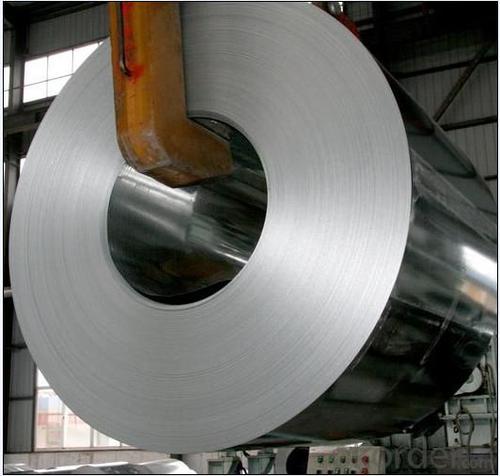
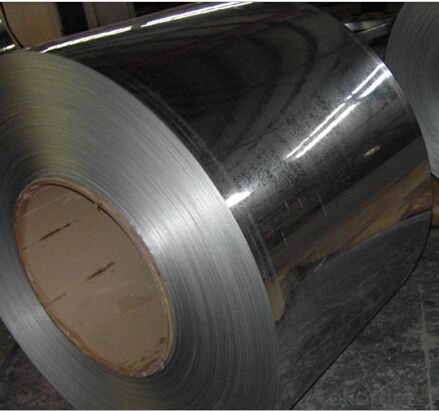
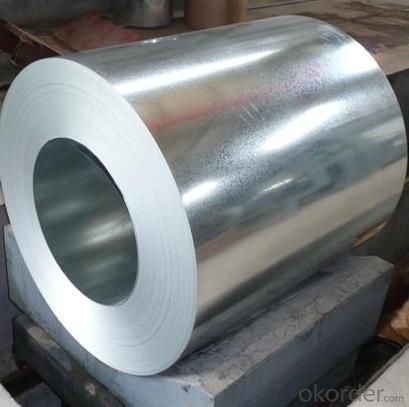
Galvanized Steel for Building and Constructions
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Details
Basic Info.
Model NO.: dx51d DX52D DX53D
Standard:ASTM, JIS
Steel Grade:Q195
Certification: ISO, SGS
Surface Treatment:Galvanized
Technique:Cold Rolled
Application:Building and Construction
Edge:Mill
Stock:Not Stock
Thickness:0.16-3.0mm
Width:Upon Customr′s Requirement
Length:Upon Customr′s Requirement
Surface:Regular Spangle
Inside Diameter:508 610mm
Outside Diameter:Upon Customer′s Requirement
Packing Condition:with Wood Pattet
Sample:Available
Export Markets:Global
Additional Info.
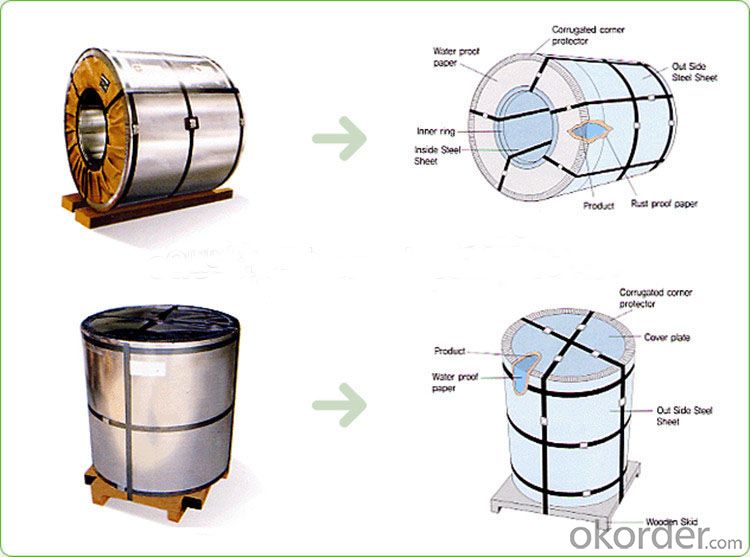
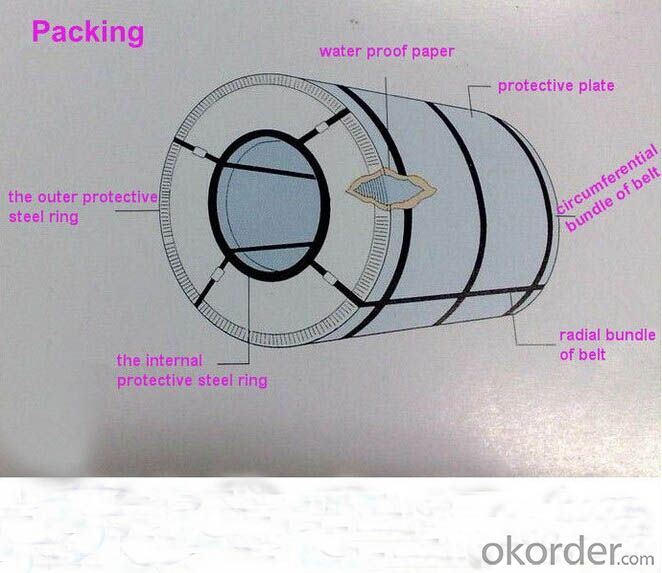
Packing:Sea Worthy Packing
Standard:JIS 3302, EN 10142
Origin:China
HS Code:72104900
Production Capacity:300, 000tons/year
Product Description
Hot-dip galvanized steel coils are available with a pure zinc coating through the hot-dip galvanizing process. It offers the economy ,strength and formability of steel combined with the corrosion resistance of zinc. The hot-dip process is the process by which steel gets coated in layers of zinc to protect against rust. It is especially useful for countless outdoor and industrial applications,
Hot-dip aluzinc steel sheet is substrated on cold rolled steel (CRC) in various strength and specification. Coating composition is 55% aluminum in weight ratio, 43.4% zinc, and 1.5% silicon, with excellent corrosion and heat resistance performance.
