Mould Powders / Continuous Casting Powders and Granules For Steel Mill
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
The Mould Powders are composed essentially of CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 with addition of fluxing agents and carbon.
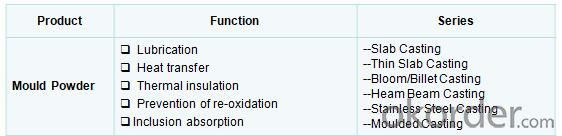
Mold Powders have different functions:
Lubrication between the solidifying strand and mould wall
Control of heat transfer between the strand and mould
Thermal insulation of the liquid steel surface
Prevention of re-oxidation
Inclusion absorption
The above functions are controlled by the following properties:
Basicity
Viscosity
Melting speed
Melting behaviour
Crystallization
The choice of a mould powder depends on:
Mould size
Oscillation conditions
Casting speed
Steel grade
Technical Data:
FAQ
Q:Are you a trading company or manufacturer?
A:CNBM is a large-scale central governmental industrial group with its own manufacturing sector, research and development sector, trading sector and logistics sector.
Q:I have some special requirement about specifications.
A:We have a well-rounded product range, which endows us with the capability of applying many special specifications. Please feel free to contact us with yours.
Q:Do you accept OEM service?
A:Yes, we do.
Q:What is your delivery time?
A:It depends on the size/complexity of your order and our own production schedule. Usually we provide a faster delivery than the industry's average.
Q:What is the payment term?
A:Our payment terms are negotiable.
Q:Can I have my own logo on the product?
A:Sure, we can apply your own logo on the products according to your drawings.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories have a crucial role in enhancing the performance of ladles and tundishes in multiple ways. To begin with, their high thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock are well-known. When ladles and tundishes are subjected to extreme temperatures and thermal cycling during the transfer of molten metal, monolithic refractories provide exceptional insulation and structural integrity. This ensures that the ladles and tundishes can endure these harsh conditions without suffering from cracks or failures. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer outstanding resistance to corrosion. In the environments of ladles and tundishes, the presence of molten metal, slag, and other chemicals can lead to corrosion and erosion of the lining. However, monolithic refractories are specifically designed to resist these corrosive agents, extending the lifespan of ladles and tundishes and reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Another advantage of monolithic refractories lies in their ability to form a seamless and tight lining. Unlike traditional brick or tile linings, which can deteriorate over time due to joints, monolithic refractories are typically applied as a single, continuous layer. This seamless lining significantly reduces the risk of metal and slag penetration, ensuring better containment of the molten metal and preventing contamination. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer versatility and ease of installation. They can be easily shaped and applied to various complex geometries, allowing for customized linings in ladles and tundishes. This versatility also enables faster installation and reduces downtime during maintenance and repairs. In conclusion, the utilization of monolithic refractories in ladles and tundishes leads to improved performance, increased operational efficiency, and reduced costs. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures, resist corrosion, provide a tight lining, and offer ease of installation makes them the preferred choice in the steel and foundry industries.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories protect lining in ladles and tundishes?
- Monolithic refractories protect lining in ladles and tundishes by forming a strong and durable barrier against the harsh conditions of high temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion. They are designed to withstand the extreme heat and mechanical stresses that occur during metal pouring and handling, ensuring the integrity and longevity of the lining. Additionally, monolithic refractories provide excellent insulation properties, reducing heat loss and conserving energy in the ladles and tundishes.
- Q:Can monolithic refractories be used for the lining of blast furnace runners and troughs?
- Yes, blast furnace runners and troughs can have their lining done with monolithic refractories. Monolithic refractories, unlike traditional refractory bricks that are made by assembling individual units, are composed of a single, homogeneous structure. There are several advantages to using monolithic refractories for lining blast furnace runners and troughs. Firstly, they exhibit excellent thermal shock resistance, which is vital in this application given the extreme temperature fluctuations the lining is exposed to. Additionally, monolithic refractories have a good resistance to chemical attack from the molten metal and slag, which helps prolong the lining's lifespan in the harsh working environment of blast furnaces. Moreover, monolithic refractories can be easily installed in intricate shapes and structures, allowing for greater flexibility in designing the lining of blast furnace runners and troughs. This ease of installation also results in reduced downtime during maintenance and repair, as monolithic refractories can be applied quickly and efficiently. To summarize, monolithic refractories are a suitable option for lining blast furnace runners and troughs due to their thermal shock resistance, chemical resistance, and easy installation. Their use can contribute to improving the longevity and performance of these critical components in blast furnace operations.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories contribute to reducing emissions in iron and steel processes?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing emissions in iron and steel processes by providing superior insulation, increased energy efficiency, and improved control over the production process. These refractories are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh conditions, effectively minimizing heat loss and reducing the need for excessive fuel consumption. By creating a highly insulated environment, monolithic refractories enable better temperature control, leading to optimized combustion and reduced emissions of greenhouse gases. Additionally, their high resistance to wear and corrosion helps prevent the formation of pollutants, thereby contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable iron and steel industry.
- Q:What are the key properties of patching mixes used for monolithic refractory repairs?
- The key properties required for patching mixes used in the repair of monolithic refractories include: 1. High temperature resistance: The patching mixes should have the ability to withstand high temperatures without compromising their structural integrity. They must be capable of enduring temperatures ranging from 2000 to 3000 degrees Fahrenheit. 2. Chemical resistance: These patching mixes should be resistant to chemical reactions that occur in the presence of molten metals, slag, or other corrosive substances. They should not deteriorate or react with these materials, ensuring the longevity of the repaired refractory. 3. Thermal shock resistance: The patching mixes must have the ability to withstand sudden and extreme temperature changes without cracking or spalling. Refractory linings are often subjected to intense thermal cycling, and the patching material should be able to endure these conditions without failure. 4. Adhesion: The patching mixes should possess excellent adhesion properties to create a strong bond with the existing refractory material. This is crucial to prevent any separation or detachment of the patching material, which could result in further damage or failure. 5. Workability: The patching mixes should have good workability, allowing for easy and efficient application. They should be easily moldable and capable of effectively filling cracks, gaps, or damaged areas. 6. Setting and curing time: The patching mixes should have a reasonable setting and curing time. They should be able to harden quickly to minimize downtime during repairs, while also providing sufficient time for proper application and shaping. 7. Density and porosity: The patching material should have an appropriate density and porosity to resist penetration by molten metal or slag. Low porosity ensures that the repaired refractory maintains its thermal insulation properties. 8. Mechanical strength: The patching mixes should exhibit adequate mechanical strength to withstand physical stresses, such as abrasion or impact, that may occur during operation. 9. Compatibility: It is important that the patching mixes are compatible with the existing refractory material to ensure a seamless integration and prevent any potential chemical reactions or incompatibilities that could compromise the repair. By considering these key properties, patching mixes used for monolithic refractory repairs can effectively restore the integrity and performance of refractory linings, prolonging their lifespan and ensuring efficient and safe operation in high-temperature environments.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories perform in rotary kiln applications?
- Monolithic refractories perform exceptionally well in rotary kiln applications due to their high thermal shock resistance, excellent chemical resistance, and superior strength at high temperatures. Their ability to withstand extreme heat and harsh chemical environments makes them ideal for lining the interior of rotary kilns. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and maintenance, ensuring efficient and reliable kiln operations.
- Q:What are the recent developments in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry?
- In recent years, there have been several significant developments in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry. Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in the production of iron and steel, as they provide high-temperature resistance and insulation to the lining of furnaces and other equipment used in the industry. One of the key advancements in monolithic refractories is the development of advanced alumina-based castables. These castables offer superior thermal shock resistance, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for use in the iron and steel industry. They can withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stresses, ensuring longer service life and reduced downtime for maintenance. Another notable development is the introduction of low-cement and ultra-low cement castables. These castables have a reduced cement content compared to traditional castables, resulting in improved refractory properties. They offer higher hot strength, reduced porosity, and enhanced resistance to slag and metal corrosion. This allows for increased productivity and efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing processes. Furthermore, there have been advancements in the use of insulating refractories in the iron and steel industry. Insulating castables and bricks are now being used to line ladles, tundishes, and other equipment, providing better insulation and energy efficiency. These materials help to reduce heat loss and improve thermal efficiency, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Additionally, the development of monolithic refractories with improved installation techniques has been a significant development. Traditional brick lining methods require skilled labor and a longer installation time. However, with the introduction of gunning and shotcreting techniques, the installation process has become faster and more efficient. These techniques involve spraying refractory materials onto the lining surface, ensuring better adherence and reducing the risk of lining failure. Overall, the recent developments in monolithic refractories for the iron and steel industry have focused on improving thermal shock resistance, corrosion resistance, insulation properties, and installation techniques. These advancements have resulted in increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved productivity in the iron and steel manufacturing processes.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories help in improving the quality of iron and steel products?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in improving the quality of iron and steel products in several ways. Firstly, these refractories are used to line the furnaces and other high-temperature equipment in the iron and steel industry. By providing a high level of thermal insulation, monolithic refractories help maintain a consistent and controlled temperature inside the furnace, ensuring efficient heating and melting of metals. The use of monolithic refractories also helps in reducing heat loss, thereby increasing the energy efficiency of the process. This not only saves costs but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with high energy consumption. Additionally, the insulation properties of monolithic refractories contribute to the reduction of thermal stresses within the furnace, preventing cracks and other structural damages that can affect the quality of the iron and steel products. Moreover, monolithic refractories possess excellent resistance to chemical reactions, corrosion, and erosion caused by molten metals, slag, and other harsh substances. This resistance helps to maintain the integrity of the refractory lining, preventing contamination of the iron and steel products by unwanted impurities. As a result, the quality of the final products, such as steel bars, sheets, or pipes, is improved, meeting the desired specifications and industry standards. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to provide a smooth and clean lining surface. This smoothness minimizes the adherence of slag, molten metal, and other by-products, reducing the risk of defects and ensuring a higher-quality finish for the iron and steel products. The clean lining surface also facilitates easy maintenance and cleaning, allowing for efficient and effective operations. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute significantly to the improvement of iron and steel product quality through their exceptional thermal insulation, resistance to chemical reactions, erosion, and corrosion, as well as their ability to provide a smooth and clean lining surface. By ensuring consistent temperatures, reducing heat loss, preventing structural damages, and maintaining a clean environment, monolithic refractories enhance the overall efficiency and integrity of the iron and steel production process, resulting in high-quality end products.
- Q:What are the different types of monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry?
- In the iron and steel industry, several types of monolithic refractories are used due to their excellent thermal resistance, high strength, and durability. These refractories are essential in various applications to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh conditions. The different types of monolithic refractories commonly used in the iron and steel industry include: 1. Castables: These are precast refractory materials that are mixed with water to form a slurry, which is then poured or cast into molds. Castables are widely used in iron and steel industries for lining ladles, tundishes, and other furnaces due to their high strength and excellent resistance to thermal shock. 2. Ramming Mass: Ramming mass is a refractory material that is used for lining induction furnaces and other melting units. It is made up of refractory aggregates, binders, and additives. Ramming mass is applied by ramming or tamping it into place, forming a dense lining that can withstand high temperatures and chemical attacks. 3. Gunning Mix: Gunning mix is a refractory material that is applied using a pneumatic gunning machine. It is used for repairing or lining various areas of furnaces and is particularly useful for hot repairs. Gunning mix consists of refractory aggregates, binders, and additives, which are sprayed onto the lining surface and then compacted. 4. Plastic Refractories: Plastic refractories are mixtures of refractory aggregates and binders that have a high plasticity and can be easily molded or shaped. They are used for repairing or patching refractory linings in iron and steel industries. Plastic refractories are typically applied by hand or using a trowel and are suitable for both hot and cold applications. 5. Mortars: Refractory mortars are used for jointing or repairing refractory bricks or other monolithic refractories. They are made up of refractory powders, binders, and water. Mortars provide excellent adhesion between bricks or monolithic materials, ensuring a strong and durable lining in furnaces, ladles, and other high-temperature equipment. These different types of monolithic refractories play a vital role in the iron and steel industry by providing reliable and long-lasting linings, ensuring efficient operations and minimizing downtime.
- Q:How are monolithic refractories recycled or disposed of at the end of their lifespan?
- Monolithic refractories at the end of their lifespan are typically recycled or disposed of through various methods. Recycling involves collecting the used refractory materials and processing them to remove any contaminants. The processed refractories can then be used as raw materials in the production of new refractory products. Disposal methods include landfilling in designated areas or utilizing waste-to-energy facilities to convert the refractories into energy. The choice between recycling and disposal depends on factors such as the condition of the refractories and the availability of recycling facilities in the area.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Mould Powders / Continuous Casting Powders and Granules For Steel Mill
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords






























