Zhenfa-AC1.68KW Solar Home System
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
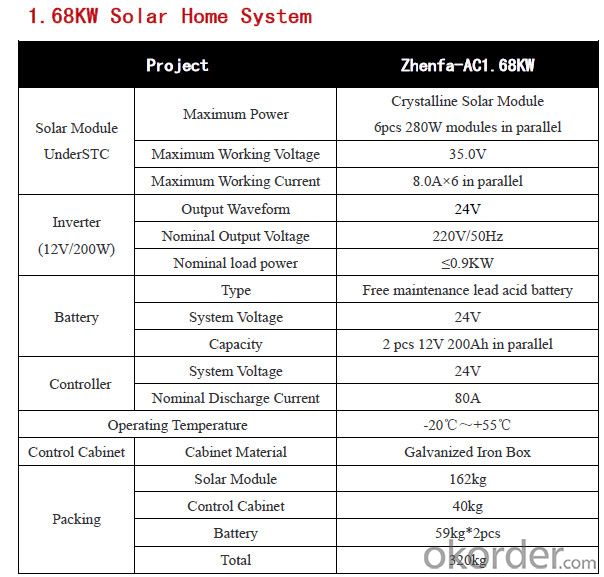
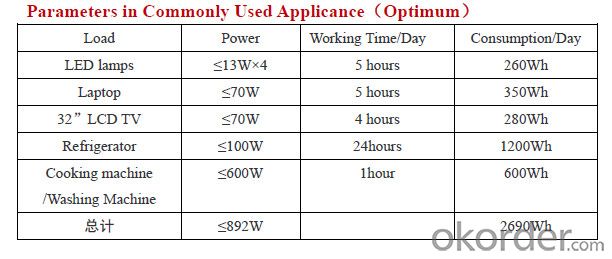

In certain emerging markets, Zhenfa new energy offers home owners complete residential solar system solutions to meet their green energy needs. Zhenfa's residential solar power systems are designed to meet different building applications in system sizes of 1.68kW and 3.9kW. Zhenfa also provides customized solar system solutions for special solar power systemapplications.
- Q:Are there any limitations to the amount of electricity a solar energy system can generate?
- Yes, there are limitations to the amount of electricity a solar energy system can generate. The primary limitation is the availability of sunlight. Solar panels require direct sunlight to generate electricity, so factors such as weather conditions, geographical location, and time of day can affect the amount of sunlight received. Cloudy or rainy days can significantly reduce the electricity output of a solar energy system. Another limitation is the physical space available for installing solar panels. The size and number of panels that can be installed depend on the available roof or ground space. Limited space can restrict the overall capacity of the system and, consequently, the amount of electricity it can generate. Additionally, the efficiency of solar panels is a determining factor. The efficiency of converting sunlight into electricity varies depending on the type and quality of solar panels used. Higher efficiency panels can generate more electricity than lower efficiency ones. Furthermore, solar energy systems are also subject to degradation over time. Solar panels experience a gradual decrease in efficiency as they age due to factors like exposure to sunlight, temperature fluctuations, and environmental conditions. This degradation can reduce the overall electricity generation capacity of the system. Finally, energy storage is a limitation. Solar energy systems generate electricity during the day, but the demand for electricity often remains constant throughout the day and night. Without an efficient energy storage system, excess electricity generated during the day is wasted if not used immediately. Therefore, the inability to store excess electricity limits the overall amount that can be generated by a solar energy system. In summary, while solar energy systems offer a sustainable and renewable source of electricity, there are limitations to the amount they can generate due to factors such as sunlight availability, physical space, panel efficiency, system degradation, and energy storage capabilities.
- Q:Can solar energy systems be used in disaster relief efforts?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used in disaster relief efforts. In fact, they have become increasingly popular and valuable in such situations. When disasters strike, they often disrupt the electricity supply, leaving affected areas without power for days or even weeks. This lack of electricity hampers relief efforts, making it difficult to provide basic necessities like lighting, medical care, communication, and clean water. Solar energy systems, on the other hand, can provide a reliable and sustainable source of power in these situations. They consist of solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power various devices and appliances. These systems can be quickly deployed to disaster-stricken areas, providing immediate access to electricity without relying on traditional power grids. There are several advantages to using solar energy systems in disaster relief efforts. Firstly, solar power is renewable and abundant, ensuring a continuous supply of electricity even during prolonged emergencies. Secondly, solar energy systems are generally low maintenance, reducing the need for constant fuel supply or repairs. This makes them more cost-effective and reliable in disaster-prone areas. Solar energy systems can be used in a variety of ways during disaster relief efforts. They can power mobile charging stations, allowing people to charge their phones and stay connected with their loved ones. Solar-powered lighting can be used to illuminate temporary shelters, hospitals, and walkways, improving safety and security for victims and aid workers alike. Solar energy can also be used to power water purification systems, ensuring a supply of clean drinking water in areas where water infrastructure has been damaged or contaminated. Furthermore, solar energy systems can be integrated into existing relief infrastructure. For example, solar panels can be installed on the roofs of hospitals, schools, and community centers, ensuring a reliable source of electricity for critical operations. This reduces the dependence on diesel generators or other fossil fuel-powered alternatives, which are often expensive, noisy, and emit harmful pollutants. In summary, solar energy systems are highly beneficial in disaster relief efforts. They provide a sustainable and reliable source of power, enabling essential services and improving the overall relief operations. As the world faces more frequent and severe natural disasters, the use of solar energy systems in disaster relief will continue to grow in importance.
- Q:What is the environmental impact of solar energy systems?
- Solar energy systems have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to conventional energy sources. With no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, solar power helps reduce carbon dioxide and other harmful pollutants that contribute to climate change. Although the manufacturing process does require energy and materials, the long-term benefits of solar energy in reducing emissions and dependence on fossil fuels far outweigh its initial environmental costs. Furthermore, the land used for solar installations can often be dual-purposed, such as for agriculture or wildlife conservation, minimizing any ecological disruption. Overall, solar energy systems play a crucial role in mitigating environmental degradation and transitioning towards a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
- Q:Can solar energy systems be used in areas with limited roof access for maintenance?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used in areas with limited roof access for maintenance. In such cases, alternative mounting options like ground-mounted systems or solar canopies can be utilized, allowing for easier access and maintenance of the solar panels. These alternative solutions ensure that solar energy can still be harnessed effectively in areas where roof access is limited.
- Q:Are solar panels weather resistant?
- Yes, solar panels are weather resistant. They are designed to withstand various weather conditions, including rain, snow, hail, and high winds. The materials used in their construction are durable and can handle exposure to the elements for many years. Additionally, solar panels are often installed at an angle to allow for self-cleaning and minimize the accumulation of dirt and debris, further enhancing their weather resistance.
- Q:Can solar energy systems be used for emergency power backup?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used for emergency power backup. By installing battery storage systems along with solar panels, excess energy generated during the day can be stored and used during power outages or emergencies. This provides a reliable and sustainable source of backup power, reducing dependence on traditional power grids and ensuring continuous electricity supply.
- Q:Are there any environmental impacts associated with solar energy systems?
- Yes, solar energy systems have some environmental impacts, but they are significantly lower compared to traditional fossil fuel sources. The production and disposal of solar panels can generate some waste and emissions, but these are relatively minimal compared to the ongoing pollution caused by burning fossil fuels. Additionally, land use for large-scale solar installations can impact local ecosystems. However, proper planning and implementation can minimize these impacts, and the long-term benefits of solar energy in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change far outweigh any potential negative environmental effects.
- Q:Can a solar energy system be used in areas prone to hurricanes or tornadoes?
