Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
General Information of Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
FIREF alumina spinel castable for ladle and tundish made as per international standards, is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, long operating life and high refractoriness. Further, it can be provided in different specifications as required.
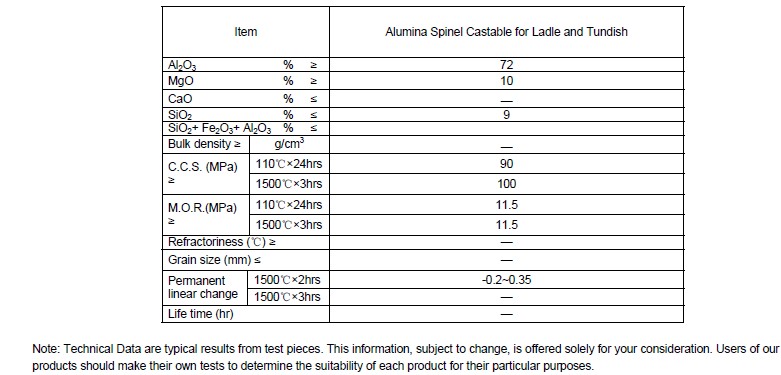
Technical data of Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
Production line and packing of Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish


Feature of Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
Long operating life
Excellent corrosion resistance
High refractoriness
Application of Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
FIREF alumina spinel castable for ladle and tundish can be used widely in ladle and tundish.
- Q:What are monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories, in contrast to individual bricks or precast shapes, are refractory materials that are manufactured as a single unit. They can be shaped and installed without the need for joints or mortar, making them convenient for lining furnaces, boilers, kilns, and other high-temperature industrial equipment. These refractories consist of a carefully selected mixture of refractory aggregates, binders, and additives. This combination provides desired properties such as high temperature resistance, thermal shock resistance, and chemical durability. Aggregates like alumina, magnesia, zirconia, and silica are used, while binders such as clay, cement, or phosphate hold the aggregates together. One advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to adapt to complex shapes and designs, allowing for customized linings that meet specific equipment requirements. They can be applied through pouring, gunning, ramming, or spraying onto the surface to be lined, leading to quick and efficient installation. This eliminates the need for time-consuming bricklaying and jointing, reducing installation time and labor costs. Monolithic refractories also possess superior thermal conductivity, enabling them to withstand high temperatures and sudden temperature changes. They offer excellent insulation properties, preventing heat loss and improving energy efficiency in industrial processes. Additionally, these refractories exhibit good resistance to chemical attack from molten metals, slags, gases, and other corrosive substances found in various industrial environments. This makes them highly suitable for applications in steel, cement, glass, petrochemical, and non-ferrous metals industries. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are a versatile and efficient solution for high-temperature applications. Their ability to be shaped and installed without joints or mortar, combined with their excellent thermal conductivity and chemical resistance, make them a valuable choice for lining industrial equipment operating under extreme conditions.
- Q:What are the advantages of using insulating castables in the iron and steel industry?
- There are several advantages of using insulating castables in the iron and steel industry. Firstly, insulating castables provide excellent thermal insulation. They have low thermal conductivity, which helps to minimize heat loss from the furnaces and other equipment. This is particularly important in the iron and steel industry, where high temperatures are required for various processes. The insulation provided by castables helps to maintain a stable temperature within the furnace, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced fuel consumption. Secondly, insulating castables have high strength and excellent resistance to thermal shock. This is crucial in the iron and steel industry, where extreme temperature changes are common. The castables can withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or compromising their structural integrity. This ensures the longevity and durability of the refractory lining, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and repairs. Furthermore, insulating castables are lightweight and easy to install. Their low density makes them easier to handle and transport, resulting in reduced labor costs and shorter installation times. This is particularly advantageous in large-scale iron and steel plants, where time and cost efficiency are critical. Moreover, insulating castables offer good corrosion resistance. The harsh environment in the iron and steel industry, with the presence of molten metal, slag, and various chemicals, can cause corrosion and erosion of refractory materials. Insulating castables are designed to withstand these corrosive conditions, ensuring the longevity of the lining and minimizing the risk of downtime and production disruptions. Lastly, insulating castables are versatile and can be customized to meet specific requirements. They are available in various compositions and densities, allowing for tailored solutions to different applications within the iron and steel industry. This versatility ensures optimal performance and efficiency in various furnace and equipment designs. In conclusion, the advantages of using insulating castables in the iron and steel industry include excellent thermal insulation, high strength, resistance to thermal shock, lightweight installation, corrosion resistance, and versatility. These benefits contribute to improved energy efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, increased durability, and enhanced overall productivity in the industry.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories withstand high temperatures in iron and steel processing?
- Due to their unique composition and design, monolithic refractories have the capability to endure high temperatures in iron and steel processing. Unlike refractories composed of multiple layers, these refractories are made from a single, solid material, which grants them superior thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock. One crucial factor that enables monolithic refractories to withstand high temperatures is their high melting point. Typically composed of materials like alumina, magnesia, silica, or zirconia, these refractories possess melting points that exceed the temperatures encountered in iron and steel processing. This ensures that the refractories do not deteriorate or melt when exposed to such extreme temperatures. Additionally, monolithic refractories exhibit excellent thermal insulation properties. With low thermal conductivity, they effectively impede heat transfer from the hot molten metal or gases to the surrounding environment. This insulation property helps sustain high temperatures within the processing units, ensuring efficient and effective iron and steel production. Another significant aspect contributing to the ability of monolithic refractories to withstand high temperatures is their resistance to thermal shock. In iron and steel processing, rapid temperature changes are frequent, which can lead to cracking or spalling in traditional refractories. However, monolithic refractories possess a more homogeneous structure and greater flexibility, enabling them to endure these sudden temperature fluctuations without significant damage. Apart from their composition, the installation method of monolithic refractories also plays a role in their ability to withstand high temperatures. Typically, these refractories are installed using a technique called gunning or shotcreting, where a mixture of refractory material and water is sprayed onto the surface, forming a dense and solid lining. This installation method ensures a strong bond between the refractory and the substrate, enhancing the overall strength and durability of the lining. Overall, monolithic refractories can withstand high temperatures in iron and steel processing due to their high melting point, excellent thermal insulation properties, resistance to thermal shock, and proper installation techniques. These refractories are essential in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of the processing units, facilitating the production of high-quality iron and steel products.
- Q:What are the common manufacturing processes used for monolithic refractories?
- The common manufacturing processes used for monolithic refractories include: 1. Mixing: The first step in the manufacturing process is the proper mixing of the raw materials. This involves carefully measuring and combining the different ingredients to ensure a homogeneous mixture. 2. Wetting: Once the ingredients are mixed, water or a liquid binder is added to wet the mixture. This helps in improving the workability and plasticity of the material, making it easier to shape and mold. 3. Forming: The wet mixture is then shaped into the desired form using various techniques such as casting, gunning, ramming, or extrusion. Casting involves pouring the wet mixture into a mold and allowing it to solidify, while gunning uses a spray gun to apply the material onto a surface. Ramming involves compacting the wet mixture into a mold using a ramming tool, and extrusion involves forcing the wet mixture through a die to create specific shapes. 4. Drying: After forming, the shaped monolithic refractory is dried to remove any excess moisture. This is typically done in a controlled environment with specific temperature and humidity conditions to prevent cracking or warping. 5. Firing: Once dried, the monolithic refractory is fired at high temperatures to achieve its desired properties. This process, known as sintering, helps in bonding the particles together and increasing the strength and stability of the material. 6. Finishing: After firing, the monolithic refractory may undergo additional finishing processes such as grinding, polishing, or coating to improve its surface quality and enhance its performance. These common manufacturing processes ensure the production of high-quality monolithic refractories with consistent properties and performance characteristics.
- Q:What are the advantages of using self-flow castables in the iron and steel industry?
- There are several advantages of using self-flow castables in the iron and steel industry. Firstly, self-flow castables offer excellent flowability, which means they can easily fill complex shapes and intricate molds. This allows for greater design flexibility and the ability to create more intricate and precise components. Additionally, the high flowability ensures that there are no gaps or voids in the casting, resulting in a higher quality product with improved mechanical properties. Secondly, self-flow castables have a high degree of homogeneity. This means that the composition of the castable is evenly distributed, resulting in consistent properties throughout the casting. This is particularly important for the iron and steel industry, where uniformity is crucial for achieving desired performance characteristics. Moreover, self-flow castables have a low water demand, which leads to reduced drying and curing times. This is beneficial in terms of production efficiency, as it allows for faster casting cycles and shorter overall production times. Additionally, the reduced water demand also leads to lower drying shrinkage, minimizing the risk of cracking or distortion during the curing process. Another advantage of using self-flow castables is their excellent thermal shock resistance. This is particularly important in the iron and steel industry, where materials are subjected to extreme temperatures. Self-flow castables have the ability to withstand rapid and drastic temperature changes without cracking, which ensures the longevity and durability of the cast components. Furthermore, self-flow castables have good abrasion resistance, which is essential in applications where the castings are exposed to abrasive materials or environments. The high resistance to wear and tear ensures a longer service life and reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements. In conclusion, the advantages of using self-flow castables in the iron and steel industry include excellent flowability, high homogeneity, low water demand, good thermal shock resistance, and strong abrasion resistance. These benefits contribute to improved casting quality, increased production efficiency, enhanced durability, and reduced maintenance costs.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories perform in blast furnace taphole applications?
- Monolithic refractories perform excellently in blast furnace taphole applications due to their high thermal resistance, mechanical strength, and resistance to chemical attack. They are able to withstand the extreme temperatures and abrasive conditions of the blast furnace discharge, ensuring reliable and efficient operation of the taphole. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and maintenance, reducing downtime and improving overall productivity in the blast furnace.
- Q:In iron and steel industry, the main raw materials for blast furnace ironmaking are iron ore, coke and limestone. What's the use of limestone here?
- At high temperatures, limestone (calcium carbonate) breaks down into lime (calcium oxide, which is useful) and carbon dioxide.
- Q:What are the factors affecting the lifespan of monolithic refractories?
- There are several factors that can affect the lifespan of monolithic refractories. These include the type of material used in the refractory, the operating conditions such as temperature and pressure, the presence of corrosive or abrasive substances, the frequency and intensity of thermal cycling, and the quality of installation and maintenance. Additionally, factors like mechanical stresses, chemical reactions, and thermal shock can also contribute to the degradation and reduced lifespan of monolithic refractories.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories improve the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheating furnaces?
- Monolithic refractories greatly contribute to the efficiency of ladle and tundish preheating furnaces. These refractories, made from a single material, are easily installed, repaired, and replaced, making them versatile and cost-effective. The efficiency of these furnaces is improved thanks to the outstanding thermal insulation properties of monolithic refractories. With low thermal conductivity, they effectively retain heat and prevent its escape. This insulation capability ensures an efficient preheating process, reducing energy consumption and costs by minimizing heat loss. Additionally, monolithic refractories possess high thermal shock resistance, which is crucial in ladle and tundish preheating furnaces. These furnaces experience rapid temperature changes during the pouring of molten metal, which can lead to cracking or failure of traditional refractories. However, monolithic refractories are specifically designed to withstand thermal shock, remaining intact and maintaining their insulating properties even in extreme conditions. This durability reduces downtime and maintenance requirements, thus enhancing overall efficiency. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide a seamless and uniform lining surface, improving heat transfer within the furnace. The absence of joints or seams reduces the risk of heat leakage and ensures even distribution of heat throughout the lining. This promotes uniform heating of the ladle or tundish, allowing for more efficient preheating and better temperature control. In conclusion, the use of monolithic refractories in ladle and tundish preheating furnaces results in improved efficiency due to their exceptional thermal insulation properties, high thermal shock resistance, and ability to provide a seamless and uniform lining. These refractories minimize heat loss, reduce energy consumption, and enhance the overall performance of the preheating process.
- Q:What are the recommended drying procedures for monolithic refractories?
- Drying methods for monolithic refractories differ based on the specific type and composition of the material. Nevertheless, there exist general guidelines that can be adhered to. Initially, it is crucial to eliminate any excess moisture from the refractory material prior to drying. This can be achieved by storing the refractory in a dry environment or utilizing a dehumidifier if necessary. Once the refractory material has been adequately dried, the drying process can commence. It is advisable to initiate the process with a low drying temperature in order to prevent cracking or spalling. Gradually raising the temperature over time will allow for the gradual release of moisture. This can be accomplished by employing a controlled drying oven or furnace. The duration of the drying process will differ depending on the thickness and composition of the refractory. It is imperative to adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines for the specific refractory material being utilized, as they will provide the recommended drying duration and temperature range. Throughout the drying process, it is important to closely monitor the refractory for any indications of cracking or spalling. Should any cracks or damage occur, the drying process should be immediately halted to prevent further harm. It may be necessary to repair or replace the damaged areas before proceeding with the drying process. Once the refractory material has been fully dried, it is crucial to gradually cool it down to avoid thermal shock. This can be achieved by gradually reducing the temperature over time or allowing the refractory to naturally cool in a controlled environment. In conclusion, the recommended drying procedures for monolithic refractories involve gradually increasing the temperature over time, closely monitoring for any signs of damage, and slowly cooling down the refractory to prevent thermal shock. It is essential to adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines and recommendations for the specific refractory material being utilized to ensure proper drying and optimal performance.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | Henan, China |
| Year Established | 2007 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 60 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Eastern Europe; North America |
| Company Certifications | ISO 9001:2008 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin |
| Export Percentage | 31% - 50% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 21-50 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 36,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 5 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
Alumina Spinel Castable for Ladle and Tundish
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords




























