Solar Energy Systems NZ - CNBM On Grid System 3000W with Certificate UL TUV CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
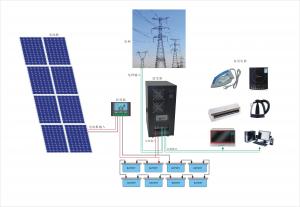
CNBM On Grid System 3000W with Certificate UL TUV CE
Product description
They range from small residential and commercial rooftop systems to large utility-scale solar power stations. Unlike stand-alone power systems, a grid-connected system rarely includes an integrated battery solution, as they are still very expensive. When conditions are right, the grid-connected PV system supplies the excess power, beyond consumption by the connected load, to the utility grid.
Connection of the photovoltaic power system can be done only through an interconnection agreement between the consumer and the utility company. The agreement details the various safety standards to be followed during the connection.[4]
Systems such as Net Metering and Feed-in Tariff which are offered by some system operators, can offset a customers electricity usage costs. In some locations though, grid technologies cannot cope with distributed generation feeding into the grid, so the export of surplus electricity is not possible and that surplus is earthed.
Grid-connected PV systems are comparatively easier to install as they do not require a battery system.[1][6]
Grid interconnection of photovoltaic (PV) power generation systems has the advantage of effective utilization of generated power because there are no storage losses involved.[7]

Application
Industrial
Commercial
Residential
Feature
Residential, grid-connected rooftop systems which have a capacity more than 10 kilowatts can meet the load of most consumers.[2] They can feed excess power to the grid where it is consumed by other users. The feedback is done through a meter to monitor power transferred. Photovoltaic wattage may be less than average consumption, in which case the consumer will continue to purchase grid energy, but a lesser amount than previously. If photovoltaic wattage substantially exceeds average consumption, the energy produced by the panels will be much in excess of the demand. In this case, the excess power can yield revenue by selling it to the grid. Depending on their agreement with their local grid energy company, the consumer only needs to pay the cost of electricity consumed less the value of electricity generated. This will be a negative number if more electricity is generated than consumed.[3] Additionally, in some cases, cash incentives are paid from the grid operator to the consumer.
Packaging
With carton and box
- Q: How does the efficiency of solar panels vary across different installation orientations?
- The efficiency of solar panels can vary significantly across different installation orientations. The orientation of a solar panel refers to the direction it faces relative to the sun's path. The two main orientations are horizontal (facing directly upwards) and tilted (angled towards the sun). In general, solar panels facing south tend to have the highest efficiency, as they receive the most sunlight throughout the day. This is especially true for locations in the northern hemisphere, where the sun is positioned towards the south. South-facing panels capture the maximum amount of sunlight, resulting in optimal energy production. East and west-facing solar panels have slightly lower efficiency compared to south-facing panels. East-facing panels receive more sunlight in the morning, while west-facing panels receive more sunlight in the afternoon. However, both orientations receive less sunlight overall than south-facing panels, leading to reduced efficiency. Solar panels that are installed horizontally, such as on flat rooftops, have the lowest efficiency among the common orientations. These panels do not have a specific direction to maximize sunlight absorption and are often less inclined towards the sun's path. As a result, they receive less direct sunlight throughout the day, causing lower energy generation compared to tilted or south-facing panels. It is important to note that the efficiency of solar panels is also affected by other factors such as shading, climate, and panel quality. Shading from nearby buildings, trees, or other obstructions can decrease efficiency by blocking sunlight. Additionally, the climate of a region and the quality of the solar panels themselves can also impact their efficiency. In conclusion, the efficiency of solar panels varies across different installation orientations. South-facing panels generally have the highest efficiency, while east, west, and horizontal orientations have lower efficiency levels. Factors such as shading, climate, and panel quality also play a role in determining the overall efficiency of solar panels.
- Q: How do solar energy systems impact energy reliability?
- Solar energy systems can greatly enhance energy reliability by diversifying the energy mix. By harnessing the power of the sun, solar energy systems offer a clean and renewable source of electricity, reducing dependence on traditional fossil fuels. This diversification helps to mitigate the risks associated with potential energy supply disruptions, enhancing overall energy reliability for communities and reducing the impact of power outages.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for outdoor lighting?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used for outdoor lighting. Solar-powered lighting systems utilize solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity, which is stored in batteries. This stored energy is then used to power outdoor lights during the night or in areas where electricity is not readily available. Solar outdoor lighting is an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution that can be used for various applications, including pathway lighting, garden lighting, and security lighting.
- Q: How do solar energy systems handle excess energy production?