- Solar energy systems can indeed be utilized in regions that are susceptible to hurricanes or tornadoes. Although these natural calamities can potentially inflict harm on solar panels and other system components, employing appropriate preparation and installation methods can alleviate these risks. The design and structural integrity of solar panels themselves are crucial considerations. High-quality panels are constructed to withstand powerful winds and extreme weather conditions. They undergo rigorous testing and certification processes to meet specific standards, including wind resistance ratings. In hurricane or tornado-prone areas, it is essential to install panels explicitly engineered to endure the potential wind speeds and impacts associated with these events. Furthermore, employing proper installation techniques can enhance the resilience of a solar energy system. For instance, utilizing reinforced mounting structures, securing panels with additional brackets or fasteners, and ensuring secure connections between panels, inverters, and batteries can prevent damage caused by strong winds or airborne debris. In certain cases, homeowners may opt to invest in solar panel tracking systems that automatically adjust panel positions to minimize wind resistance during severe weather occurrences. This feature protects the panels and increases their likelihood of surviving hurricanes or tornadoes with minimal damage. Moreover, having a backup power storage system, such as batteries, is essential to ensure uninterrupted power supply during and after severe weather events. This backup system stores excess energy generated by the solar panels, enabling the system to function independently of the grid during power outages caused by hurricanes or tornadoes. Overall, although there are risks associated with utilizing a solar energy system in hurricane or tornado-prone areas, careful planning, proper installation, and the use of resilient components allow for the harnessing of solar power even in these challenging environments.
- Q:What is the impact of snow or hail on solar panels?
- Snow or hail can have a significant impact on the performance and efficiency of solar panels. When snow accumulates on the surface of the panels, it can block sunlight from reaching the photovoltaic cells, reducing the system's energy production. This reduced sunlight exposure can lead to a decline in the overall power output of the solar installation. Similarly, hail can cause physical damage to the panels if the ice pellets are large enough or the velocity of their impact is high. This damage can result in cracks, shattered glass, or even internal structural issues within the panels. Once the solar panels are damaged, their ability to convert sunlight into electricity is compromised, leading to a decrease in their overall efficiency. To mitigate the impact of snow or hail on solar panels, various measures can be taken. In snowy areas, panels can be installed at an angle to allow snow to slide off more easily, reducing the accumulation on the surface. Additionally, heating elements can be integrated into the panels to melt the snow and ice. However, these heating systems require additional energy, which may offset some of the benefits of solar power during snowy periods. For hail, the use of tempered or impact-resistant glass for solar panels can help to minimize the damage caused by hailstones. Furthermore, mounting systems that provide a level of flexibility and shock absorption can help to absorb the impact and reduce the risk of physical harm to the panels. Overall, while snow and hail can have negative effects on solar panels, proper installation, maintenance, and protective measures can help to mitigate these impacts and ensure that the solar system continues to generate clean and renewable energy efficiently.
- Q:How does shading affect the performance of solar panels?
- Shading significantly affects the performance of solar panels as it reduces the amount of sunlight reaching the photovoltaic cells. When a solar panel is shaded, even partially, the shaded cells generate less electricity than the unshaded cells. This is because solar panels are typically connected in series, meaning that the current passing through the shaded cell is limited by the shaded cell's reduced output. Consequently, the overall power output of the solar panel is significantly reduced. Shading can occur due to various factors such as nearby buildings, trees, or even temporary obstructions like clouds or debris. It is crucial to minimize shading on solar panels to maximize their performance and the energy generated. To mitigate the impact of shading, certain design considerations can be implemented. One approach is to install solar panels in a location that receives maximum sunlight throughout the day, ideally with no obstructions. If shading is unavoidable, careful panel arrangement can be employed to minimize the impact. For instance, using bypass diodes, which allow current to bypass the shaded cells, can prevent significant power loss. This technique ensures that only the shaded cells are bypassed, allowing the unshaded cells to continue generating electricity efficiently. Furthermore, advanced technologies like micro-inverters or power optimizers can be used to optimize the output of each individual solar panel, even when some panels are partially shaded. These devices allow each panel to operate independently, mitigating the negative effects of shading and maximizing overall power generation. Overall, shading has a substantial impact on the performance of solar panels, reducing their efficiency and power output. However, through careful planning, installation, and the use of advanced technologies, the negative effects of shading can be minimized, enabling solar panels to generate as much energy as possible.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Zhenfa-AC1.68KW Solar Home System
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords































