hot-Dip Galvanized/ Aluzinc Steel in SGCC grade in China
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
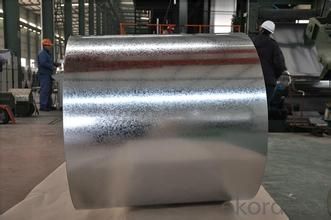
Description:
Hot-dip galvanized steel coils are available with a pure zinc coating through the hot-dip galvanizing process. It offers the economy, strength and formability of steel combined with the corrosion resistance of zinc. The hot-dip process is the process by which steel gets coated in layers of zinc to protect against rust. It is especially useful for countless outdoor and industrial applications.
Specifcation:
1.Mateials:SGCC,DX51D / DX52D /S250,280GD
2.Size:width:600-1250mm(900mm,1215mm,1250mm,1000mm the most common)
thickness:0.15-2.0mm
length:1000-6000mm,as your require
3.Zinc coating :60-180g( as required)
4.Coil id:508mm
5.Coil weight: 3-5MT(as required)
6. Surface:regular/mini/zero spangle, chromated, skin pass, dry etc.
Images:

We can ensure that stable quality standards are maintained, strictly meeting both market requirements and customers’ expectations. Our products enjoy an excellent reputation and have been exported to Europe, South-America, the Middle-East, Southeast-Asia, Africa and Russia etc.. We sincerely hope to establish good and long-term business relationship with your esteemed company.
- Q: I work the Copper plating line at a custom plating facility in MI.I like to use jumper cables with the jumper cable clamps to help confirm electric current is getting to my parts that I am plating. The acids in the Acid copper is constantly eating the steel and copper clamps. WIll I get a good enough current through stainless steel clamps? I use stainless steel hooks, but our maintenance man thinks that is one of the reasons why I have prblems with my parts turning out. I still think it has to do with the clamps getting eatin up. My question is Is stainless steel as good or reliable enough to run an electrical current to my parts if I am using stainless steel or is it best to use another method to try and get a better connection.Please state your sources or experience with working with electricity. I need to get honest answers and not this is my opinion. We are talking about my making a living so this is important to me so I can bring food home to my table. Thanks for all the help.
- Stainless steel is not such a good conductor as copper and the only metal with better conductivity is silver. Additionally, stainless steel will corrode in certain very corrosive environments without the presence of oxygen - i.e. when immersed in salt water. If you're getting problems caused by corrosion of the copper contacts you use there may well be a trade off so my advice is to do a trial and see what works best. You can check the conductivity of metals by simple online search for the period table:
- Q: What is the lifespan of coated steel coils?
- The lifespan of coated steel coils can vary depending on various factors such as the type and quality of the coating, the environmental conditions it is exposed to, and the maintenance and care provided. Generally, high-quality coated steel coils can have a lifespan of 25 to 50 years or even more. However, it is important to note that this is just an estimate and the actual lifespan may vary. Regular inspections, proper installation, and timely maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of coated steel coils. Additionally, factors such as exposure to harsh weather conditions, corrosive environments, and improper handling can potentially shorten the lifespan. It is recommended to consult with manufacturers or industry experts to determine the most suitable coating and expected lifespan for specific applications.
- Q: At what temperature does steel start to warp or soften.
- Steel will only warp due to temperature under two conditions: 1. It is not heated evenly - in this case, the hotter parts will expand more than the cooler parts. 2. There are internal stresses in the steel (often from welding or cold-working - as an example, an I-beam or C-channel is usually hot worked, but some cold work can happen, so they can sometimes warp if you heat them ). This means that the steel won't warp due to temp if it's not 1 or 2. However, it could soften and fail if it has a load on it. As for softening, it really depends on what steel alloy you're looking at. Some steels (mainly the expensive alloys) don't really change until above 400 C (750 F), but mild steel really starts to weaken around 150-200 C (300-400 F) Rajashekhar has a point when it comes to forging. Steel isn't really soft enough to forge properly until above 1000C (1830 F), but if you're worried about using steel in a higher temp situation (like around a blast furnace or industrial oven), then make sure you choose a steel that has been rated to work at that temp.
- Q: i see a lot of connexes say repair only with corten steel. what is the difference between corten steel and regular steel. and if i was going to stick weld it what type of electrode would i use?and while i'm at it what is the best electrode to use when welding galvenized steel?
- 6010 and 6011 Electrodes for welding galvenized steel. Weathering steel, best-known under the trademark COR-TEN steel and sometimes written without the hyphen as Corten steel, is a group of steel alloys which were developed to obviate the need for painting, and form a stable rust-like appearance if exposed to the weather for several years. The corrosion-retarding effect of the protective layer is produced by the particular distribution and concentration of alloying elements in it. The layer protecting the surface develops and regenerates continuously when subjected to the influence of the weather. In other words, the steel is allowed to rust in order to form the 'protective' coating. For welding corten steel: 1A.W.S ClassificationE 7018 - 1AWS A 5 - 1 - 78 2IS classificationE 5424 JXIS 814 (Part I II)H 3BS classificationE 51.54 B 12 17HBs 639 - 1976
- Q: I am working on a hydrogen generator, but the stainless steel I am using corrodes and turns the water brown. Can anyone tell me if there is stainless steel that does not corrode, and if so, what is it called and where can I get some.Thank you.
- You are not using stainless steel.
- Q: What are the different types of coil slitting machines?
- There are several different types of coil slitting machines available in the market, each designed to meet specific requirements and preferences. Some of the common types include: 1. Rotary shear slitters: These machines use rotary knives mounted on a rotating drum to cut the coil into narrow strips. They are ideal for high-speed operations and can handle large volumes of material. 2. Loop slitters: Loop slitting machines feed the coil through a loop to maintain tension and prevent material damage during the slitting process. They are suitable for delicate materials or those prone to deformation. 3. Turret slitters: Turret slitting machines have multiple sets of slitting knives mounted on a rotating turret. This allows for quick and easy changeover between different slitting configurations, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. 4. Drag slitters: Drag slitting machines use a stationary knife and a moving clamp to hold and pull the coil through the cutting process. They are versatile and can handle a wide range of materials, including thick or heavy coils. 5. Crush slitters: Crush slitting machines use a set of opposing rollers to crush and cut the coil material. They are commonly used for softer materials or those that are difficult to cut with traditional knives. 6. Laser slitters: Laser slitting machines use a high-powered laser beam to precisely cut through the coil material. They offer unmatched accuracy and are suitable for high-end applications or materials with complex shapes. Each type of coil slitting machine has its own advantages and limitations. The choice of machine depends on factors such as the type of material, required speed, desired accuracy, and production volume.
- Q: I need to penetrate steel on my car but don't know which bit to use. Are there special bits for steel?
- I think you mean through being that said, they make special bits for drilling metal that you can pick up at any good hardware store ps if drilling on your car, be sure you don't drill into the gas tank, muffler, etc
- Q: For robotics homework, I need to find out how steel is galvanized and why. I researched a little bit, and I'm not sure I grasp the entire concept. Simple words would be helpful :) Thank you!!!
- Steel can be galvinised by electroplating process. Galvinising means providing a zinc coating on steel surface. It protects the material from rusting and loosing the shinining.
- Q: Ok so i have a certain amount of money that I want to invest in either GE or US Steel. Tickers: ge, x. GE looks like a strong co, but less risk. Whereas US Steel looks risky, but high reward. :). i am willing to take risks. Any comments?
- I would go with some in one and less in the other. Given that steel prices have collapsed (and seeing as the Chinese economy is going into a recession, they will probably stay low for a while) I would say that because US Steel is a blue chip company it will be around for the long term, but, it won't make much for a while. GE on the other hand has been beaten down thanks to some mismanagement issues under current CEO Jeffrey Immelt, however, they have a range of strong products (save for their broadcast division, RCA/NBC). Given that the stock is at a severe low with the company itself being worth quite a bit (with a fair amount of bailout funds coming to its' financial division) and the Obama administrations' green initiatives coming online over the next couple of years the demand for their products will be high. I would simply say 70/20 GE/US. Good luck.
- Q: How are steel coils used in the production of shipping containers?
- Steel coils are used in the production of shipping containers as they are formed and shaped into the required structure and size. The coils are unrolled and cut into sheets, which are then molded and welded to create the walls, roof, and floor of the container. This process ensures the container's strength, durability, and ability to withstand harsh shipping conditions.
Send your message to us
hot-Dip Galvanized/ Aluzinc Steel in SGCC grade in China
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords
































