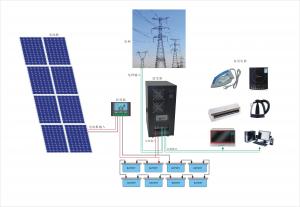
35kw CNBM Monocrystalline Silicon Solar Energy Systems Panel for Home Use in Italy
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
35KW CNBM Monocrystalline Silicon Panel for Home Using
Production description
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun harnessed using a range of ever-evolving technologies such assolar heating, photovoltaics, solar thermal energy, solar architecture and artificial photosynthesis.
It is an important source of renewable energy and its technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar oractive solar depending on the way they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into solar power. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic systems

Feature
1.High conversion efficiencies resulting in superior power output performance.
2.Outstanding power output even in low light or high temperature conditions
3.Optimized design for ease of soldering and lamination
Physical characteristic
1. Rigorous quality control meets the highest international standards.
2. High-transmissivity low-iron tempered glass, strong aluminium frame.
3. Using UV-resistant silicon.
4. IS09001/14001/CE/TUV/UL
Packaging
26pcs in one carton 6pallets in 20foot container 14pallets in 40 foot container.
- Q: How do solar energy systems impact utility bills?
- Solar energy systems can have a significant impact on utility bills by reducing or even eliminating the need for traditional energy sources. By harnessing the power of the sun, these systems generate electricity that can be used to power homes and businesses. This can result in substantial savings on monthly utility bills as less energy is consumed from the grid. In some cases, excess energy generated by solar panels can even be sold back to the utility company, further reducing costs. Overall, solar energy systems can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels, minimize environmental impact, and provide long-term financial benefits by lowering utility bills.
- Q: Do solar energy systems require surge protection?
- Indeed, surge protection becomes imperative when it comes to solar energy systems. The susceptibility of these systems to power surges caused by lightning strikes, grid fluctuations, or other electrical disturbances necessitates the presence of surge protection. The fragile electronic components of a solar energy system, like inverters or charge controllers, can be severely compromised or even annihilated by power surges. Hence, the deployment of surge protection devices, such as surge protectors or surge arresters, is crucial in diverting excessive voltage away from the system, thereby safeguarding it from harm and ensuring its durability. Furthermore, the inclusion of surge protection is often mandated by electrical codes and regulations to guarantee the safety and dependability of solar energy systems.
- Q: How do solar energy systems impact the environment?
- Solar energy systems have a positive impact on the environment as they produce clean and renewable energy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. They also require minimal water usage compared to traditional energy sources and do not contribute to resource depletion or environmental degradation.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used in areas with limited access to solar inverters?
- No, solar energy systems cannot be effectively used in areas with limited access to solar inverters. Solar inverters are an integral part of solar energy systems as they convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power electrical devices. Without inverters, solar energy cannot be utilized efficiently, making it impractical to implement solar systems in areas with limited access to solar inverters.
- Q: What is the role of optimizers in a solar energy system?
- The role of optimizers in a solar energy system is to maximize the overall efficiency and performance of the system. They are electronic devices that are connected to each individual solar panel in order to monitor and optimize its output. Optimizers work by performing a range of functions. Firstly, they ensure that each solar panel operates at its maximum power point (MPP), which is the point at which it generates the most power. By continuously tracking and adjusting the voltage and current of each panel, optimizers ensure that they are always operating at their MPP, even in situations where shading or other factors may cause some panels to underperform. In addition, optimizers also provide module-level monitoring and diagnostics. They collect data on the performance of each individual panel, including its voltage, current, and temperature. This information is transmitted to a central monitoring system, which allows for the detection and troubleshooting of any issues or malfunctions in real-time. This level of granularity and visibility into the performance of each panel helps to improve maintenance and overall system reliability. Furthermore, optimizers also enhance the safety of the solar energy system. They include built-in safety features such as rapid shutdown capabilities, which enable the system to quickly and safely shut down in the event of an emergency or maintenance requirement. This helps to protect both the system and the individuals working on it. Overall, the role of optimizers in a solar energy system is crucial for maximizing energy production, improving overall system efficiency, ensuring safety, and facilitating effective monitoring and maintenance. By optimizing the performance of each individual solar panel, optimizers contribute to the overall success and viability of solar energy systems.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be installed on sloped roofs?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be installed on sloped roofs. In fact, sloped roofs are quite common for solar panel installations. The angle and orientation of the roof are important factors in determining the efficiency of the solar energy system. Ideally, a sloped roof with a south-facing orientation will maximize the amount of sunlight exposure throughout the day. However, solar panels can still be installed on roofs with different orientations or slopes, albeit with some adjustments in panel placement and tilt angles. It is important to consult with a professional solar installer who can assess the specific roof conditions and design a customized solar energy system that works best for the slope and orientation of the roof.
- Q: What is the role of batteries in solar energy systems?
- The role of batteries in solar energy systems is to store excess electricity generated by solar panels for use during times of low or no sunlight. This allows for constant power supply and enables the system to operate independently from the grid, increasing self-sufficiency and reliability.
- Q: How do solar energy systems impact the health of the population?
- Solar energy systems have a positive impact on the health of the population. They help reduce air pollution by replacing fossil fuel-based power generation, which leads to improved air quality and decreased respiratory ailments. Additionally, solar energy systems do not emit harmful greenhouse gases, reducing the risk of climate-related health issues such as heat strokes and vector-borne diseases. By providing clean and sustainable energy, solar systems contribute to a healthier and more sustainable future for all.
- Q: Can a solar energy system be installed on a building with multiple levels?
- Yes, a solar energy system can be installed on a building with multiple levels. The installation process may vary depending on the specific layout and structure of the building, but with proper planning and design, solar panels can be successfully installed on roofs, walls, or even as shading structures on multiple levels of a building to generate renewable energy from the sun.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used in powering concert halls or auditoriums?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used to power concert halls or auditoriums. These systems can be installed on the rooftop or nearby areas to harness sunlight and generate electricity. The generated solar power can then be used to run the lighting, sound systems, and other electrical equipment required for concerts or performances. Additionally, solar energy systems can be integrated with battery storage solutions to ensure a continuous power supply, even during periods of low sunlight or at night.
Send your message to us
35kw CNBM Monocrystalline Silicon Solar Energy Systems Panel for Home Use in Italy
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords