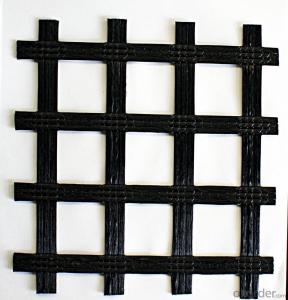
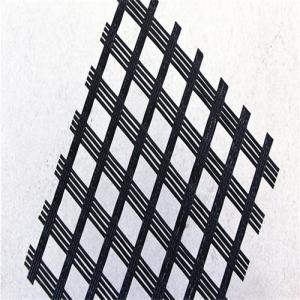
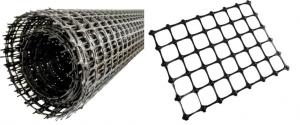
Extruded Geogrid
Extruded Geogrid Related Searches
Fridge With Freezer On Bottom Driveway Pillars With Lights Blu Ray Player With Recorder Blu Ray Player With Internet Geogrid In Retaining Walls 1708 Biaxial Fiberglass Tape Pullout Resistance Of Geogrid Geogrid Warp Knitting Machine Srw 3 Series Geogrid Biaxial Plastic GeogridHot Searches
Fiberglass Scaffolding For Sale Fiberglass Panels For Sale Fiberglass Greenhouses For Sale Geogrid Fabric For Sale Gas Powered Core Aerator For Sale Revolution 4 Propeller For Sale Alabaster Carving Stone For Sale Geogrid For Sale Near Me Tensar Geogrid For Sale Geogrid For Sale Ex Display Log Cabins For Sale Photoelectric Cells For Sale Athletic Lockers For Sale Cubicle Partitions For Sale Stearman Propeller For Sale Palram Greenhouses For Sale Gumbo Bowls For Sale Suzuki Propellers For Sale Freight Crates For Sale Outhouse Sheds For SaleExtruded Geogrid Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Okorder.com is a professional Extruded Geogrid supplier & manufacturer, offers integrated one-stop services including real-time quoting and online cargo tracking. We are funded by CNBM Group, a Fortune 500 enterprise and the largest Extruded Geogrid firm in China.Hot Products
FAQ
- Yes, geogrids are suitable for use in soil reinforcement for pipeline river crossings. Geogrids offer excellent soil stabilization and reinforcement properties, providing enhanced tensile strength and load-bearing capacity. They are particularly effective in areas with challenging soil conditions or high water flow rates. Geogrids can effectively distribute the loads from the pipeline, prevent soil erosion, and ensure long-term stability, making them a reliable choice for reinforcing soil in pipeline river crossings.
- Yes, geogrids are suitable for use in temporary retaining walls. Geogrids are often used to reinforce and stabilize soil in retaining walls, providing increased strength and stability. They can be easily installed and removed, making them a viable option for temporary structures.
- Yes, geogrids can be used in slope stabilization for mining waste dumps. Geogrids are commonly used in civil engineering projects to reinforce and stabilize slopes. By incorporating geogrids into the design and construction of mining waste dumps, the stability of the slopes can be improved, preventing potential slope failures and reducing the risk of environmental hazards.
- Yes, geogrids can be used in the reinforcement of soft ground. Geogrids are commonly used in civil engineering projects to improve the stability and strength of weak or soft soils. They are designed to distribute loads and prevent soil movement, making them an effective solution for reinforcing soft ground and preventing settlement or failure.
- Geogrids improve the performance of mechanically stabilized slopes by providing reinforcement and stability to the soil. They distribute the stress and load more evenly, reducing the potential for slope failure or movement. Additionally, geogrids increase the overall strength and integrity of the slope, allowing for steeper slopes to be constructed.
- There are several advantages of using geogrids in ground improvement for liquefaction mitigation. Firstly, geogrids provide increased stability to the soil by reinforcing it. They are placed in the ground to create a strong and stable layer, preventing soil liquefaction during earthquakes or other seismic events. This reinforcement helps to improve the overall strength and load-bearing capacity of the soil, making it less susceptible to liquefaction. Secondly, geogrids can improve the drainage properties of the soil. By creating a network of interconnected voids, they allow water to drain more efficiently, reducing the excess pore water pressure that contributes to liquefaction. This improved drainage helps to maintain the integrity and stability of the soil, even under seismic loading. Additionally, geogrids are cost-effective compared to other ground improvement techniques. They are relatively easy to install and require minimal excavation, reducing construction time and costs. Moreover, their long lifespan and durability make them a sustainable solution for liquefaction mitigation, minimizing the need for frequent maintenance or replacement. Overall, the use of geogrids in ground improvement for liquefaction mitigation offers enhanced stability, improved drainage, and cost-effectiveness, making them a valuable tool in mitigating the risks associated with soil liquefaction.
- Geogrids help in reducing construction labor requirements by providing stability and reinforcement to the soil, thus eliminating the need for extensive excavation and compaction. They distribute loads more evenly, reducing the amount of material needed and the labor involved in handling and compacting it. This ultimately leads to faster and more efficient construction processes with fewer workers required.
- How to determine geogrid reinforcement or crack resistance
- Highway such as half fill half dug, soft foundation zone to prevent the differential settlement, fill inspection batch to distinguish between, please know that. Thank you