Rv Solar Cells
Rv Solar Cells Related Searches
Pv Solar Cells Rv Solar Inverter Residential Solar Cells Rv Solar Inverter Systems Ruthenium Solar Cells Rec Solar Cells Photovoltaic Pv Solar Cells Rv Solar Power Inverter Iii V Solar Cells Raw Solar Cells Solar Inverter Rv Rv Solar Inverter Kits Photovoltaic Solar Cells Solar Inverter For Rv Iii-V Solar Cells Inverter For Rv Solar Pv Cells In Solar Panels Rv Solar System With Inverter Solar Power Inverter For Rv Rv Solar Inverter Kit High Voltage Solar Cells Round Solar Cells Organic Solar Cells Solar Energy Cells Pecvd Solar Cells Rv Solar Inverter Charger Best Rv Solar Inverter Rv Solar Kits With Inverter Solar Panel Inverter For Rv Lightweight Solar CellsRv Solar Cells Supplier & Manufacturer from China
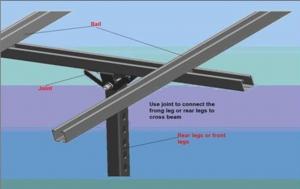
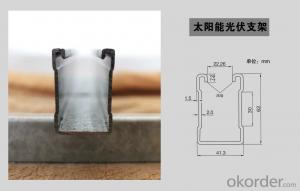
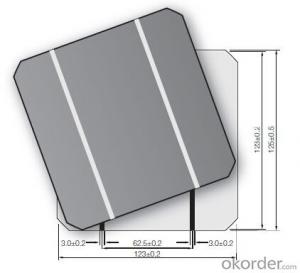
Rv Solar Cells are a type of photovoltaic product designed to convert sunlight into electricity, harnessing renewable energy for various applications. These solar cells are engineered with high efficiency and durability, making them ideal for a wide range of uses. They are commonly utilized in RVs, boats, and other mobile applications where reliable power supply is essential.Rv Solar Cells are particularly beneficial in scenarios where access to traditional power sources may be limited or unavailable. They provide a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels, reducing the carbon footprint while ensuring a steady power supply. Whether it's for powering the electrical systems of an RV during a camping trip or supplying energy to navigational equipment on a boat, these solar cells offer a practical and efficient solution.
Okorder.com is a reputable wholesale supplier of Rv Solar Cells, boasting a vast inventory to cater to the diverse needs of customers. With a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, Okorder.com ensures that the Rv Solar Cells they provide meet the highest industry standards. Their extensive stock allows for quick delivery and competitive pricing, making them a preferred choice for those seeking reliable and efficient solar energy solutions.
Hot Products