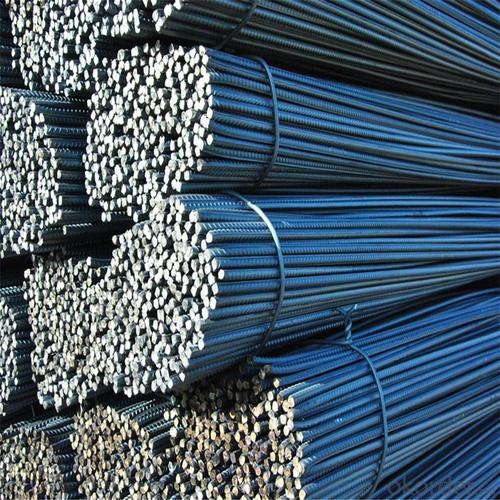
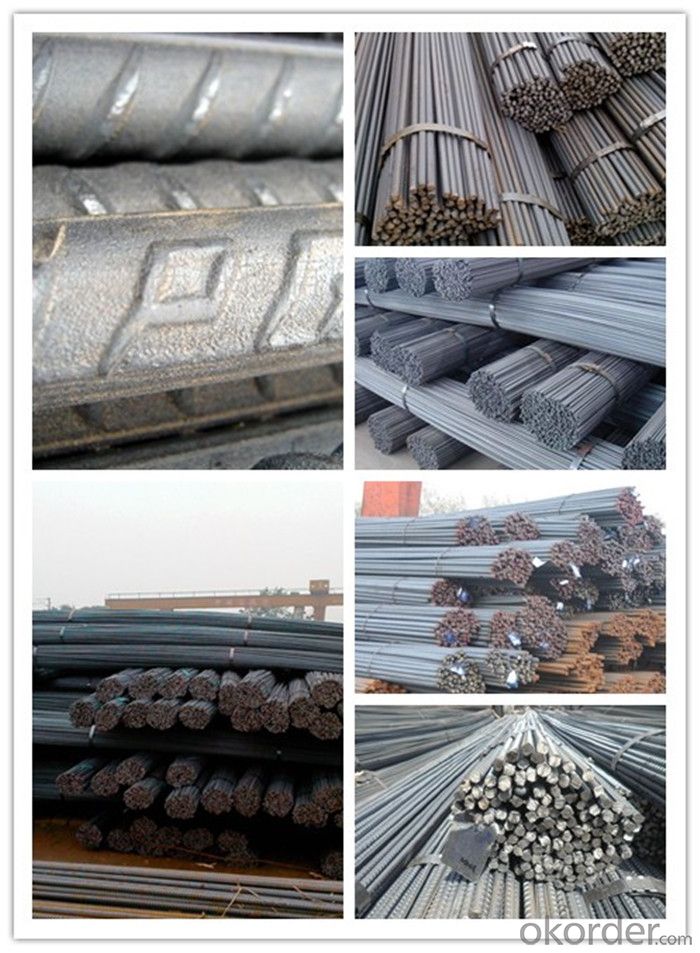
Rebar Steel Grade 60 Supplier from Tianjin
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Rebar Steel Grade 60 Supplier from Tianjin
Description of Rebar Steel Grade 60:
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm rounds reinforcing steel bar
10m- 40 rods reinforcing Rebar Steel Grade 60
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or as your requests.
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or cold drawn to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealed, normalized, temperied, quenched
4, Surface Treatment: Black , Bright, Polish or as your requirements.
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
Chemical Composition of Rebar Steel Grade 60:
Grade | Chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
Product Show of Rebar Steel Grade 60:
Company Information:
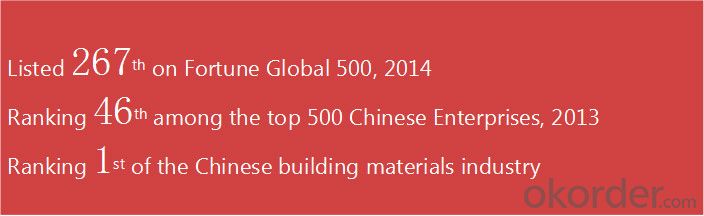
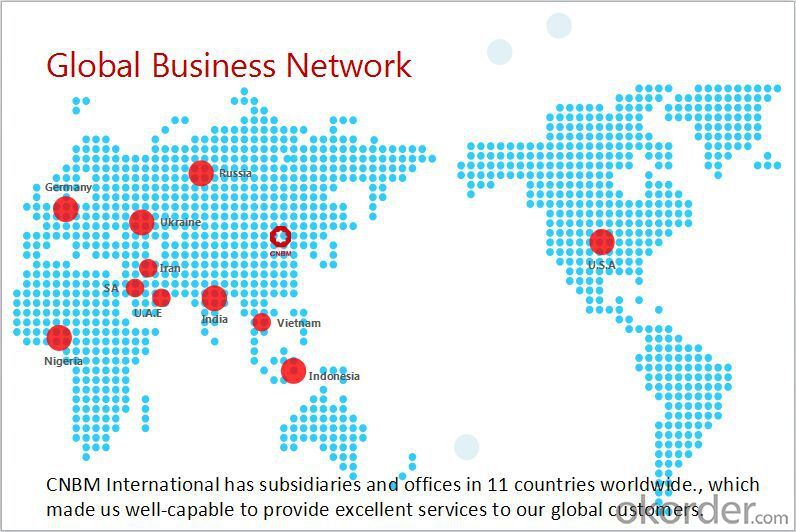
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
FAQ:
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time. We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: What are the challenges in manufacturing special steel?
- Some of the challenges in manufacturing special steel include the high cost of raw materials, the complex and precise production processes, ensuring consistent quality and performance, meeting specific customer requirements, and staying up-to-date with rapidly advancing technologies and industry standards. Additionally, the demand for customization and shorter lead times can also present challenges in terms of production planning and logistics.
- Q: What are the different surface finishes available for special steel?
- There are several different surface finishes available for special steel, including polished, brushed, satin, matte, and textured.
- Q: What are the main elements in special steel alloys?
- The main elements in special steel alloys vary depending on the specific alloy, but commonly include elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and vanadium. These elements are added to enhance the properties of steel, such as corrosion resistance, strength, hardness, or heat resistance, making them suitable for specific applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the energy generation industry?
- Special steel contributes to the energy generation industry by providing high-strength, corrosion-resistant, and heat-resistant materials that are crucial for the construction and maintenance of power plants, turbines, and other energy infrastructure. This ensures the reliability, efficiency, and longevity of these structures, enabling them to withstand extreme conditions and maximize energy production.
- Q: How is special steel produced?
- Special steel is produced through a combination of refining iron ore, adding alloying elements, and employing advanced manufacturing techniques such as hot rolling, forging, or heat treatment to achieve the desired properties and quality required for specific applications.
- Q: How does special steel perform in magnetic applications?
- Special steel, also known as stainless steel, generally performs well in magnetic applications. However, it is important to note that not all types of stainless steel are magnetic. The magnetic properties of special steel depend on its composition and the presence of certain elements such as nickel, manganese, and chromium. Austenitic stainless steel, which is the most common type, is non-magnetic due to its high nickel content. This makes it ideal for applications where magnetic interference is undesirable, such as in sensitive electronic devices or medical equipment. On the other hand, ferritic and martensitic stainless steels, which have lower nickel content, are magnetic. These types of special steel are commonly used in applications where magnetic properties are required, such as in magnetic separators, transformers, and electric motors. It is worth mentioning that the magnetic strength of stainless steel is relatively weak compared to other magnetic materials like iron or nickel. Therefore, if a strong magnetic field is needed, alternative materials may be more suitable. Overall, special steel can perform well in magnetic applications depending on the specific type and composition. It is important to consider the desired magnetic properties and consult with experts or refer to material specifications to ensure the appropriate selection for a particular application.
- Q: How is special steel used in the medical industry?
- Special steel is used in the medical industry for a variety of applications. It is commonly used in the production of surgical instruments, implants, and medical devices due to its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Special steel ensures that these instruments and implants can withstand the harsh conditions of medical procedures and maintain their integrity over time, ensuring better patient outcomes.
- Q: What are the different corrosion-resistant grades of special steel?
- Some of the different corrosion-resistant grades of special steel include stainless steel grades such as 304, 316, and 2205, as well as nickel-based alloys like Inconel and Hastelloy. These grades are specifically designed to resist corrosion in various environments and applications.
- Q: What are the different testing methods for special steel?
- To ensure the quality and performance of special steel, there are various testing methods commonly used. These methods encompass: 1. Chemical Analysis: Determining the steel's chemical composition, including elements and impurities, is crucial. It confirms adherence to specific chemical composition requirements. 2. Mechanical Testing: Evaluating mechanical properties like strength, ductility, hardness, and toughness is achieved through tests such as tensile, impact, hardness, and fatigue testing. 3. Microstructure Analysis: Assessing the steel's internal structure, grain size, and shape requires microscopic examination. Techniques like optical and electron microscopy, as well as X-ray diffraction, help identify any defects or abnormalities. 4. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Inspecting the steel without causing damage is possible through NDT methods. These include ultrasonic, magnetic particle, liquid penetrant, and radiographic testing to detect surface and subsurface defects. 5. Corrosion Testing: In applications where corrosion resistance is vital, various methods like salt spray, electrochemical, and immersion testing are employed. They evaluate the steel's resistance and corrosion rate. 6. Metallography: Preparing a cross-section of the steel sample, polishing it, and etching it reveals its microstructure. This aids in assessing quality, heat treatment effects, and grain size distribution. 7. Dimensional and Surface Inspection: Ensuring the steel meets required dimensional tolerances and surface quality is crucial. Techniques like dimensional measurement, surface roughness measurement, and visual inspection verify conformity. By implementing these testing methods, manufacturers and quality control personnel ensure that special steel meets the necessary standards, specifications, and customer requirements.
- Q: What are the key differences between special steel and tool steel?
- Special steel and tool steel are both types of steel that have specific properties and applications. However, there are some key differences between the two. 1. Composition: Special steel is a broad term that encompasses a variety of steel alloys with specific properties for different applications. It can include stainless steel, high-strength alloy steel, and heat-resistant steel, among others. On the other hand, tool steel is a specific type of special steel that is designed to be used in the production of tools, dies, and molds. Tool steel typically contains higher levels of carbon and other alloying elements like chromium, vanadium, or tungsten, which enhance its hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. 2. Hardness and wear resistance: Tool steel is known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, which makes it ideal for cutting, shaping, and forming materials. It can withstand high temperatures and resist deformation, ensuring the longevity of tools and dies. Special steel, on the other hand, may not have the same level of hardness and wear resistance as tool steel, as its properties vary depending on the specific alloy and application. Special steel alloys may prioritize other properties like corrosion resistance or strength. 3. Manufacturing processes: Tool steel is often produced through specialized manufacturing processes like hot working, cold working, or heat treatment to achieve the desired properties. The production of tool steel involves precise control of temperature and cooling rates to achieve the required hardness and toughness. Special steel, on the other hand, may undergo various manufacturing processes depending on the desired properties. These can include forging, casting, or heat treatment, among others. 4. Applications: Tool steel is primarily used in the production of tools, dies, and molds for manufacturing processes such as cutting, shaping, and forming materials. It is commonly used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and machinery. Special steel, on the other hand, has a wide range of applications depending on the specific alloy and properties. It can be used in industries such as construction, energy, and manufacturing, where specific properties like corrosion resistance, heat resistance, or strength are required. In summary, the key differences between special steel and tool steel lie in their composition, hardness, wear resistance, manufacturing processes, and applications. While special steel is a broad term for various steel alloys with specific properties, tool steel is a specific type of special steel designed for tooling applications. Tool steel is characterized by its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for cutting and shaping materials, while special steel can have a broader range of properties depending on the specific alloy and application.
Send your message to us
Rebar Steel Grade 60 Supplier from Tianjin
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


