- Solar energy systems handle excess energy production in a few different ways. One common method is through net metering, where any excess energy that is produced by the solar system is fed back into the grid. This excess energy is then credited to the homeowner's account, effectively spinning their meter backward and reducing their energy bill. Another way to handle excess energy production is through the use of battery storage systems. These systems allow homeowners or businesses to store the excess energy generated by their solar panels for use during times of high energy demand or when the sun is not shining. The stored energy can be used during the evening or on cloudy days, maximizing the value and efficiency of the solar system. Additionally, some solar energy systems are designed to automatically shut down or reduce their output when excess energy is being produced. This is known as curtailment and is often used in large-scale solar farms or utility-scale installations. By reducing the output, the excess energy is not wasted and can be more effectively managed and distributed. Overall, solar energy systems have various mechanisms in place to handle excess energy production, whether it be through net metering, battery storage, or curtailment. These methods ensure that the surplus energy is not wasted and can be effectively utilized, making solar energy a highly efficient and sustainable source of power.
- Q: Can a solar energy system be installed on a hospital or healthcare facility?
- Yes, absolutely. Solar energy systems can be installed on hospitals or healthcare facilities. In fact, many hospitals and healthcare facilities are adopting solar energy as a sustainable and cost-effective solution to meet their energy needs. These systems can provide clean and renewable energy, reducing the facility's carbon footprint and operating costs. Additionally, solar energy installations can help hospitals maintain a reliable power supply during emergencies or power outages, ensuring uninterrupted patient care.
- Q: How do solar energy systems impact grid stability?
- Solar energy systems can have both positive and negative impacts on grid stability. On one hand, solar energy systems can help improve grid stability by reducing the overall demand for electricity during peak times. This is because solar energy production typically aligns with peak electricity demand, which helps balance the grid and reduces the need to rely on other power sources. On the other hand, the intermittent nature of solar power can pose challenges to grid stability. Sudden fluctuations in solar energy production due to weather conditions can create voltage and frequency variations, which can affect the stability of the grid. However, with proper integration and management techniques, such as energy storage systems and advanced grid control technologies, the negative impacts of solar energy systems on grid stability can be minimized.
- Q: What are the disadvantages of using solar energy?
- One disadvantage of using solar energy is its intermittent nature, as it is dependent on sunlight availability. Factors such as cloudy weather or nighttime can limit its energy generation. Additionally, solar panels and the necessary equipment can be expensive to install, which may deter some individuals or businesses from adopting solar energy.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used in areas with high levels of hail or other severe weather conditions?
- Areas with high levels of hail or severe weather conditions can indeed utilize solar energy systems. Although hail has the potential to damage solar panels, modern designs have been specifically engineered to endure various weather conditions, including hail of a specific size and velocity. Solar panels are typically constructed using durable materials like tempered glass and undergo rigorous testing to withstand hail of a particular size and impact force. They are built to be resilient enough to withstand hailstorms without breaking or compromising their efficiency. Furthermore, panels are often installed at an angle to allow hailstones to slide off rather than directly impact the surface, reducing the risk of damage even further. Moreover, advancements in solar technology have resulted in the production of stronger and more robust solar panels. Some manufacturers even offer panels with enhanced features that make them more resistant to hail, such as reinforced glass or protective coatings. These features provide additional durability, particularly in regions prone to severe weather conditions. It is essential to consider the severity and frequency of hailstorms when planning and installing solar energy systems. Evaluating local weather patterns and historical data can help assess the level of risk and determine appropriate measures to protect the panels, such as using hail guards or installing extra protective layers. To summarize, solar energy systems can be effectively utilized in areas with high levels of hail or severe weather conditions, as long as the panels are designed and installed to withstand such conditions. Careful planning, the use of resilient materials, and regular maintenance can ensure the long-term performance and durability of solar energy systems in these areas.
- Q: How do solar energy systems impact the quality of indoor air?
- Solar energy systems have a positive impact on the quality of indoor air. By harnessing the sun's energy, solar systems eliminate the need for fossil fuel-based energy sources, thus reducing the emission of harmful pollutants such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. This reduction in emissions leads to cleaner air indoors, promoting better health and reducing the risk of respiratory problems for occupants.
- Q: How does the efficiency of solar panels vary across different installation locations?
- The efficiency of solar panels varies across different installation locations due to various factors such as the amount of sunlight received, the angle and orientation of the panels, shading, temperature, and local weather conditions.
Send your message to us
Solar Energy Systems NZ - CNBM On Grid System 3000W with Certificate UL TUV CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords