All Categories
- - Steel Wire Rod
- - Steel Coils
- - Steel Profiles
- - Steel Pipes
- - Stainless Steel
- - Tinplate
- - Special Steel
- - Steel Sheets
- - Steel Rebars
- - Steel Strips
- - Hot Rolled Steel
- - Cold Rolled Steel
- - Pre-painted Steel
- - Seamless Steel Pipe
- - Welded Steel Pipe
- - Hollow Steel Tubes
- - Galvanized Pipe
- - Stainless Steel Coil
- - Stainless Steel Sheet
- - Stainless Steel Plate
- - Stainless Steel Strips
- - Electrolytic Tinplate Coil
- - Electrolytic Tinplate Sheet
- - Stainless Steel Rebars
- - Solar Panels
- - Solar Water Heater
- - Solar Related Products
- - Solar Inverter
- - Solar Cells
- - Solar Light
- - Solar Energy Systems
- - Solar Controllers
- - Solar Mounting System
- - Solar Pump
- - Solar Chargers
- - Fiberglass Chopped Strand
- - Fiberglass Mesh Cloth
- - Composite Pipes
- - FRP Pultrusion Profiles
- - Fiberglass Mat Tissue
- - Fiberglass Fabrics
- - Fiberglass Mesh
- - Composite Tank
- - Fiberglass Mesh tape
- - Polymer
- - FRP Roofing Panel
- - Fiberglass Roving
- - Monolithic Refractories
- - Ceramic Fiber Products
- - Refractory Bricks
- - Raw Materials For Refractory
- - Suspended Platform
- - Cranes
- - Concrete Machinery
- - Earthmoving Machinery
- - Building Hoist
- - Road Building Machinery
- - Plastic Pipe Fittings
- - Plastic Tubes
- - Plastic Sheets
- - Agricultural Plastic Products
- - Plastic Nets
 All Categories
All Categories
Q & A
How do geogrids impact soil settlement and consolidation in geosynthetic applications?
Geogrids have a significant impact on soil settlement and consolidation in geosynthetic applications. These materials enhance the stability and load-bearing capacity of soil by reinforcing it. By distributing the applied load and reducing the stress on the soil, geogrids minimize settlement and consolidation. Additionally, geogrids improve the overall performance of the soil by preventing lateral movement and increasing its shear strength. Overall, geogrids play a crucial role in minimizing soil settlement and consolidation, ensuring the longevity and integrity of geosynthetic applications.
What is the significance of geogrid aperture size in soil reinforcement?
The significance of geogrid aperture size in soil reinforcement is that it affects the interaction between the geogrid and the soil particles. The aperture size determines the level of confinement provided by the geogrid, which affects the ability of the soil to resist deformation and maintain its strength. A larger aperture size allows for more soil particles to pass through, reducing the confinement and potentially compromising the effectiveness of the reinforcement. Conversely, a smaller aperture size enhances soil confinement and improves the overall stability and load-bearing capacity of the reinforced soil structure. Therefore, selecting an appropriate geogrid aperture size is crucial in achieving desired soil reinforcement performance.
What are the advantages of geogrid-reinforced slopes?
Geogrid-reinforced slopes offer several advantages, including increased stability and safety, reduced soil erosion, and cost-effectiveness. The geogrids distribute and reinforce the weight of the soil, improving slope stability and preventing potential landslides. Additionally, they enhance the load-bearing capacity of the slope, allowing for the construction of steeper and taller slopes. Geogrids also minimize soil erosion by providing a barrier against water flow and protecting the underlying soil. Moreover, using geogrids in slope reinforcement projects can be more cost-effective compared to traditional methods, as they require less excavation and grading, resulting in reduced construction time and labor costs.
What is the difference between geogrids and geotextiles?
Geogrids and geotextiles are both geosynthetic materials used in civil engineering and construction projects, but they serve different purposes.
Geogrids are typically made of high-strength polymers and have a grid-like structure. They are primarily used to reinforce soil and provide stability to structures like retaining walls and roadways. Geogrids are designed to distribute loads and prevent soil movement, increasing the overall strength and durability of the project.
On the other hand, geotextiles are made of woven or non-woven fabrics and are mainly used for filtration, drainage, and separation purposes. Geotextiles allow water to pass through while preventing the mixing of different soil layers. They are commonly used in erosion control, road construction, and landfills to improve drainage and prevent soil erosion.
In summary, the key difference between geogrids and geotextiles is their function: geogrids provide reinforcement and stability to structures, while geotextiles focus on filtration, drainage, and separation.
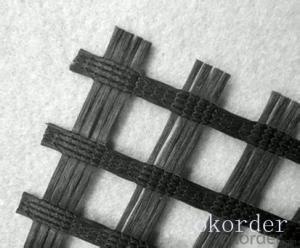
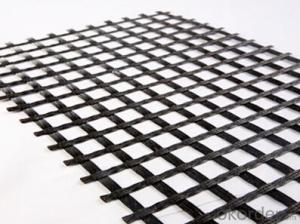
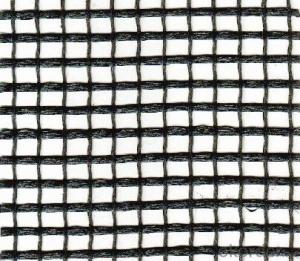
Wholesale Geogrids from supplier in Uruguay
We are a Geogrids supplier serving the Uruguay, mainly engaged in the sale, quotation, and technical support services of various Geogrids products in the Uruguay region. We are a subsidiary platform of the Fortune Global 500 company CNBM, able to provide you with one-stop Geogrids procurement services in the Uruguay. Not only do we have a wide range of Geogrids products, but after years of market development in the Uruguay, we can also provide valuable experience for your projects.