12 Volt MPPT Solar Inverter Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG100K3
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1. Structure of Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG100K3 Description
A solar inverter, or PV inverter, or Solar converter, converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic (PV) solar panel into
autility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercial electrical grid or used by a local, off-grid electrical network.
It is acritical BOS–component in a photovoltaic system, allowing the use of ordinary AC-powered equipment. Solar inverters have
special functions adapted for use with photovoltaic arrays, including maximum power point tracking and anti-islanding protection.
Suitable for 50Hz/60Hz grid, could be used in Asia, Australia and Europe.
2. Main Features of the Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG100K3
* Advanced Technology, Grid-friendly
• Optional low-voltage and zero-voltage ride through to cope with various grid conditions
• SVG function at night, response to grid directives around the clock
• Reactive power control with power factor from 0.9 lagging to 0.9 leading
* More Compact, Saving Space for PV Plant
• Power density enhanced 40%, one of the central inverters with highest power density in the PV industry
• Save installation spaces and lower the plant initial cost
• Front maintenance, able to install against the wall, convenient installation and maintenance, saving operation cost of the PV plant
* Efficient, More Yields
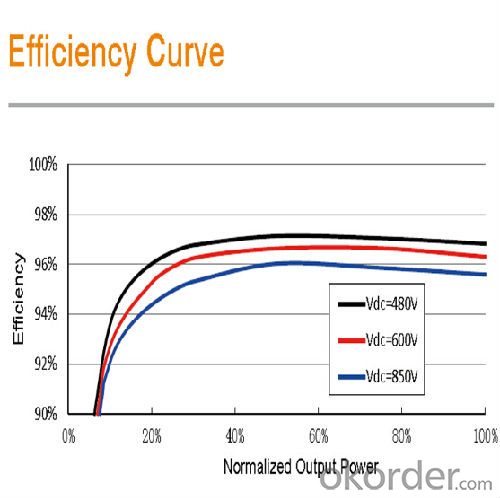
• Max. efficiency at 97.3% with transformer
• Efficient MPPT control strategy, improve power yields
• 28335 chips adopted, more accurate calculation, more power yields
* More Advantages
• Perfect protection and fault alarm system, safe and reliable
• User-friendly dynamic graphics LCD
• Efficient PWM algorithm, low consumption of switch
• Operate without power derating at -25℃ - +55℃
• Reliable and continues operation in high altitude environment
• Auxiliary heater (opt.)
• CGC certification, compliance with BDEW
3. Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG100K3 Images


4. Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG100K3 Specification
Input Side Data |
|
Max. PV input power | 113KW |
Max. PV input voltage | 1000V |
Set-up voltage | 500V |
Min. operation voltage | 480V |
Max. PV input current | 236A |
MPP voltage range | 480~850V |
No. of DC inputs | 4 |
Output Side Data |
|
Nominal AC output power | 100KW |
Max. AC output apparent power | 110KVA |
Max. AC output current | 158A |
THD | <3%(Nominal power) |
Nominal AC voltage | 400V |
AC voltage range | 310V~450V |
Nominal grid frequency | 50/60Hz |
Grid frequency range | 47~52Hz/57~62Hz |
Power factor | >0.99@default value at nominal power, adj. 0.9 overexcited ~0.9 underexcited |
Isolated transformer | Yes |
DC current injection | <0.5 % In |
Efficiency |
|
Max. efficiency | 97.30% |
European efficiency | 96.70% |
Protection |
|
Input side disconnection device | Breaker |
Output side disconnection device | Breaker |
DC overvoltage protection | Yes |
AC overvoltage protection | Yes |
Grid monitoring | Yes |
Ground fault monitoring | Yes |
Insulation monitoring | Yes |
General Data |
|
Dimensions(W×H×D) | 806×1884×636mm |
Weight | 760kg |
Operating ambient temperature range | -25~+55℃ |
Night power consumption | <40W |
External auxiliary supply voltage | No |
Cooling method | Temperature controlled air-cooling |
Ingress protection rating | IP21 |
Allowable relative humidity range | 0~95% no condensing |
Max. operating altitude | 6000m(>3000m derating) |
Fresh air consumption | 870m³/h |
Display | LCD |
Communication | RS485/Modbus, Ethernet(Opt.) |
5. FAQ of Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG100K3
Q1. What is the difference between inverter and solar inverter?
A1. Inverter only has AC inpput, but solar inverter both connect to AC input and solar panel, it saves more power.
Q2. What is the difference between MPPT&PWM?
A2. MPPT has higher efficiency, it can track the max power point and won't waste energy.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle variations in ambient temperature?
- A solar inverter handles variations in ambient temperature by incorporating temperature compensation mechanisms. These mechanisms allow the inverter to adjust its operation and optimize performance based on the temperature conditions. By monitoring the temperature, the inverter can regulate voltage levels, adjust power outputs, and protect itself from overheating. This ensures that the inverter operates efficiently and reliably under different ambient temperature conditions.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with other renewable energy sources like wind or hydro power?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with other renewable energy sources like wind or hydro power. Inverters are designed to convert the direct current (DC) generated by these renewable sources into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power homes or businesses. By integrating multiple renewable energy sources through a single inverter, it becomes possible to create a more diverse and reliable renewable energy system.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with a ground-mounted solar array?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with a ground-mounted solar array. A solar inverter is responsible for converting the DC (direct current) electricity produced by the solar panels into AC (alternating current) electricity that can be used to power homes or businesses. Whether the solar array is ground-mounted or roof-mounted, the solar inverter plays a crucial role in converting the electricity for use in the desired location.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle shading on the solar panels?
- A solar inverter typically handles shading on solar panels by using a technology called Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). MPPT enables the inverter to constantly monitor the performance of each individual solar panel and adjust its voltage and current to ensure maximum power output. When shading occurs on a panel, the MPPT algorithm detects the drop in power and adjusts the system to bypass the shaded panel or operate it at a different voltage, allowing the other unshaded panels to continue producing power efficiently. This helps to mitigate the impact of shading on the overall system performance.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle voltage transients?
- A solar inverter handles voltage transients by continuously monitoring the voltage levels and adjusting its internal circuitry to maintain a stable output voltage. It uses advanced control algorithms and protective features to mitigate the effects of sudden changes in input voltage, such as voltage spikes or dips, ensuring the smooth and reliable operation of the solar power system.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with different communication protocols?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with different communication protocols. Many modern inverters are designed to be compatible with various communication protocols such as Modbus, RS485, Wi-Fi, or Zigbee. This allows them to communicate and integrate with different monitoring systems, smart home devices, or other renewable energy components, providing flexibility and compatibility for users.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in systems with different module tilts?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in systems with different module tilts. Solar inverters are designed to convert the DC power generated by solar modules into AC power that can be used in electrical systems. They are typically compatible with a wide range of module tilts and orientations. However, it is important to ensure that the inverter is properly configured to match the specific tilt angles of the solar modules for optimal performance and maximum energy generation.
- Q: Are there any specific installation requirements for solar inverters?
- Solar inverters have specific installation requirements that should be taken into consideration. Here are some important factors to keep in mind: 1. Placement: To ensure optimal performance and durability, solar inverters should be installed in a well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and potential heat sources. Additionally, they should be placed in a clean and dry environment. 2. Mounting: Solar inverters can be mounted on walls or placed on flat surfaces. However, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for proper mounting techniques and ensure that they are securely fastened. 3. Wiring: Adequate wiring is essential for connecting the solar panels to the inverter and the inverter to the electrical grid. The wiring should be appropriately sized based on the system's specifications to handle voltage and current requirements without any voltage drop or overheating. 4. Electrical connections: The inverter should be connected to a dedicated circuit breaker or fuse in the main electrical panel. This circuit breaker or fuse must be properly sized to protect the inverter and the electrical system from potential hazards. 5. Clearances: Specific clearances are required to ensure proper ventilation and prevent overheating of solar inverters. The manufacturer's guidelines should be followed to determine the necessary clearances around the inverter. 6. Monitoring and safety devices: Certain inverters may require additional monitoring and safety devices, such as surge protectors, arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs), or rapid shutdown devices. These devices should be installed according to the manufacturer's instructions and local electrical codes. 7. Compliance with regulations: Compliance with local electrical codes and regulations is crucial during the installation of solar inverters. This may include obtaining necessary permits and inspections to ensure a safe and compliant installation. To ensure that all specific requirements are met for your particular system, it is highly recommended to seek guidance from a professional solar installer or electrician who has expertise in solar inverter installations.
- Q: What is the role of a fault detection feature in a solar inverter?
- The role of a fault detection feature in a solar inverter is to monitor and identify any malfunctions or abnormalities within the system. It is responsible for detecting faults such as overvoltage, under-voltage, over-temperature, short circuits, ground faults, or any other potential issues that may arise. This feature helps ensure the safe and efficient operation of the solar inverter by promptly alerting the user or system operator about the fault, allowing for quick troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with different types of solar panel mounting systems?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with different types of solar panel mounting systems. The function of a solar inverter is to convert the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power household appliances or fed into the grid. The compatibility of the inverter with different mounting systems depends on the electrical specifications and requirements of the panels and the inverter. As long as the electrical connections and voltage requirements are met, a solar inverter can be used with various types of solar panel mounting systems such as roof-mounted, ground-mounted, or pole-mounted systems.
Send your message to us
12 Volt MPPT Solar Inverter Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG100K3
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