The Feature of Galvanized Steel:
Commodity: Galvanized Steel in coil or sheet
Standard: JIS G3302 SGCC, commercial quality of the Steel base.
Thickness range of the Galvanized Steel coil: 0.14mm to 3.0mm
Zinc coating from 50-275g/m2
Tolerance of thickness of the Galvanized Steel Roll: +/-0.03mm
Width range: 700mm to 1250mm
Tolerance of width: +/-3.00mm (aiming to +/-2.00mm)
Coil weight of Galvanized Steel coil: According to Clients' requests.
Coil ID: 508 mm
Packing of Galvanized Steel coil: Seaworthy, in container
Note of the GI: Special width can be requested, the small order can be negotiated.
Package:
FAQ:
1. What is the minimum order quantity ?
Our MOQ is 50mt for each size. And we will consider to give more discount if you make big order like 1000 tons and more. Further more, the more appropriate payment term your offer the better price we can provide.
2. How long can we receive the product after purchase?
Usually within thirty working days after receiving buyer’s advance payment or LC. We will arrange the factory manufacturing as soon as possible. The cargo readiness usually takes 15-25 days, but the shipment will depend on the vessel situation.
3. How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
4.What is the validity of your quotation?
Normally 7 days.
5.What is your advantage?
24 hour quick response /Customer oriented/ Credit foremost/ Top quality Excellent
- Q: How are steel coils used in the manufacturing of tools and equipment?
- Steel coils are used in the manufacturing of tools and equipment as they are typically shaped and cut into various components such as blades, springs, and handles. These coils provide the necessary strength and durability required for the tools and equipment to withstand heavy usage and perform effectively.
- Q: How are steel coils transported and stored?
- Steel coils are typically transported using flatbed trailers, coil carriers, or railcars. These coils are securely strapped or banded to prevent movement during transportation. Once they reach their destination, they are usually stored in warehouses or outdoor storage yards. The coils are stacked on top of each other, often with the help of specialized equipment, to optimize space utilization. They may also be stored horizontally on racks or stored vertically in specially designed coil racks. Proper handling and storage procedures are followed to ensure the safety of personnel and to prevent damage to the steel coils.
- Q: What are the challenges in the production of steel coils?
- The production process of steel coils encounters several obstacles. Firstly, ensuring consistent quality throughout the process is a major challenge. It is necessary for steel coils to possess uniform thickness, width, and flatness. However, achieving this consistently can prove to be difficult due to variations in raw materials, equipment, and operating conditions. Another hurdle involves effectively managing the intense temperatures involved in the production process. Steel coils are formed by heating steel slabs or billets to extremely high temperatures and subsequently rolling them into coils. Maintaining the necessary temperatures and ensuring proper cooling can be a complex task, as any deviations can result in inconsistencies in the final product. Furthermore, the production of steel coils demands a significant amount of energy. The steel industry ranks among the largest energy consumers worldwide. The constant challenge lies in reducing energy consumption while maintaining production efficiency. To tackle this challenge, the implementation of energy-efficient technologies and process optimization is imperative. Moreover, the production of steel coils generates a substantial amount of waste and emissions. Steel manufacturing involves various chemical reactions that release pollutants such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter. Meeting environmental regulations and minimizing these emissions are significant challenges for the industry. Additionally, the production of steel coils often involves large quantities, necessitating efficient logistics and transportation systems. Ensuring timely delivery and minimizing damage during transportation can be challenging due to the weight and size of the coils. Lastly, the steel industry confronts market challenges, including fluctuating prices of raw materials, competition from alternative materials, and global economic conditions. Adapting to market demands and maintaining competitiveness are vital for the sustainable production of steel coils. Overall, the challenges in steel coil production encompass maintaining consistent quality, managing high temperatures, reducing energy consumption and emissions, optimizing logistics and transportation, and adapting to market dynamics. Addressing these challenges requires continuous innovation, technological advancements, and a focus on sustainability.
- Q: What are the different types of steel surface treatments for coils?
- There are several types of steel surface treatments for coils, including pickling, oiling, galvanizing, and painting. Pickling involves removing surface impurities and scale through the use of acid solutions. Oiling is a process where a thin layer of oil is applied to the coil surface to prevent rust and improve handling. Galvanizing involves coating the steel with a layer of zinc to provide corrosion resistance. Painting is another surface treatment where a protective layer of paint is applied onto the coil surface to enhance durability and aesthetics.
- Q: I want to anodize steel using heat. some steel turns gray instead of coloring when I heat it up using a torch.
- Steel doesn't anodize in the sense that aluminum and some other metals do. However, it can be heat-colored. The trick is to clean the surface first (it must be oxide free), then heat gently until the colors appear. These are called temper colors in steel. They are due to a thin adherent layer of oxide that forms and thickens as temperature is increased. They are quite temperature dependent. As the steel is heated, the first color to appear is pale yellow. This will progress through darker yellows, browns, purples, and blues as the temperature rises. Above blue, the oxide becomes the gray/black color you are apparently getting - this is the result of heating too fast and too hot. See the chart at the site below for colors in plain carbon steel. Note that the temperatures are pretty low - It all starts around 400 F and if you go above 600 F the show's all over.
- Q: I have a steel support beam can you remove one of the poles . the steel beam set on sender blocks on both side of the foundation. I have three steel beams support beam across the basement,I just want to remove one pole, can that be done.
- You need to measure the beam and go to an engineering guide and see what the load ratings are. You can never remove the end supports but the middle support may possibly be taken out if the beam can handle the load and or you add some gusseting and reinforcement to the original beam. You should probably call a building engineer to consult on this.
- Q: How are steel coils inspected for hardness using hardness testers?
- To assess the strength and durability of steel coils, hardness testers are employed to examine their hardness. Hardness testers are specialized devices used to gauge a material's resistance to indentation or penetration. For steel coils, Rockwell or Brinell testers are commonly utilized. Both methods entail exerting a precise force onto the surface of the coil and measuring the depth of indentation or size of the impression made. In the case of Rockwell testing, a steel ball or diamond cone is pressed onto the coil's surface with a predetermined force. The depth of penetration is then measured and compared to a standardized scale in order to determine the hardness value. Different scales are employed based on the size and type of indenter in use. On the other hand, Brinell testing involves using a spherical indenter made of tungsten carbide or hardened steel. This indenter is pressed onto the coil's surface with a known force, and the resulting indentation is measured and compared to a standardized table to determine the hardness value. Both methods provide a quantitative measure of the steel coil's hardness, which serves as an indicator of its ability to resist deformation, wear, and cracking. The hardness test results are subsequently utilized to ensure that the steel meets specific quality standards or customer requirements. It is important to note that the inspection process may involve sampling, where representative sections of the steel coil are tested, or it may involve testing the entire coil, depending on the specific inspection requirements. Additionally, accurate and reliable results necessitate proper calibration and maintenance of the hardness testers.
- Q: I am trying to clean up a stainless steel back splash and some kitchen appliances that have brown spots that look like rust spots. I was able to remove most of them with stainless steel cleaner but does anyone know any tricks?
- if okorder /
- Q: How are steel coils used in the production of steel screws?
- Steel coils are used in the production of steel screws by being unwound and fed into a machine that cuts and shapes them into individual screw blanks. These blanks are then threaded and undergo various processes to create the final steel screws.
- Q: Does Steel Cut Oatmeal have the same health benefits as Old Fashioned Oatmeal? What is the difference in processing?
- Steel Cut Oats Steel-cut oats are whole oat kernels cut into small chunks rather than being smashed flat as in oatmeal. This gives the oats more of a chew texture and also slows both cooking time and digestion time. That means that they have a lower glycemic index and are thus preferable for increasing satiety, lowering the insulin response to the meal, and keeping blood sugar levels from peaking. This also results in delaying hunger so a person is less likely to snack or get overly hungry before the next meal. Here is how I like to cook oats for breakfast. Ingredients 1/2 cup Dry steel cut oats 1 cup Water (You may want a little more than a cup, experiment to your liking) 2 T Raisins (optional or replace with chopped dried apricots etc.) 2 T Ground flax meal (optional, but high in healthy n-3 fatty acids and fiber) Salt to your taste (try Lite salt to lower sodium intake) 2T Sunflower seeds or almonds 1 cup Fresh berries or a banana Directions Heat water to a boil. While water is heating, add the salt, raisins, and flax meal. When the water boils, add the steel cut oats. Stir once. Turn heat down to simmer and cook covered for 7-8 minutes. Provides two small servings. Double for large servings or small servings for 4 people. Serve and eat while hot. Add soy milk or low fat milk. Slice fresh fruit on top to add extra flavor. My wife likes banana slices. I like fresh berries, peaches, or sugar free applesauce. For extra crunch sprinkle almonds or sunflower seeds on top.
Send your message to us
Galvanized Steel for Building and Constructions
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























