Hot Rolled Carbon Steel Round Bars S50C
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 120000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Hot Rolled Carbon Steel Round Bars S50C
Product Specification
1, Chemical Composition %
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | S | P | Cr | Ni | Cu |
| S50C | 0.47-0.53 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.30 |
2, Mechanical Properties
| Strength of Extension σb | Yield Strength σs | Reduction of Area ψ | Elogation δ5 | Hardness |
| ≥630(64) Mpa | ≥375(38) Mpa | ≥40% | ≥14% | ≤241HB |
3, Diameter: 16mm - 300mm
Length: Max 12m
Application
1, Used as base plate of cold working die.
2, Used as fix plate of drill jig.
3, Used as standard template material.
Product Main Points
1, Heat Treatment: normalizing, annealing, tempering, quenching
2, Surface Treatment: black, grinding, bright, polish
3, Product Process: hot rolled, cold drawn, forged
FAQ
1, Payment Terms:
30% T/T deposit & 70% T/T before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight
2, Trade Terms:
EXW, FOB, CIF, CNF
3, Delivery Time:
Normally 30-40 days. According to quantity.
4, Manufacture or Trading Company:
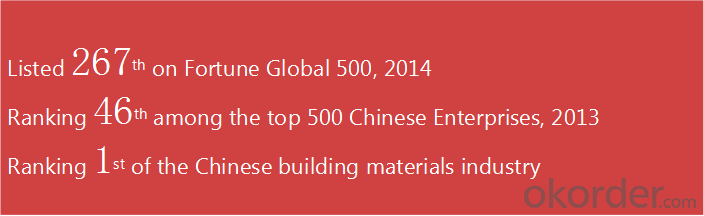
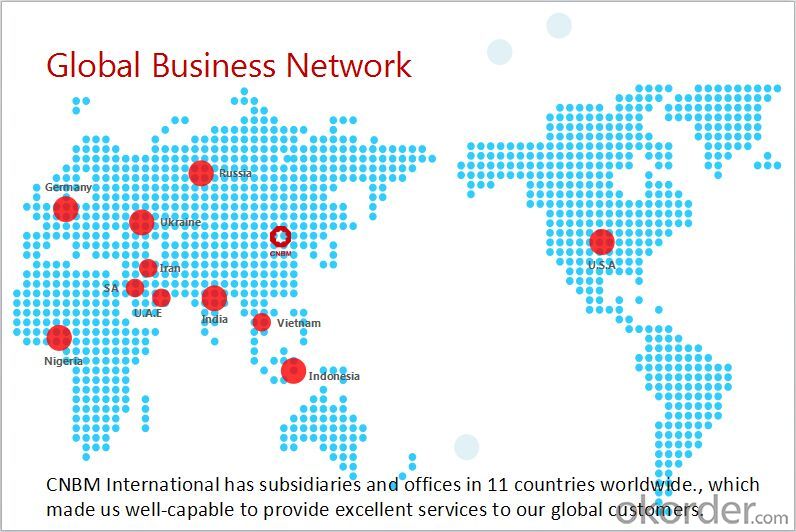
CNBM is a state-owned fortune global 500 trading company. We have intergrated supply system.
There are about 20 overseas locations in different countries.
Product Show
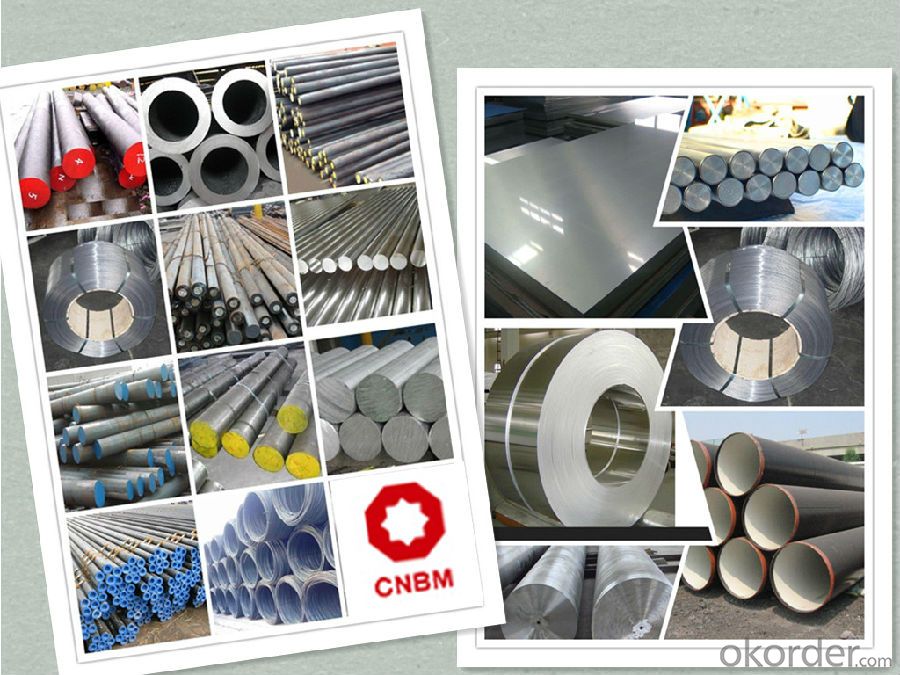

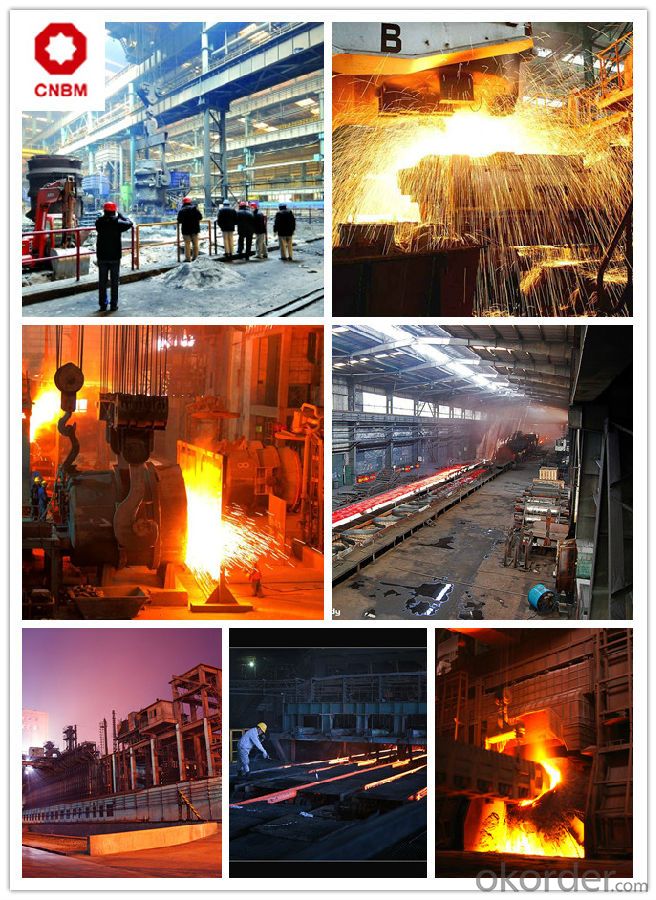
Work Shop

About Us
- Q: How do you store steel round bars to prevent damage?
- In order to store steel round bars and prevent damage, it is important to follow several crucial steps. Firstly, it is essential to keep the bars in a dry and well-ventilated area to avoid the buildup of moisture, which can lead to rusting. Additionally, moisture can cause the bars to become brittle and weaken over time. Next, it is recommended to store the round bars horizontally instead of vertically. This will prevent warping or bending caused by the weight of the bars pressing down on each other. If vertical storage is necessary, it is vital to use appropriate racks or supports that evenly distribute the weight. Furthermore, it is important to avoid stacking the bars too high, as excessive weight can cause deformation or collapse. If stacking cannot be avoided, sturdy supports should be used and the weight should be evenly distributed across the stack. Moreover, it is advisable to separate different sizes or types of steel round bars to prevent scratching or damage. This can be achieved by using separators or dividers to create distinct compartments for each type of bar. Lastly, regular inspection of the stored round bars for any signs of rust, corrosion, or damage is necessary. If any issues are detected, prompt measures should be taken to address them. This may involve applying rust inhibitors, cleaning the bars, or seeking assistance from professionals. By adhering to these storage guidelines, the steel round bars can be effectively protected from damage, ensuring their longevity and quality.
- Q: Are steel round bars prone to fatigue failure?
- Fatigue failure is a common occurrence in steel round bars, which can be attributed to repeated cyclic loading or stress. This leads to a gradual weakening of the material, eventually causing it to fail, even if the applied stress is below its ultimate strength. Due to their inherent characteristics, steel round bars, like other structural materials, are susceptible to fatigue failure. Various factors can contribute to fatigue failure in steel round bars, including improper design, inadequate material selection, manufacturing defects, and excessive cyclic loading. Additionally, surface defects, notches, stress concentrations, and corrosive environments can further accelerate the fatigue process. Engineers and designers take several measures to mitigate the risk of fatigue failure. These include implementing appropriate design practices, selecting high-quality materials, conducting thorough inspections, applying stress-relieving treatments, and considering the impact of cyclic loading during the structural design phase. It is important to understand that the susceptibility of steel round bars to fatigue failure depends on multiple factors, such as the specific steel grade, loading conditions, environmental factors, and overall structural design. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully assess these factors and employ appropriate mitigation measures to ensure the safe and reliable performance of steel round bars in various applications.
- Q: What are the advantages of using structural steel round bars?
- There are several advantages of using structural steel round bars in various applications. Firstly, structural steel round bars offer exceptional strength and durability. The circular shape of the bar allows for even distribution of weight and stress, making it highly resistant to bending and breaking. This strength is particularly beneficial in applications where the bars are subjected to heavy loads or extreme weather conditions. Additionally, structural steel round bars are highly versatile. They can be easily shaped and manipulated to fit specific project requirements, allowing for greater design flexibility. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, including construction, manufacturing, and engineering projects. Another advantage of using structural steel round bars is their cost-effectiveness. Steel is a relatively affordable material, and the efficiency of the manufacturing process makes it a cost-effective choice for various projects. Furthermore, the durability and longevity of steel round bars reduce the need for frequent maintenance or replacement, resulting in long-term cost savings. Furthermore, structural steel round bars offer excellent resistance to corrosion. Steel is inherently resistant to rust and other forms of corrosion, making it highly suitable for outdoor or high-moisture environments. This resistance extends the lifespan of the bars and ensures their structural integrity over time. Lastly, structural steel round bars are readily available and easily sourced. Steel is a widely used material, and it is produced in large quantities, making it readily available in various sizes and grades. This accessibility ensures that steel round bars can be easily obtained, reducing project delays and increasing overall efficiency. In conclusion, the advantages of using structural steel round bars include exceptional strength and durability, versatility, cost-effectiveness, resistance to corrosion, and easy availability. These benefits make structural steel round bars a preferred choice for a wide range of applications, providing a reliable and efficient solution for various construction and engineering projects.
- Q: What is the difference between a solid round bar and a hollow round bar?
- A solid round bar is a cylindrical shape made entirely of a single material, typically metal or plastic, with a solid core throughout its entire length. It has a consistent diameter from one end to the other and does not have any empty space inside. On the other hand, a hollow round bar also has a cylindrical shape but contains a hollow space in its center. This hollow space creates an empty tube-like structure within the bar. The diameter of the outer surface remains consistent, but the inner diameter will vary depending on the specific design and intended use of the hollow round bar. The main difference between a solid round bar and a hollow round bar lies in their structural characteristics and potential applications. A solid round bar offers high strength and rigidity due to its solid core, making it suitable for applications that require robust support or load-bearing capabilities. It is commonly used in construction, manufacturing, and engineering projects where strength and durability are crucial. On the other hand, a hollow round bar provides a unique combination of strength and lightweight properties. The presence of the hollow space reduces the overall weight of the bar while still maintaining structural integrity. This makes hollow round bars ideal for applications where weight reduction is a priority, such as in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries. Additionally, the hollow space can be utilized for various purposes, such as passing fluids, wires, or other components through the bar. In summary, while both solid and hollow round bars share a cylindrical shape, the presence or absence of a hollow space differentiates them. Solid round bars offer strength and rigidity, while hollow round bars provide a balance between strength and reduced weight, along with the potential for additional functionality. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements and intended application of the bar.
- Q: What is the maximum hardness achievable for steel round bars?
- The maximum hardness attainable for steel round bars relies on various factors, including the steel's composition, the heat treatment process, and the desired properties for the specific application. Typically, steel can reach a maximum hardness of approximately 65 HRC or higher. This level of hardness is commonly achieved through procedures like quenching and tempering. Quenching entails rapidly cooling the steel from a high temperature to room temperature, resulting in a hardened structure. Subsequently, tempering is carried out to decrease brittleness and enhance the steel's toughness while maintaining a high level of hardness. It is crucial to acknowledge that pushing the hardness of steel beyond a certain point may result in reduced toughness and increased brittleness. Hence, the maximum attainable hardness must be balanced with the desired properties for the particular application, such as strength, ductility, and resistance to wear or impact.
- Q: How is the weight of a steel round bar calculated?
- To determine the weight of a steel round bar, one must employ a formula that incorporates the bar's diameter, length, and the density of the steel variant in question. The formula is as follows: Weight = (π/4) x (diameter)^2 x length x density Within this formula, the symbol π denotes the mathematical constant pi (approximately 3.14159), the diameter signifies the measurement across the broadest point of the round bar, the length refers to the measurement from one end of the bar to the other, and the density pertains to the mass per unit volume of the specific steel type. By substituting the values of diameter, length, and density into this formula, it becomes possible to compute the weight of a steel round bar. It is important to note that the weight will be expressed in units of mass, such as kilograms or pounds, depending on the adopted system of measurement.
- Q: Can steel round bars be used for making fuel system components?
- No, steel round bars are not suitable for making fuel system components as they lack the necessary corrosion resistance and compatibility with fuels.
- Q: How do steel round bars compare to brass round bars?
- Steel round bars and brass round bars have several key differences that make them suitable for different applications. Firstly, steel round bars are much stronger and more durable compared to brass round bars. Steel has a higher tensile strength, making it ideal for applications that require high strength and resistance to heavy loads. It is commonly used in construction, manufacturing, and automotive industries where strength and durability are crucial. On the other hand, brass round bars are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, which gives it a unique combination of properties. It is often used in applications that require good electrical conductivity, such as electrical connectors, plumbing fittings, and musical instruments. Brass also has an attractive golden appearance, making it a popular choice for decorative purposes. In terms of cost, steel round bars are generally more affordable compared to brass round bars. Steel is widely available and produced in large quantities, resulting in a lower cost per unit. Brass, being an alloy of copper, which is a relatively expensive metal, is generally more expensive. Another important factor to consider is machinability. Steel round bars are generally easier to machine and work with compared to brass round bars. Steel has good cutting and drilling properties, making it easier to fabricate into various shapes and sizes. Brass, on the other hand, tends to have a higher machinability rating, meaning it is easier to cut and shape compared to other metals. In summary, steel round bars are stronger, more durable, and generally more affordable than brass round bars. They are suitable for applications that require high strength and resistance to heavy loads. Brass round bars, on the other hand, offer excellent corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and an attractive appearance. They are commonly used in applications that require good electrical conductivity and for decorative purposes. The choice between steel and brass round bars ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application.
- Q: What is the maximum length of a steel round bar available?
- The maximum length of a steel round bar available depends on various factors such as the manufacturing capabilities of the steel supplier, transportation limitations, and practical considerations. However, typical maximum lengths range from 20 to 40 feet (6 to 12 meters), but it is always best to consult with a steel supplier to determine the specific lengths they offer.
- Q: How many tons of pressure can the round steel of 70 inches bear?
- If the steel will generally approximate compressive strength considering tensile strength, even if is only 4 tons / square centimeters, each round cross section of 26 mm diameter is 5.3 cm, maximum 5.3*4 about 20 tons of pressure, the actual use should take into account the safety factor;
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Carbon Steel Round Bars S50C
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 120000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

































