Solar Energy Systems Wholesale - CNBM On Grid System 40000W with Certificate UL, TUV, CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
CNBM On Grid System 40000W with Certificate UL TUV CE
Product description
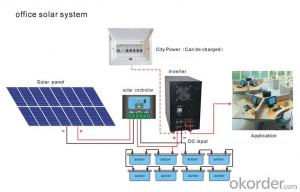
A photovoltaic (in short PV) module is a packaged, connected assembly of typically 6×10 solar cells. Solar Photovoltaic panels constitute the solar array of a photovoltaic system that generates and supplies solar electricity in commercial and residential applications. Each module is rated by its DC output power under standard test conditions, and typically ranges from 100 to 365 watts. The efficiency of a module determines the area of a module given the same rated output – an 8% efficient 230 watt module will have twice the area of a 16% efficient 230 watt module. There are a few commercially available solar panels available that exceed 22% efficiency[1] and reportedly also exceeding 24%.[2][3] A single solar module can produce only a limited amount of power; most installations contain multiple modules. A photovoltaic system typically includes a panel or an array of solar modules, a solar inverter, and sometimes a battery and/or solar tracker and interconnection wiring.
The price of solar power, together with batteries for storage, has continued to fall so that in many countries it is cheaper than ordinary fossil fuel electricity from the grid (there is "grid parity").[4]
Off-the-grid is a system and lifestyle[1] designed to help people function without the support of remote infrastructure, such as an electrical grid. In electricity, off-grid can be stand-alone power system or mini-grids typically to provide a smaller community with electricity. Off-grid electrification is an approach to access electricity used in countries and areas with little access to electricity, due to scattered or distant population. The term off-the-grid (OTG) can refer to living in a self-sufficient manner without reliance on one or more public utilities. People who adopt this lifestyle are called off-gridders.[2]

Application
Industrial
Commercial
Residential
Feature
Residential, grid-connected rooftop systems which have a capacity more than 10 kilowatts can meet the load of most consumers.[2] They can feed excess power to the grid where it is consumed by other users. The feedback is done through a meter to monitor power transferred. Photovoltaic wattage may be less than average consumption, in which case the consumer will continue to purchase grid energy, but a lesser amount than previously. If photovoltaic wattage substantially exceeds average consumption, the energy produced by the panels will be much in excess of the demand. In this case, the excess power can yield revenue by selling it to the grid. Depending on their agreement with their local grid energy company, the consumer only needs to pay the cost of electricity consumed less the value of electricity generated. This will be a negative number if more electricity is generated than consumed.[3] Additionally, in some cases, cash incentives are paid from the grid operator to the consumer.
Packaging
With carton and box
- Q: How does the efficiency of solar panels vary with temperature?
- The efficiency of solar panels typically decreases as temperature increases.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering electric cars or buses?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used to power electric cars or buses. Solar panels can be installed on the roofs or other parts of the vehicles to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This clean and renewable energy source can then be used to charge the batteries of electric vehicles, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used in developing countries without access to reliable electricity?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used in developing countries without access to reliable electricity. Solar power can provide a reliable and sustainable source of energy for various purposes such as lighting, heating, cooking, and powering small appliances. These systems are often cost-effective, easy to install, and can be tailored to meet the specific energy needs of communities in developing countries. By harnessing the abundant sunlight available in these regions, solar energy systems can greatly improve the quality of life, promote economic development, and reduce reliance on traditional and polluting energy sources.
- Q: What are the advantages of using solar energy systems?
- There are several advantages of using solar energy systems. Firstly, solar energy is a renewable and abundant source of power, meaning it will never run out and can be harnessed anywhere in the world. Additionally, using solar energy helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change, as it produces no harmful pollutants during operation. Solar energy systems also provide energy independence, allowing individuals and communities to generate their own power and reduce reliance on traditional energy sources. Furthermore, solar energy can lead to cost savings in the long run, as it reduces electricity bills and offers potential financial incentives such as tax credits or feed-in tariffs. Lastly, solar energy systems require minimal maintenance and have a long lifespan, making them a reliable and durable option for generating clean energy.
- Q: Are there any risks of electrical malfunction or failure with solar energy systems?
- Yes, there are some risks of electrical malfunction or failure with solar energy systems. One of the main risks is a faulty or damaged electrical connection, which can result in a loss of power generation or even electrical fires. Additionally, extreme weather conditions such as lightning strikes or strong winds can damage the solar panels or inverters, leading to a temporary or permanent failure of the system. Another risk is the degradation of solar panels over time, which can result in decreased efficiency and eventually require replacements. Furthermore, improper installation or maintenance can lead to system failure or electrical malfunctions. It is essential to ensure that solar energy systems are installed by qualified professionals and regularly inspected and maintained to minimize these risks.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for transportation?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used for transportation. Solar-powered vehicles, such as solar cars, solar boats, and solar planes, have been developed and successfully used for transportation purposes. These vehicles harness the energy from the sun through solar panels, converting it into electricity to power their propulsion systems. While solar energy may have limitations in terms of efficiency and range, advancements in technology are continuously improving the viability of solar-powered transportation.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for space heating?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used for space heating. Solar thermal systems can be designed to capture and convert sunlight into heat energy, which can then be used to warm indoor spaces. This can be achieved through the use of solar collectors and heat transfer mechanisms, making solar energy a viable option for space heating purposes.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering industrial manufacturing plants?
- Industrial manufacturing plants can indeed utilize solar energy systems for power. In fact, many such plants worldwide are already using these systems to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and minimize their impact on the environment. Solar energy systems comprise photovoltaic (PV) panels that convert sunlight into electricity. These panels can be installed on the roofs or open spaces of manufacturing plants to harness ample solar energy. The electricity generated by the solar panels can be used to power various processes and equipment within the industrial plant, including machinery, lighting, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Using solar energy to power industrial manufacturing plants offers several advantages. Firstly, solar power is a renewable and clean energy source, helping to decrease greenhouse gas emissions and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. This aligns with the increasing need for sustainable practices and carbon footprint reduction in industries. Secondly, solar energy systems can significantly lower electricity costs for manufacturing plants. Once the initial investment for installing the solar panels is made, operational costs remain relatively low. Furthermore, some countries provide incentives and subsidies for implementing solar energy systems, further alleviating the financial burden. In addition, solar energy systems can provide a stable and reliable source of electricity. With advancements in battery storage technology, excess solar energy can be stored and used during periods without sunlight or when demand is high. This ensures an uninterrupted power supply and reduces reliance on the power grid. However, it is important to consider various factors before determining the feasibility of using solar energy systems for powering industrial manufacturing plants. These factors include sunlight availability, plant size, energy requirements, and the initial investment cost. Additionally, certain manufacturing processes may require a consistent and higher level of electricity that solar energy alone may not fully meet. Overall, solar energy systems have demonstrated their viability and sustainability for powering industrial manufacturing plants. Their use can contribute to carbon emission reduction, lower electricity costs, and foster a greener and more environmentally friendly industrial sector.
- Q: What is the role of tracking systems in solar energy systems?
- The role of tracking systems in solar energy systems is to optimize the efficiency and output of the solar panels by tracking the movement of the sun throughout the day. These systems automatically adjust the position of the panels to maximize the amount of sunlight they receive, which results in increased energy production.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for transportation?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used for transportation. Solar-powered vehicles, such as solar cars, solar boats, and solar planes, have been developed and successfully used for transportation purposes. These vehicles harness the energy from the sun through solar panels, converting it into electricity to power their propulsion systems. While solar energy may have limitations in terms of efficiency and range, advancements in technology are continuously improving the viability of solar-powered transportation.
Send your message to us
Solar Energy Systems Wholesale - CNBM On Grid System 40000W with Certificate UL, TUV, CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords