Seamless Ferritic Alloy-Steel Pipe for High-Temperature
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Abstract
This specification covers seamless ferritic alloy-steel pipe for high-temperature service. The pipe shall be suitable for bending, flanging (vanstoning), and similar forming operations, and for fusion welding. Grade P2 and P12 steel pipes shall be made by coarse-grain melting practice. The steel material shall conform to chemical composition, tensile property, and hardness requirements. Each length of pipe shall be subjected to the hydrostatic test. Also, each pipe shall be examined by a non-destructive examination method in accordance to the required practices. The range of pipe sizes that may be examined by each method shall be subjected to the limitations in the scope of the respective practices. The different mechanical test requirements for pipes, namely, transverse or longitudinal tension test, flattening test, and hardness or bend test are presented.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers nominal wall and minimum wall seamless ferritic alloy-steel pipe intended for high-temperature service. Pipe ordered to this specification shall be suitable for bending, flanging (vanstoning), and similar forming operations, and for fusion welding. Selection will depend upon design, service conditions, mechanical properties, and high-temperature characteristics.
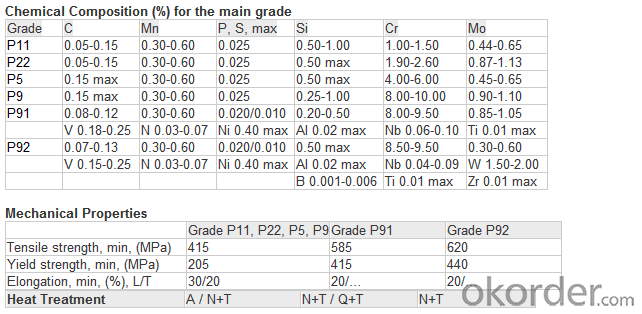
1.2 Several grades of ferritic steels (see Note 1) are covered. Their compositions are given in Table 1.
Note 1—Ferritic steels in this specification are defined as low- and intermediate-alloy steels containing up to and including 10 % chromium.
1.3 Supplementary requirements (S1 to S7) of an optional nature are provided. These supplementary requirements call for additional tests to be made, and when desired, shall be so stated in the order together with the number of such tests required.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation of this specification is specified in the order.
Note 2—The dimensionless designator NPS (nominal pipe size) has been substituted in this standard for such traditional terms as “nominal diameter,” “size,” and “nominal size.”
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
A New designation established in accordance with Practice E527 and SAE J1086, Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS).
B Grade P 5c shall have a titanium content of not less than 4 times the carbon content and not more than 0.70 %; or a columbium content of 8 to 10 times the carbon content.
C Alternatively, in lieu of this ratio minimum, the material shall have a minimum hardness of 275 HV in the hardened condition, defined as after austenitizing and cooling to room temperature but prior to tempering. Hardness testing shall be performed at mid-thickness of the product. Hardness test frequency shall be two samples of product per heat treatment lot and the hardness testing results shall be reported on the material test report.
2. Referenced Documents (purchase separately)
ASTM Standards
A999/A999M Specification for General Requirements for Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe
E92 Test Method for Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials
E213 Practice for Ultrasonic Testing of Metal Pipe and Tubing
E309 Practice for Eddy-Current Examination of Steel Tubular Products Using Magnetic Saturation
E381 Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets, Blooms, and Forgings
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
E570 Practice for Flux Leakage Examination of Ferromagnetic Steel Tubular Products
ASME Standard
B36.10M Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe
ASTM A335 Seamless Alloy-Steel Pipe
Standard: BS 1139, BS 3059-2, JIS G3454-2007
Grade: 10#-45#, 15NiCuMoNb5, 10Cr9Mo1VNb
Detailed introduction to ASTM A335 seamless alloy steel pipe:
ASTM A335 seamless alloy steel pipe

FAQ:
1) why you chose us ?
Professional Manufacturer and supplier of Steel pipe
More than 14 years’ professional producing experience
We can get the lowest ex-factory prices. The price are quite reasonable and it is lower than our commercial peers. also, we can guarantee the qualities of our products.
BV, ISO certificates and SGS test can be provided to assure the quality of our products.
2) Our minimum order quantity:
10 Metric Tons or one 20ft or 40ft Container.
3) How about the Delivery Time?
The steel pipe will be produced since we getting your deposit by T/T or Your original L/C. For normal size, some stocks in our factory now, we can supply once you need.
4)What kind of payment does your company support?
T/T, 100% L/C at sight, Cash, Western Union are all accepted.
5) Do you charge for the samples?
According to our company principle, we just charge for samples, you pay for the freight /courier charge.
6) Main market:
Mid East, South America, Africa, Southeast Asia, India etc
- Q:What are the different methods of insulating steel pipes?
- There are several methods of insulating steel pipes, including using insulation wraps, foam insulation, fiberglass insulation, and pre-insulated pipe systems. Insulation wraps are typically made of materials like rubber or polyethylene and are wrapped around the pipe to provide thermal insulation. Foam insulation involves applying a layer of foam insulation directly onto the surface of the pipe. Fiberglass insulation is another common method, where fiberglass material is wrapped around the pipe to provide insulation. Pre-insulated pipe systems are complete pipe systems that come with built-in insulation and are ready to be installed. These methods help prevent heat loss or gain in the pipes, maintain temperature control, and prevent condensation.
- Q:Can steel pipes be used for cooling systems?
- Yes, steel pipes can be used for cooling systems. Steel pipes are commonly used in various industrial cooling applications due to their durability, high strength, resistance to corrosion, and ability to withstand high pressure and temperature conditions.
- Q:What are the safety precautions to follow while working with steel pipes?
- When working with steel pipes, it is important to follow certain safety precautions to ensure a safe working environment. Here are some key safety measures to consider: 1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety goggles, gloves, steel-toed boots, and a hard hat. This will protect you from potential hazards such as falling objects, sharp edges, or flying particles. 2. Use proper lifting techniques: Steel pipes can be heavy and awkward to handle. Use proper lifting techniques, such as bending your knees and using your legs to lift, to avoid straining your back or causing musculoskeletal injuries. 3. Secure the work area: Clear the work area of any clutter or obstacles that could pose a tripping hazard. Ensure that the pipes are properly stored and secured to prevent them from rolling or falling. 4. Be cautious of sharp edges: Steel pipes often have sharp edges, which can cause cuts or punctures. Handle them with care and consider using protective covers or gloves to avoid injuries. 5. Use appropriate tools: Utilize the correct tools and equipment for cutting, welding, or manipulating steel pipes. Follow manufacturer instructions and guidelines to ensure safe usage. 6. Avoid working in confined spaces: Working in confined spaces poses serious risks. If it is necessary to work in such an area, ensure proper ventilation and follow confined space entry protocols to prevent asphyxiation or other hazards. 7. Follow proper welding procedures: If welding is involved, follow proper welding procedures and ensure proper ventilation in the workspace. Use fire-resistant blankets or screens to protect nearby combustible materials. 8. Be aware of hot surfaces: Steel pipes can become hot during welding or other processes. Use appropriate insulation or heat-resistant gloves to protect yourself from burns or heat-related injuries. 9. Establish communication: Establish clear communication channels with colleagues when working with steel pipes, especially when lifting or moving heavy objects. Use hand signals or verbal communication to ensure everyone is on the same page and to prevent accidents. 10. Regularly inspect tools and equipment: Before starting any task, inspect tools, equipment, and scaffolding for any damage or defects. Report and replace any faulty equipment to prevent accidents. Remember, safety is paramount when working with steel pipes. By following these precautions and using common sense, you can ensure a safe working environment for yourself and your colleagues.
- Q:What is the buckling type thin-wall steel pipe? What is a tight set of thin-walled steel tubes? What's the difference between the two?
- The nut body and the junction box are connected at one end by adopting metric fine tooth thread, and the pipe is connected with the pipe, and one end is the same as the straight pipe joint (direct). Withhold the box joint points inside and outside teeth two. The diameter of straight pipe joint is divided into 16mm, 20mm, 25mm, 32mm, 40mm, 50mm.
- Q:RC is it welded steel pipe or galvanized steel pipe?
- RC pipe is galvanized steel pipe, usually followed by the diameter, such as RC50, that is, 50mm galvanized steel pipe.
- Q:Can steel pipes be used for telecommunications cables?
- No, steel pipes cannot be used for telecommunications cables. Telecommunications cables are typically made of fiber optic or copper materials. Steel pipes are used for various applications in construction and plumbing, but they are not suitable for transmitting data or electrical signals. Fiber optic cables are designed to carry high-speed data over long distances, while copper cables are used for transmitting both data and electrical signals. These cables have specific insulation and shielding properties that steel pipes do not possess, making them unsuitable for telecommunications purposes.
- Q:What are the different types of steel pipe bends for pipeline routing?
- There are several different types of steel pipe bends commonly used for pipeline routing. These include 90-degree bends, 45-degree bends, and custom bends with specific angles as per the pipeline design requirements. Each type of bend serves a specific purpose in redirecting the flow of fluids or gases through the pipeline while maintaining structural integrity.
- Q:What are steel pipes?
- Steel pipes are hollow cylindrical tubes made from steel, which are mainly used for transporting fluids and gases in various industries such as oil and gas, construction, and plumbing. They are known for their strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making them an essential component in infrastructure and industrial applications.
- Q:What are the non-destructive testing methods used for steel pipes?
- Some of the non-destructive testing methods used for steel pipes include ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, liquid penetrant testing, radiographic testing, and eddy current testing.
- Q:When can I use the PVC pipe and when to use the galvanized pipe?
- PVC pipeline use temperature is -5 to 90 degrees or so, according to the current market price of around 6000 yuan per ton, the price is cheap. Its corrosion resistance is good, can resist most of the acid and alkali, and unlike the steel pipe that is easy to rust, so in the construction of the upper and lower water pipes and other fields have gradually replaced the trend of steel pipe.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Seamless Ferritic Alloy-Steel Pipe for High-Temperature
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords































