Photovoltaic On-Grid Connected Inverter SG20KTL
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 500000 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1. Structure of Solar Photovoltaic On-Grid Connected Inverter SG20KTL Description
A solar inverter, or PV inverter, or Solar converter, converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic (PV) solar panel into
autility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercial electrical grid or used by a local, off-grid electrical network.
It is acritical BOS–component in a photovoltaic system, allowing the use of ordinary AC-powered equipment. Solar inverters have
special functions adapted for use with photovoltaic arrays, including maximum power point tracking and anti-islanding protection.
Suitable for 50Hz/60Hz grid, could be used in Asia, Africa and Europe. Available for hand installation, no need for lifting machinery
assistance.
2. Main Features of the Photovoltaic On-Grid Connected Inverter SG20KTL
• Full 20 kW effective power at power factor of 0.9 due to apparent power reserves up to 22.2 kVA
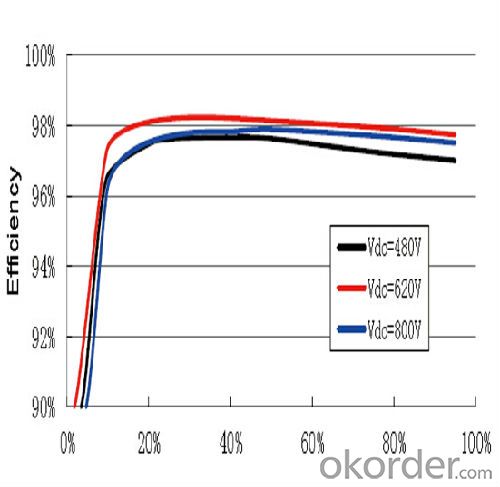
• Photon test results "very good", with a maximum efficiency of 98% (Photon Profi 2-2012)
• Dual MPP trackers control
• Active power continuously adjustable (0~100%)
•Reactive power control with power factor 0.8 overexcited ~ 0.8 underexcited
•Includes RS-485 interface, compatible with all common monitoring systems
• Product certification: TÜV, CE, CEI 0-21, G59/2, AS4777, BDEW, VDE AR-N-4105, CGC, compliance with Italian medium voltage grid requirement
• Manufacturer certification: ISO 9001, ISO 14001, OHSAS 18000
3. Photovoltaic On-Grid Connected Inverter SG20KTL Images

4. Photovoltaic On-Grid Connected Inverter SG20KTL Specification
Input Side Data | |
Max. PV input power | 21000W(10500W/10500W) |
Max. PV input voltage | 1000V |
Startup voltage | 300V |
Nominal input voltage | 620V |
MPP voltage range | 280~950V |
MPP voltage range for nominal power | 480~800V |
No. of MPPTs | 2 |
Max. number of PV strings per MPPT | 3 |
Max. PV input current | 42A(21A/21A) |
Max. current for input connector | 12A |
Output Side Data | |
Nominal AC output power | 20000W |
Max AC output power(PF=1) | 22200W |
Max. AC output apparent power | 22200VA |
Max. AC output current | 33A |
Nominal AC voltage | 3/N/PE, 230/400Vac |
AC voltage range | 310~480Vac |
Nominal grid frequency | 50Hz/60Hz |
Grid frequency range | 47~53Hz/57~63Hz |
THD | < 3 % (Nominal power) |
DC current injection | <0.5 %In |
Power factor | >0.99@default value at nominal power |
(adj. 0.8overexcited ~0.8underexited ) | |
Protection | |
Anti-islanding protection | Yes |
LVRT | Yes |
DC reverse connection protection | Yes |
AC short circuit protection | Yes |
Leakage current protection | Yes |
DC switch | Yes |
DC fuse | No |
Overvoltage protection | Varistors |
System Data | |
Max. efficiency | 98.00% |
Max. European efficiency | 97.30% |
Isolation method | Transformerless |
Ingress protection rating | IP65 |
Night power consumption | <1W |
Operating ambient temperature range | -25~60℃(>45℃ derating) |
Allowable relative humidity range | 0~100% |
Cooling method | Smart forced air cooling |
Max. operating altitude | 4000m (>3000m derating) |
Display | Graphic LCD |
Communication | RS485(RJ45 connector) |
DC connection type | MC4 |
AC connection type | Plug and play connector |
Certification | EN62109-1, EN62109-2, EN61000-6-2,EN61000-6-3, VDE0126-1-1, |
CEI 0-21, AS/NZS3100, AS4777.2, AS4777.3, | |
VDE-AR-N-4105, BDEW, CGC | |
Mechanical Data | |
Dimensions(W×H×D) | 648×686×246mm |
Mounting method | Wall bracket |
Weight | 55kg |
5. FAQ of Photovoltaic On-Grid Connected Inverter SG20KTL
Q1. What is the difference between inverter and solar inverter?
A1. Inverter only has AC inpput, but solar inverter both connect to AC input and solar panel, it saves more power.
Q2. What is the difference between MPPT&PWM?
A2. MPPT has higher efficiency, it can track the max power point and won't waste energy.
- Q:Can a solar inverter be used with different types of tracking algorithms?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with different types of tracking algorithms. The inverter is designed to convert the DC power generated by solar panels into usable AC power for various applications. The tracking algorithm, on the other hand, is responsible for optimizing the solar panel's orientation to maximize energy production. Different tracking algorithms like fixed tilt, single-axis, or dual-axis can be employed with the solar inverter to enhance energy harvesting based on factors such as sun's position, time of day, and weather conditions.
- Q:Can a solar inverter be used in systems with different module orientations?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in systems with different module orientations. Solar inverters are designed to convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) for use in homes or businesses. They are compatible with various module orientations, including those that are east-west or south-facing. The inverter's maximum power point tracking (MPPT) technology allows it to optimize energy production regardless of the module orientation, ensuring efficient utilization of solar energy.
- Q:Can a solar inverter be connected to a smart home or monitoring system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be connected to a smart home or monitoring system. This integration allows for real-time monitoring, remote control, and data analysis of the solar energy production and consumption within a smart home or monitoring system.
- Q:Can a solar inverter be used in standalone power systems?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in standalone power systems. Standalone power systems, also known as off-grid systems, are not connected to the traditional electrical grid. In such systems, solar inverters convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power various electrical devices and appliances. The solar inverter is an essential component in standalone power systems as it enables the efficient utilization of solar energy for off-grid applications.
- Q:How does a solar inverter handle voltage regulation?
- A solar inverter handles voltage regulation by converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that is suitable for use in our homes and businesses. It ensures that the voltage produced by the solar panels matches the voltage requirements of the electrical grid or the appliances connected to it. This is achieved through advanced electronics that monitor and adjust the voltage levels to maintain stability and efficiency in the power generation process.
- Q:What is the role of a maximum power point tracker (MPPT) in a solar inverter?
- In a solar inverter, the maximum power point tracker (MPPT) plays a crucial role in optimizing the efficiency and power output of the solar panel system. Since solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity while most appliances and the electrical grid operate on alternating current (AC), the MPPT continuously adjusts the operating conditions of the solar panels to extract the maximum power available from sunlight. The MPPT tracks the maximum power point (MPP) at which the solar panels can efficiently generate the most electricity. This is vital because the output of a solar panel depends significantly on factors like temperature, shading, and the angle of the sun. To ensure maximum power output, the MPPT continuously monitors and adjusts the voltage and current of the solar panel system, keeping it at the MPP. It achieves this by dynamically altering the electrical load on the solar panels to find the optimal operating point. Additionally, the MPPT acts as a converter, transforming the DC power generated by the solar panels into the AC power required for appliances or for feeding back into the electrical grid. This conversion process involves adjusting the voltage and frequency of the electricity to match the requirements of the appliances or the grid. In summary, the primary function of a maximum power point tracker in a solar inverter is to optimize the efficiency and power output of the solar panel system, ensuring the extraction of the maximum amount of energy from sunlight and its effective utilization for various applications.
- Q:What is the role of a power backup system in a solar inverter?
- The role of a power backup system in a solar inverter is to provide a reliable source of electricity during periods of insufficient sunlight or power grid outages. It ensures uninterrupted power supply to critical loads, such as essential appliances or equipment, by utilizing stored energy from batteries or alternative power sources. This backup system enhances the overall reliability and functionality of the solar inverter, making it more suitable for both grid-tied and off-grid applications.
- Q:Can a solar inverter be used in off-grid systems?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in off-grid systems. In off-grid systems, solar inverters are essential as they convert the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power appliances and devices. They also play a crucial role in managing the battery storage and regulating energy flow in off-grid setups.
- Q:What are the safety features of a solar inverter?
- The safety features of a solar inverter typically include surge protection, overvoltage protection, short circuit protection, ground fault detection, and overtemperature protection. These features help to prevent damage to the inverter and the electrical system, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
- Q:How does the total harmonic distortion affect the performance of a solar inverter?
- The total harmonic distortion (THD) can significantly impact the performance of a solar inverter. Higher levels of THD can cause electrical noise, which can interfere with the operation of sensitive equipment connected to the inverter. This can result in reduced efficiency, increased heat generation, and potential damage to the connected devices. Additionally, high THD can also lead to power quality issues, such as voltage and current distortions, which can further degrade the performance of the solar inverter and its associated components. Therefore, it is crucial to minimize THD to ensure optimal performance and reliability of the solar inverter system.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Photovoltaic On-Grid Connected Inverter SG20KTL
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 500000 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 3000000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































