Section Steel Roll From China With High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 41000 m.t./month
- Option:
- 650X1780X5540; 650X1780X5540; 680X2080X5920
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Item specifice
Company Profile
CNBM International Corporation (CNBM International) is the most important trading platform of CNBM Group Corporation, a state-owned company under the direct supervision of State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council.
CNBM Group is integrated with four business segments: Manufacture, R&D,Sets of equipment and Logistics trading.Mill rolls are our main products.
CNBM International is highly recognized by its business partners and clients all over the world and has established good business relationship with the customers in over 120 countries and regions all over the world.
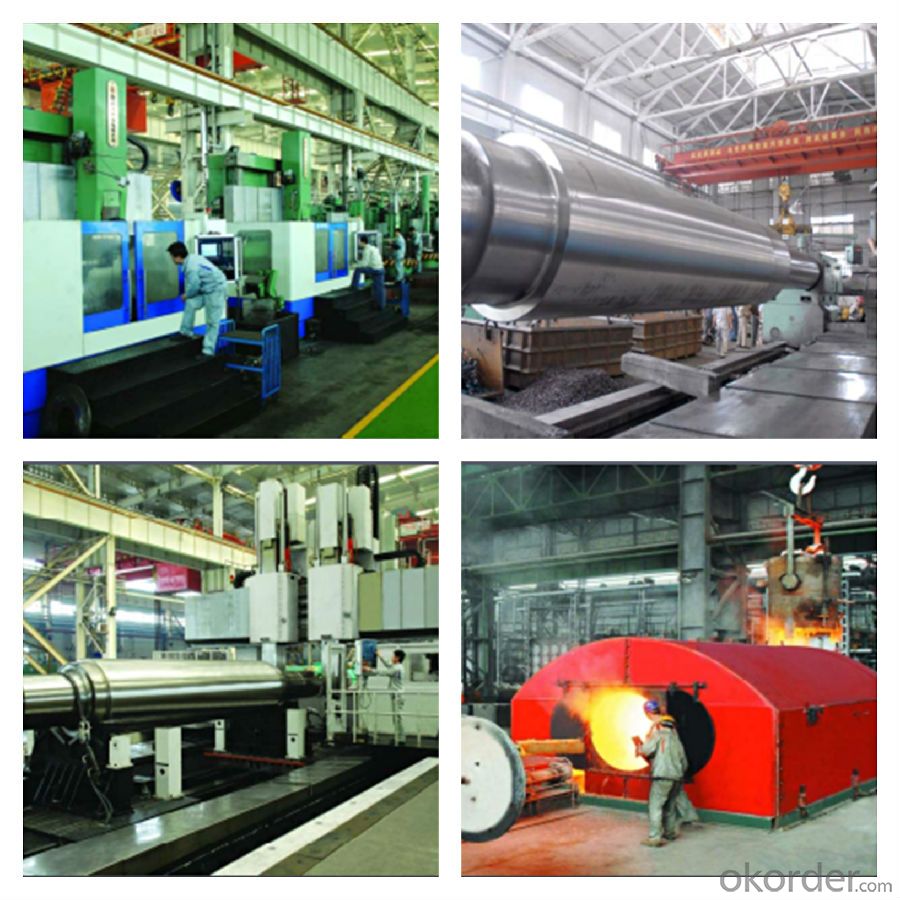
The product introduction of mill roll
Equipped with advanced technological facilities on melting, casting, forging, heat treating and mechanical machining, our factory has formed 9 professional complete roll manufacturing lines of cast steel, cast iron and forged steel rolls such as strip mill rolls, heavy section mill rolls, wire & bar rolls, special shaped rolls and small-sized cold rolls and specialized production lines of bloom and slab CCM, coke oven equipments and wind power products. Annual production capacity of mill rolls is 500,000 tons, metallurgical equipment is 80,000 tons.


Workshop
Workshop is the core of our company and undertakes all of scientific research work. The company specially produces and supplies all kinds of roll used for hot strip mill, cold strip mill, plate & heavy plate mill, large-sized section mill, universal mill etc.

Products & Specification
| Mill | Application | Material | Product Specification | ||
| Hot Strip Mill | Large-sized vertical roll | Special alloy cast roll, Adamite | All Sizes | ||
| Small-sized vertical roll | Adamite, HiCr iron | ||||
| Roughing work roll | Special alloy cast steel, Adamite, HiCr steel, Semi-HSS, HiCr iron | ||||
| Finish rolling | Early stand work roll | HiCr iron, HSS | |||
| Later stand work roll | ICDP, HSS | ||||
| Finishing back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | |||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | ||||
| Temper rolling | Work roll | HiCr iron | All Sizes | ||
| Alloy forged steel | |||||
| Back-up roll | ICDP | ||||
| Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000, W≤80t | ||||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000, W≤75t | ||||
| Mill | Application | Material | Product specification |
Cold strip mill & Single stand cold mill | Work roll | Alloy forged steel | All Sizes |
| Intermediate roll | Alloy forged steel | ||
| Temper roll | Alloy forged steel | ||
| Back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | |
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | ||
Largesized universal structural mill | Break-down roll | Special alloy cast steel, alloy nodular iron | All Sizes |
| Horizontal collar | High carbon adamite (duplex) | ||
| Vertical collar | High carbon adamite, HiCr iron | ||
| Edger roll Edger roll | High carbon adamite | ||
| Shaft | Alloy forged steel |
| Mill | Application | Marterial | Product Specification | |
| CSP | Vertical Roll | Adamite, Special alloy cast steel, HiCr iron | All Sizes | |
| Roughing work roll | Semi-HSS, HiCr Steel | |||
| Finish rolling | Early stand | HiCr iron, HSS | ||
| Later stand | ICDP, HSS | |||
| Roughing & Finishing back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | ||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | |||
| Steckel Mill | Vertical roll | Adamite, Special alloy cast steel | All Sizes | |
| Roughing work roll | ICDP, HiCr iron | |||
| Finishing work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | ||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | |||
| Plate & Heavy plate mill | Rough rolling | 2-hi work roll | Special alloy cast steel, Tool steel | All Sizes |
| 4-hi work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Finishing work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Single stand work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | ||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | |||
Quality Control
The company has the most advanced experimental and testing equipments in global mill roll industry, including direct-reading spectrometer, spectrum analyzer , X-ray fluorescence analyzer, scanning electronic microscope, energy disperse spectroscopy, X-ray diffractometer, image analyzer, high/low temperature metallographic microscope, X-ray stress meter, brittleness temperature tester, thermal analogue machine, dilatometer, macro and micro hardness tester, OMNISCAM-1X automatic flaw detection, USN60 ultrasonic flaw detector, magnetic powder and non-destructive flaw detection etc,. The advanced inspection equipments and experimental methods provide guarantee for quality control and experiment on material, usability test and performance.
The factories of CNBM invested 2.3 billion RMB for large-scale
CNBM international Corporation has completed equipment and technology upgrade transformation, which was concentrated on three projects, production line of centrifugal casting rolls for hot strip and plate mill, forged roll for cold/hot strip mill, national class technology center and roll material lab. Through upgrade transformation, the following targets have been achideved:
(1)It becomes the world's biggest specialized mill roll maker with the largest production scale, the most complete specifications of products and the most extensive coverage of various rolls used on rolling mill.
(2) The technology of equipments has reached international leading level.
(3) "Mechanization, automation, intellectualization, digitization" of equipments obviously improve the quality control ability.
(4) New types of research instruments improve the R&D capacity of products.
Customers Visit

FAQ
Q:Are you a trading company or manufacturer?
A:CNBM is a large-scale central governmental industrial group with its own manufacturing sector, research and development sector, trading sector and logistics sector.
Q:I have some special requirement about specifications.
A:We have a well-rounded product range, which endows us with the capability of applying many special specifications. Please feel free to contact us with yours.
Q:Do you accept OEM service?
A:Yes, we do.
Q:What is your delivery time?
A:It depends on the size/complexity of your order and our own production schedule. Usually we provide a faster delivery than the industry's average.
Q:What is the payment term?
A:Our payment terms are negotiable.
Q:Can I have my own logo on the product?
A:Sure, we can apply your own logo on the products according to your requirement.
- Q:How does metal casting machinery ensure the uniformity of castings?
- The uniformity of castings is ensured by metal casting machinery through a combination of precise control, consistent processes, and advanced technology. To begin with, the machinery is designed to exert accurate control over the key parameters involved in the casting process. This involves regulating the temperature of the molten metal, controlling the speed and pressure of the casting process, and managing the cooling rate. By keeping these parameters within strict tolerances, the machinery guarantees that each casting is produced under similar conditions, resulting in uniformity. Moreover, metal casting machinery adheres to consistent processes that have been carefully optimized for each specific casting. This includes utilizing standardized molds, patterns, and gating systems that have been developed through extensive research and experience. These standardized processes help eliminate any variations that could cause non-uniformity in the castings. Additionally, modern metal casting machinery incorporates advanced technology, such as computerized controls and sensors, to continuously monitor and adjust the casting process in real-time. This technology enables operators to identify and rectify any deviations from the desired parameters, ensuring that each casting meets the required specifications. Furthermore, the machinery often comes equipped with quality control systems that allow for the inspection of castings during and after the process. This helps in the detection of any defects or variations in the castings, allowing for necessary adjustments to be made. In conclusion, metal casting machinery maintains uniformity in castings through precise control, consistent processes, and advanced technology. By closely regulating the casting parameters, following standardized processes, and employing advanced monitoring and inspection systems, the machinery produces castings that meet the required standards of uniformity.
- Q:How is CAD used in designing metal castings in machinery?
- Computer-aided design, commonly known as CAD, is extensively utilized in the design of metal castings for machinery. Its role in streamlining the casting process by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and cost reduction is crucial. Creating 3D models is one of the main applications of CAD in metal casting design. Engineers can employ CAD software to design intricate and complex casting shapes, considering all necessary dimensions, tolerances, and material properties. This allows for visualizing the final product and making any required adjustments before commencing the casting process. CAD also empowers engineers to simulate and analyze the casting process using casting simulation software, virtual tools that enable them to identify potential issues like porosity, shrinkage, or distortion that may arise during casting. By detecting and rectifying these problems in the virtual environment, designers can optimize the casting design, minimize defects, and enhance the overall quality of the metal casting. Additionally, CAD software facilitates the creation of detailed and precise casting molds. Mold design is a critical element of the casting process as it directly impacts the final shape and quality of the casting. CAD simplifies the generation of accurate mold designs, taking into account factors such as parting lines, gating systems, and risers. This guarantees that the mold will produce castings that are accurate and free of defects. Another advantage of using CAD in metal casting design is the ease of sharing and collaborating on designs. CAD files can be shared electronically, enabling real-time communication and feedback between designers, manufacturers, and clients. This streamlines the design process, minimizes errors, and ensures everyone involved is on the same page. In conclusion, CAD is an essential tool in the design of metal castings for machinery. It enables engineers to create precise 3D models, simulate and analyze the casting process, design accurate casting molds, and facilitates efficient collaboration. By leveraging CAD technology, the overall casting design process is significantly improved, resulting in high-quality metal castings that meet the specific requirements of machinery applications.
- Q:What are the temperature requirements for metal casting machinery?
- The temperature requirements for metal casting machinery depend on the specific type of casting process being used. Generally, metal casting machinery requires high temperatures to melt the metal and mold it into the desired shape. For example, in sand casting, one of the most common casting processes, the metal is typically melted at a temperature between 1200 and 1600 degrees Celsius (2200 and 2900 degrees Fahrenheit). The sand mold used in this process can withstand these high temperatures without deforming or breaking. In investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, the metal is typically melted at a temperature between 1150 and 1300 degrees Celsius (2100 and 2400 degrees Fahrenheit). The wax pattern used in this process is burned out at a temperature around 750 degrees Celsius (1380 degrees Fahrenheit) before the metal is poured into the mold. Die casting, another commonly used casting process, requires even higher temperatures. The metal is typically melted at a temperature between 600 and 700 degrees Celsius (1110 and 1290 degrees Fahrenheit) for aluminum alloys and between 650 and 750 degrees Celsius (1200 and 1380 degrees Fahrenheit) for zinc alloys. The high pressure used in die casting allows for the rapid solidification of the metal. It is important to note that these temperature ranges can vary depending on the specific alloys being used and the size and complexity of the casting. Additionally, different metal casting machinery may have specific temperature requirements that need to be followed for optimal performance and quality of the castings.
- Q:What are the different types of casting defects that can occur in die casting?
- There are several types of casting defects that can occur in die casting. These defects can be classified into three main categories: surface defects, internal defects, and dimensional defects. 1. Surface defects: These defects occur on the surface of the cast part and can affect its appearance and functionality. Some common surface defects in die casting include: - Porosity: This defect occurs when gas trapped in the molten metal forms bubbles during solidification, resulting in small holes or voids on the surface. - Flash: Flash is an excess material that is squeezed out between the two halves of the die. It appears as a thin metal layer on the edges of the cast part. - Cold shuts: Cold shuts happen when the molten metal solidifies before completely filling the mold cavity, resulting in a lack of fusion between two adjacent metal flows. This defect appears as a line or crack on the surface. - Shrinkage: Shrinkage defects occur when the molten metal contracts during solidification, leading to small depressions or cavities on the surface. 2. Internal defects: These defects occur within the cast part and are not visible on the surface. Some common internal defects in die casting include: - Inclusions: Inclusions are non-metallic materials, such as oxides or foreign particles, that get trapped within the metal during the casting process. They can weaken the structural integrity of the part. - Hot spots: Hot spots occur when the molten metal solidifies unevenly, resulting in areas with higher porosity or shrinkage. - Misruns: Misruns happen when the molten metal fails to fill the entire mold cavity, leaving unfinished areas within the part. This defect is typically caused by insufficient injection pressure or improper gating design. 3. Dimensional defects: These defects affect the overall dimensions and tolerances of the cast part. Some common dimensional defects in die casting include: - Warpage: Warpage occurs when the cast part distorts or bends after cooling. It can be caused by uneven cooling or insufficient support during solidification. - Oversized or undersized features: These defects occur when the cast part does not meet the required dimensions or tolerances. They can be caused by factors such as improper die design or inaccurate machining processes. Overall, preventing and minimizing these casting defects requires careful design, proper process control, and regular inspection and quality control measures during the die casting process.
- Q:How does metal casting machinery handle the removal of excess material from investment castings?
- Metal casting machinery typically handles the removal of excess material from investment castings through various processes such as grinding, sandblasting, or using automated cutting tools. These methods help to precisely remove the excess material and achieve the desired final shape and dimensions of the castings.
- Q:How does automation impact metal casting machinery?
- Automation has had a significant impact on metal casting machinery, revolutionizing the efficiency and productivity of the process. With the integration of automation technologies, metal casting machinery has become more streamlined, reliable, and accurate. One of the key advantages of automation in metal casting machinery is the reduction in labor requirements. Automation allows for the automation of repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, such as material handling, mold preparation, and casting finishing. This results in a significant decrease in human error, increased precision, and improved overall quality of the castings produced. Furthermore, automation enables metal casting machinery to operate at higher speeds and with greater consistency. Automated systems are capable of consistently maintaining precise operating parameters, such as temperature and pressure, ensuring the production of consistent and high-quality castings. This level of consistency is difficult to achieve with manual operations, as it is subject to human error and variability. Automation also enables metal casting machinery to operate continuously, reducing downtime and maximizing production efficiency. Automated systems can be programmed to run 24/7, allowing for round-the-clock production and reduced lead times. This not only increases productivity but also enhances the overall competitiveness of metal casting manufacturers in the market. Moreover, automation has also enabled the integration of advanced technologies into metal casting machinery. For example, robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) have been employed to enhance the precision and speed of metal casting processes. Robots can perform complex tasks with high accuracy, such as pouring molten metal into molds or removing finished castings from the machine. AI algorithms can analyze and optimize the casting process, improving efficiency and reducing material waste. Overall, automation has transformed metal casting machinery, making it more efficient, reliable, and precise. It has reduced labor requirements, increased production speed and consistency, and allowed for the integration of advanced technologies. As a result, metal casting manufacturers can achieve higher productivity, improved quality, and enhanced competitiveness in the industry.
- Q:How does metal casting machinery control the temperature and flow of the molten metal?
- Metal casting machinery controls the temperature and flow of the molten metal through various mechanisms and features. One of the key components is the furnace, which is responsible for heating the metal to its desired temperature. The furnace typically consists of a combustion chamber, burners, and a control system. The control system monitors and adjusts the fuel and air supply to maintain a consistent temperature within the furnace. Once the molten metal reaches the desired temperature, it is then transferred to a crucible or ladle, which acts as a reservoir for the molten metal. The crucible or ladle is equipped with heating elements or refractory materials to maintain the temperature of the molten metal during transfer and casting processes. To control the flow of the molten metal, metal casting machinery uses a variety of methods. One commonly used technique is gravity pouring, where the metal is poured into the mold using the force of gravity. In this case, the height and angle at which the crucible or ladle is positioned can be adjusted to control the flow rate. In more advanced systems, mechanical devices such as pumps or pouring robots are employed to control the flow of the molten metal. These devices are usually equipped with sensors and actuators that allow precise control over the speed and direction of the metal flow. The control system can regulate the flow rate based on the specific requirements of the casting process. Furthermore, temperature control during the casting process is crucial to ensure the quality and integrity of the final product. Metal casting machinery utilizes cooling systems, such as water-cooled molds or cooling channels, to regulate the temperature of the mold. This helps in solidifying the molten metal at the desired rate and preventing defects like shrinkage or porosity. In summary, metal casting machinery controls the temperature and flow of the molten metal through various mechanisms like heating systems, gravity pouring, mechanical devices, and cooling systems. These features work together to achieve precise and consistent control over the casting process, resulting in high-quality metal castings.
- Q:Can metal casting machinery be used for investment casting of aluminum alloys?
- Yes, metal casting machinery can be used for investment casting of aluminum alloys. Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is a versatile process that allows for the production of intricate and complex aluminum alloy parts. Metal casting machinery, such as induction furnaces and centrifugal casting machines, can be used to melt and pour the molten aluminum into ceramic molds, ensuring accurate and precise castings.
- Q:What are the different types of air pollution control measures used in metal casting machinery?
- There are several different types of air pollution control measures that are commonly used in metal casting machinery to minimize the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. These measures are crucial for ensuring the health and safety of workers and the surrounding environment. 1. Ventilation Systems: One of the most basic control measures used in metal casting machinery is the installation of ventilation systems. These systems help in capturing and removing dust, fumes, and gases generated during the casting process. They typically consist of exhaust hoods, ductwork, and fans that transport the pollutants away from the workspace. 2. Filtration Systems: Filtration systems play a vital role in removing particulate matter from the air. These systems use filters to trap and collect dust and other solid particles emitted during metal casting. Various types of filters, such as bag filters, cartridge filters, and electrostatic precipitators, are commonly used for this purpose. 3. Scrubbers: Scrubbers are air pollution control devices that remove harmful gases and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from the exhaust stream. They work by passing the contaminated air through a liquid solution or bed of materials, which chemically reacts with and absorbs the pollutants. Wet scrubbers, dry scrubbers, and biofilters are some of the commonly used scrubbing systems in metal casting machinery. 4. Emission Control Technologies: Advanced emission control technologies, such as catalytic converters and oxidation systems, are employed in metal casting machinery to reduce the release of toxic substances like carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). These devices use chemical reactions to convert harmful gases into less harmful or inert compounds before being released into the atmosphere. 5. Process Modifications: Certain process modifications can also help in minimizing air pollution from metal casting machinery. For instance, implementing cleaner production techniques, optimizing furnace design, and using low-emission fuels can significantly reduce the amount of pollutants generated during the casting process. It is important to note that the selection and effectiveness of air pollution control measures depend on various factors, including the type of metal being cast, the size of the facility, and the specific pollutants being emitted. Therefore, it is crucial for metal casting companies to conduct regular emissions monitoring and assessments to ensure that the chosen control measures are effective in reducing air pollution.
- Q:What are the common gating systems used with metal casting machinery?
- Metal casting machinery utilizes various gating systems to control the flow of molten metal into the mold cavity, ensuring defect-free filling. The following are commonly employed gating systems: 1. Sprue: Serving as the primary channel, the sprue enables the pouring of molten metal into the mold. It typically connects the pouring basin or ladle to the runner system. The sprue effectively directs the metal flow and minimizes turbulence during casting. 2. Runner: A horizontal channel links the sprue to individual mold cavities, distributing the molten metal evenly for consistent filling in multiple cavity molds. The dimensions and configuration of the runner depend on the casting design and metal type. 3. In-gate: This narrow channel connects the runner to the mold cavity, regulating the flow of metal and preventing defects like turbulence, air entrapment, and shrinkage. 4. Riser: Also known as a feed or reservoir, the riser is a separate cavity connected to the mold cavity. It provides additional molten metal to compensate for shrinkage during solidification, ensuring a defect-free casting without porosity. 5. Vents: These small channels or openings in the mold allow gases and air to escape during mold cavity filling. They prevent the formation of air pockets and promote a smooth flow of molten metal. Vents are typically located at the highest points in the mold cavity or along the parting line. The selection and optimization of these gating systems are done meticulously, considering specific casting requirements. Factors such as casting size, shape, metal type, and desired product quality influence the choice of the most suitable gating system.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Section Steel Roll From China With High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 41000 m.t./month
- Option:
- 650X1780X5540; 650X1780X5540; 680X2080X5920
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products

































