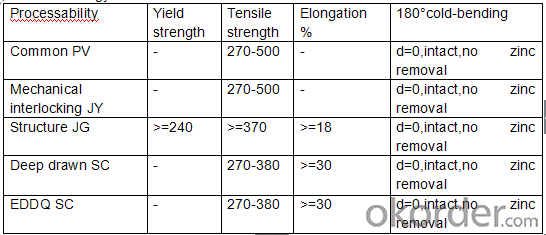
5.FAQ of Hot-Dip GI/GL Steel Sheet:
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1.How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
2. How long can we receive the product after purchase?
Usually within thirty working days after receiving buyer’s advance payment or LC. We will arrange the factory manufacturing as soon as possible. The cargo readiness usually takes 15-30 days, but the shipment will depend on the vessel situation.
- Q:How do steel sheets perform in terms of light reflection?
- Steel sheets have a high level of light reflection due to their smooth and polished surface, making them an excellent choice for applications that require good visibility and illumination.
- Q:Do steel sheets have any environmental benefits?
- Yes, steel sheets have several environmental benefits. Firstly, steel is highly recyclable, meaning that it can be reused multiple times without losing its strength or quality. This reduces the need for virgin raw materials and reduces the amount of waste being sent to landfills. Additionally, steel production has become more energy-efficient, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to other materials. Steel sheets are also highly durable and resistant to corrosion, which means they have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance, reducing the overall environmental impact.
- Q:Can steel sheets be used for elevator manufacturing?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for elevator manufacturing. Steel is a commonly used material in elevator construction due to its strength, durability, and resistance to fire and corrosion. Steel sheets are often used to fabricate the walls, floors, and doors of elevator cabins. Additionally, steel is also utilized for the structural framework and support components of the elevator system. The use of steel sheets in elevator manufacturing provides stability, safety, and longevity to the elevator, making it a reliable choice for vertical transportation.
- Q:What are the different fastening options for steel sheets?
- Depending on the specific application and requirements, there are various fastening options available for steel sheets. Some commonly used fastening options for steel sheets include the following: 1. Screws: Steel sheets can be secured using screws, which are easily accessible and simple to use. Self-tapping screws are commonly employed to fasten steel sheets as they can create their own threads in the material. 2. Bolts and nuts: Bolts and nuts offer a robust and secure fastening choice for steel sheets. They are frequently utilized in situations where adjustability or removability is required. 3. Rivets: Rivets are permanent fasteners commonly used to join two or more steel sheets together. They are often preferred in applications where a watertight or airtight seal is necessary. 4. Welding: Welding is a widely used method for fastening steel sheets. It involves melting the edges of the sheets and joining them together. Welding provides a strong and durable connection but necessitates specialized equipment and expertise. 5. Adhesives: Certain adhesives, such as epoxy or structural adhesives, can be used to bond steel sheets together. Adhesives can create a clean and visually appealing connection, although their strength may vary depending on the specific adhesive used. 6. Clips and clamps: Clips and clamps are frequently employed to secure steel sheets in place. They can be easily installed and removed, making them a popular choice for temporary or adjustable fastening requirements. 7. Magnetic fasteners: Magnetic fasteners, such as magnetic strips or magnets with hooks, can be utilized to attach steel sheets to magnetic surfaces. This offers a convenient and user-friendly fastening option. When selecting a fastening option for steel sheets, it is crucial to consider factors such as strength, durability, ease of installation, and removal. Additionally, the specific requirements of the application, including load-bearing capacity and environmental conditions, should be taken into account to ensure the chosen fastening option is suitable for the intended purpose.
- Q:What are the common surface treatments for steel sheets?
- Common surface treatments for steel sheets include galvanizing, which involves applying a protective layer of zinc to prevent rusting; painting, which provides a decorative finish and additional corrosion resistance; and powder coating, which involves applying a dry powder to the surface and then curing it to create a durable, protective coating. Other treatments may include electroplating, chromating, or phosphating, depending on the specific requirements and intended use of the steel sheets.
- Q:What are the different edge finishes available for steel sheets?
- Depending on the desired aesthetic and functional requirements, steel sheets offer various edge finishes. The most common options are as follows: 1. Mill Edge: Directly from the steel mill, this is the standard and unfinished edge. It is typically used in non-critical applications like industrial or structural use. 2. Trimmed Edge: Irregularities and burrs are removed by trimming or shearing the rough mill edge. This provides a cleaner and more uniform edge, making it suitable for applications where appearance matters. 3. Deburred Edge: Through a deburring process, sharp or jagged edges are eliminated, resulting in a smooth and rounded edge. This enhances safety, making it common in applications involving frequent handling or contact. 4. Beveled Edge: The edge is cut or ground at an angle, creating a sloping or chamfered edge. This improves both aesthetics and functionality, especially in architectural applications and jointing or welding. 5. Rolled Edge: By rolling or bending the steel sheet's edge, a rounded or folded edge is formed. Rolled edges provide a smooth and finished appearance, making them ideal for visible applications like decorative or furniture manufacturing. 6. Hemmed Edge: Folding the edge of the steel sheet over itself creates a double-layered and durable edge resistant to fraying or unraveling. Hemmed edges are commonly used in exposed areas that require added durability, such as roofing or sign manufacturing. These examples demonstrate the range of edge finishes available for steel sheets. Each finish offers unique characteristics and benefits, allowing for customization based on specific requirements and preferences.
- Q:How do steel sheets perform in high-temperature environments?
- Steel sheets perform well in high-temperature environments due to their high melting point and excellent heat resistance. They retain their strength and structural integrity, making them suitable for various applications such as furnace linings, heat exchangers, and industrial ovens. However, prolonged exposure to extremely high temperatures can cause some degradation, such as oxidation or loss of mechanical properties, so appropriate alloying and protective coatings may be necessary for optimal performance.
- Q:What are the common thicknesses for roofing steel sheets?
- Roofing steel sheets come in a variety of thicknesses, typically ranging from 0.4mm to 0.8mm. Nevertheless, the actual thickness required will be influenced by factors like the roofing system type, regional climate, and desired durability level. In regions prone to harsh weather, thicker steel sheets, like those around 0.8mm, are commonly employed, whereas thinner sheets may suffice for less challenging environments. Consulting with a roofing expert or manufacturer is crucial to ascertain the ideal thickness for a particular roofing undertaking.
- Q:What are the different types of steel sheet coatings?
- In the market, there exists a variety of steel sheet coatings, each possessing its own unique properties and advantages. Some of the most commonly utilized types are as follows: 1. Galvanized Coating: This coating is extensively employed for steel sheets due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and ability to prevent rust. It involves the application of a zinc layer onto the steel surface. Galvanized coatings find widespread use in outdoor applications such as roofing, fencing, and automotive parts. 2. Galvannealed Coating: Similar to galvanized coating, galvannealed coating also entails the application of a zinc layer onto the steel surface. However, in this process, the coated steel undergoes a high-temperature annealing process, resulting in the formation of an iron-zinc alloy coating. This type of coating offers improved paintability and weldability, making it ideal for applications that require subsequent painting or welding. 3. Aluminized Coating: Aluminized coatings involve the application of an aluminum layer onto the steel surface. This offers exceptional heat resistance and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications involving high temperatures, such as exhaust systems and ovens. Aluminized coatings also possess good reflectivity properties, which make them valuable for reflective insulation applications. 4. Organic Coatings: Several organic coatings, including epoxy, polyester, and polyurethane coatings, are available for steel sheets. These coatings are typically applied as paints or powder coatings and provide a protective layer that enhances the durability and appearance of the steel. Organic coatings can be tailored to offer specific properties, such as UV resistance, chemical resistance, or decorative finishes. 5. Tin Coating: Tin coatings are commonly utilized in the food packaging industry. They create a barrier between the steel sheet and the food product, preventing any interactions that could compromise the quality or safety of the food. 6. Other Specialty Coatings: Several other specialty coatings are available for specific applications. These include zinc-nickel coatings, which offer enhanced corrosion resistance, and ceramic coatings, which provide high-temperature resistance and excellent electrical insulation properties. In summary, the choice of steel sheet coating depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as corrosion resistance, heat resistance, or aesthetic appeal. It is crucial to carefully evaluate the properties of each coating type to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the steel sheet in its intended use.
- Q:Are steel sheets suitable for food-grade applications?
- No, steel sheets are generally not suitable for food-grade applications as they can potentially leach harmful substances into the food.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Galvanized Corrugated Steel Sheet in High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords






























