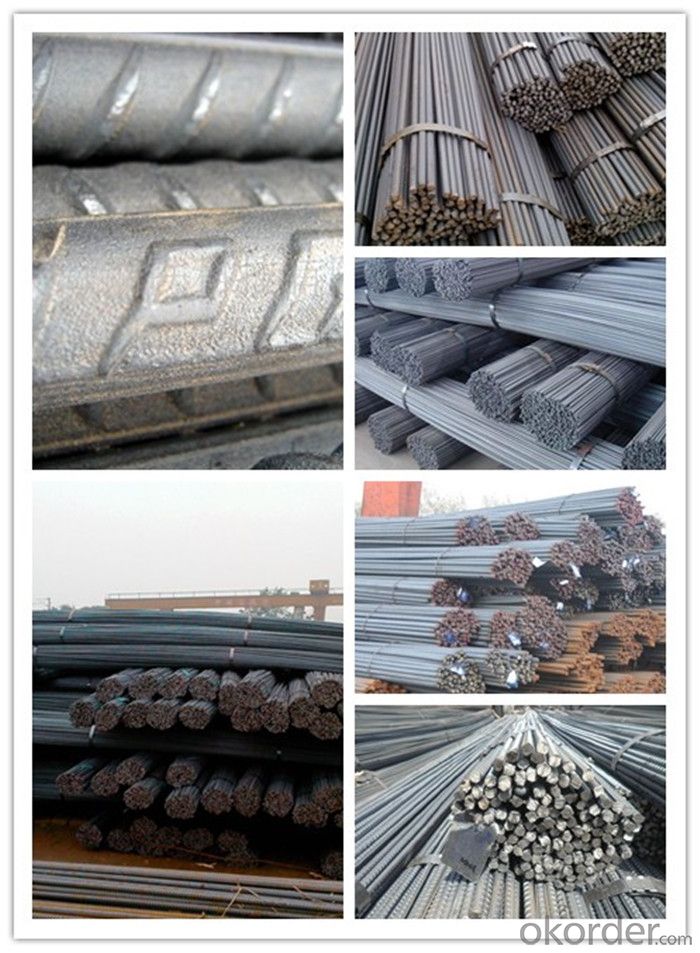
Wire Coiled Deformed Bars of Building Metal
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Item specifice
Wire Coiled Deformed Bars of Building Metal
Description of Wire Coiled Deformed Bars
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm Wire Coiled Deformed Bars
10m- 40mm Wire Coiled Deformed Bars
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of Wire Coiled Deformed Bars
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
Products Show of Wire Coiled Deformed Bars
Company Information
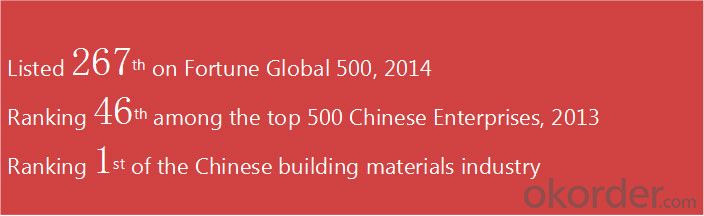
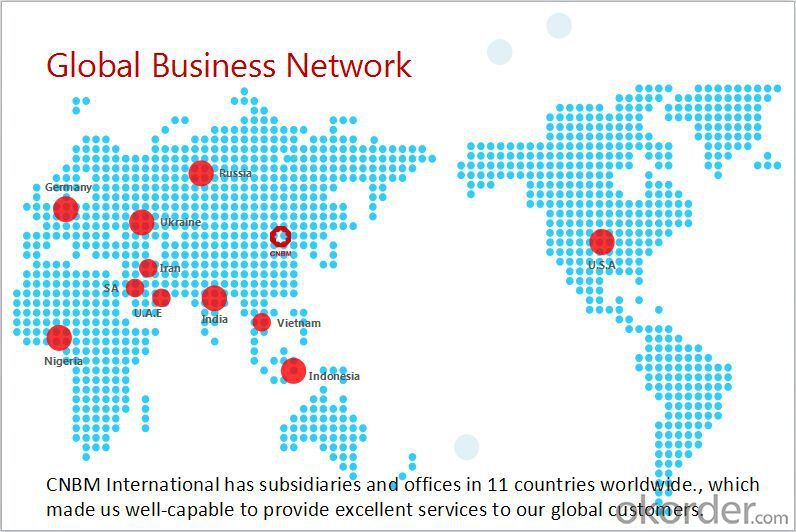
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q:Can special steel be used in the production of gearboxes?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the production of gearboxes. Special steel, such as alloy steel or heat-treated steel, is often preferred for gear manufacturing due to its high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and fatigue. These properties make special steel well-suited for transmitting power and withstanding the demands of heavy-duty applications, making it an ideal material choice for gearboxes.
- Q:What are the different forms in which special steel is available?
- Special steel is available in various forms such as bars, plates, sheets, tubes, wires, and forgings.
- Q:What are the requirements for special steel used in high-strength applications?
- Special steel used in high-strength applications typically has specific requirements to ensure its performance and durability. These requirements include: 1. High tensile strength: Special steel used in high-strength applications must have a high tensile strength to withstand heavy loads and resist deformation. This allows it to handle greater stresses without failure. 2. Excellent toughness: The steel should possess excellent toughness, which refers to its ability to absorb energy and resist fracture. This is crucial in high-strength applications as it prevents sudden and catastrophic failure under impact or dynamic loading conditions. 3. Superior hardness: High-strength steel needs to have a high level of hardness to resist wear, abrasion, and indentation. This ensures that the material maintains its structural integrity and performance even under extreme conditions. 4. Good ductility: While high tensile strength is essential, the steel should also possess good ductility, which allows it to undergo plastic deformation without fracturing. This property is vital in applications where the steel needs to be formed or shaped during manufacturing processes. 5. Resistance to corrosion: Special steel used in high-strength applications should have excellent corrosion resistance to prevent degradation caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, or harsh environments. This ensures its longevity and reliability in various conditions. 6. Heat resistance: Some high-strength applications involve exposure to high temperatures, so the steel should have good heat resistance to maintain its mechanical properties and structural stability under elevated temperatures. 7. Controlled alloying elements: Special steel used in high-strength applications often contains specific alloying elements such as chromium, molybdenum, nickel, or vanadium. These elements are added to improve the steel's strength, toughness, hardness, and other desired properties. 8. Precise composition and microstructure: The steel should have a well-controlled composition and microstructure to ensure consistent and predictable mechanical properties. This can be achieved through precise manufacturing processes, such as controlled cooling rates or heat treatments. Meeting these requirements ensures that special steel used in high-strength applications can withstand the demanding conditions it is subjected to, providing reliable performance, longevity, and safety.
- Q:What are the common failures or issues with special steel?
- There are several common failures or issues that can occur with special steel. One of the most common issues is corrosion. Special steel, like any other type of steel, can be prone to corrosion when exposed to certain environmental conditions, such as moisture or aggressive chemicals. This can lead to a decrease in its structural integrity and overall performance. Another common failure is fatigue. Special steel is often used in applications that require high strength and durability. However, repetitive loading or stress can cause the material to develop cracks or fractures over time, leading to fatigue failure. This can be particularly problematic in industries such as aerospace or automotive, where components are subjected to constant cyclic loading. In addition, improper heat treatment can result in failure. Special steel often requires specific heat treatments to achieve desired properties such as hardness or toughness. If the heat treatment process is not carried out correctly, it can lead to inconsistent material properties, resulting in reduced performance or premature failure. Welding issues can also occur with special steel. Welding is commonly used to join different components or structures made of special steel. However, if proper welding techniques and procedures are not followed, it can result in the formation of defects such as weld cracks, porosity, or inadequate fusion. These defects can weaken the weld joint and compromise the overall integrity of the structure. Lastly, dimensional instability can be a problem with special steel. Certain types of special steel, such as those with high carbon content, can exhibit dimensional changes when subjected to temperature variations. This can lead to distortion or warping of the material, affecting its fit, function, or assembly with other components. To mitigate these failures or issues with special steel, it is crucial to follow proper material selection, design, manufacturing, and maintenance practices. Conducting thorough inspections, implementing appropriate corrosion protection measures, and ensuring proper heat treatment and welding procedures can help minimize the occurrence of these failures and enhance the performance and longevity of special steel components.
- Q:What are the different methods of analyzing the microstructure of special steel?
- The microstructure of special steel can be analyzed using various methods. These methods involve examining and characterizing the steel at a microscopic level to gain insights into its composition, grain structure, and other features. Some commonly used methods include: 1. Optical Microscopy: By using light microscopy, the microstructure of special steel can be observed. This method allows for the identification of different phases, grain boundaries, inclusions, and other features. It provides valuable information about the size, distribution, and morphology of constituents in the steel. 2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): SEM is a powerful technique that utilizes a high-energy electron beam to analyze the microstructure of special steel. It offers detailed information about the steel's surface topography, morphology, and elemental composition. SEM is particularly useful for studying precipitates, segregation, and other microstructural defects. 3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM): TEM is an advanced technique that enables analysis of the microstructure at a higher resolution compared to optical and SEM methods. It involves the transmission of electrons through a thin sample, providing information about the crystal structure, dislocations, and other fine details of the microstructure. TEM is especially beneficial for studying nanostructures and interfaces in special steel. 4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD): XRD is a non-destructive method that utilizes X-rays to analyze the crystal structure and identify phases in special steel. It provides information about the crystallographic orientation, grain size, and phase composition of the steel. XRD is widely used for analyzing phase transformations and residual stress in special steel. 5. Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD): EBSD combines SEM with crystallographic analysis to provide information about the crystal orientation, texture, and grain boundaries in special steel. It is useful for studying deformation mechanisms, recrystallization, and grain growth in the steel. 6. Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS): EDS is often used in conjunction with SEM or TEM to analyze the elemental composition of special steel. It provides information about the presence and distribution of different chemical elements in the microstructure, aiding in the identification of phases and characterization of inclusions. These methods, among others, offer valuable insights into the microstructure of special steel. They enable researchers and engineers to understand the steel's properties, performance, and potential applications.
- Q:What are the requirements for special steel used in high-performance racing cars?
- In order to meet the demands of the racing environment, the requirements for special steel used in high-performance racing cars are quite strict. Some of the main requirements include: 1. Exceptional strength and durability: The special steel must possess outstanding strength and durability to endure the extreme loads and stresses encountered during high-speed racing. It must have a high tensile strength and the ability to withstand fatigue and deformation under intense conditions. 2. Lightweight: Racing cars require lightweight materials to achieve optimal performance and maneuverability on the track. The special steel used in high-performance racing cars must have a high strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for reduced weight without compromising strength or safety. 3. Excellent heat resistance: The steel must have excellent heat resistance to withstand the high temperatures generated by high-performance engines, braking systems, and exhaust systems. It must maintain its structural integrity and mechanical properties even under extreme heat conditions. 4. High corrosion resistance: Racing cars are often exposed to harsh environments, including moisture, salt, and other corrosive elements. Therefore, the special steel used in racing cars should have high corrosion resistance to prevent rust and degradation, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the components. 5. Easy machinability: The steel should be easily machinable, facilitating the precise manufacturing and fabrication of complex components. This ensures that the parts can be produced accurately and efficiently, resulting in superior performance and reliability. 6. Good weldability: The special steel used in racing cars should have good weldability, as welding is often required for the assembly of various components. It should be able to withstand the heat generated during welding without experiencing significant loss in strength or other mechanical properties. In summary, the requirements for special steel used in high-performance racing cars revolve around strength, lightweight, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, machinability, and weldability. Meeting these requirements is essential to ensure the safety, performance, and success of racing cars on the track.
- Q:What are the requirements for special steel used in food processing equipment?
- Ensuring the safety and hygiene of food during processing relies heavily on the crucial requirements for special steel used in food processing equipment. The following are key considerations: 1. Corrosion resistance: The steel utilized in food processing equipment must possess exceptional resistance against corrosion. It should withstand exposure to various food products, cleaning agents, and environmental conditions without degradation or food contamination. 2. Hygienic properties: To facilitate easy cleaning and prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms, the steel should have a smooth surface finish, devoid of cracks, pits, or crevices where bacteria or food particles can accumulate. 3. Non-reactivity: The steel employed in food processing equipment must not react with the food or modify its taste, color, or odor. It should be chemically inert, releasing no substances that could compromise the food's quality or cause contamination. 4. High temperature resistance: Food processing often involves high-temperature operations like cooking, sterilization, or pasteurization. Therefore, the special steel used in such equipment must endure these extreme temperatures without compromising its structural integrity or releasing harmful substances. 5. Mechanical strength: The steel must possess adequate mechanical strength to endure the operational stresses of the processing equipment, such as pressure, vibration, or impact. This ensures durability and prevents any failures or breakages during operation. 6. Compliance with regulations: The special steel utilized in food processing equipment must meet specific regulatory standards and certifications pertaining to food safety and hygiene, such as those set by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) or NSF (National Sanitation Foundation). Complying with these regulations guarantees the equipment's suitability for use in the food industry. In summary, the requirements for special steel used in food processing equipment focus on ensuring the equipment's durability, cleanliness, and safety while upholding the quality and integrity of the processed food.
- Q:How does special steel compare to other materials like aluminum or titanium?
- Special steel, such as stainless steel or tool steel, offers several advantages over materials like aluminum or titanium. Firstly, special steel generally exhibits higher strength and hardness, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to wear. Secondly, special steel possesses excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to dissipate heat more efficiently compared to aluminum or titanium. Additionally, special steel is often more cost-effective and readily available in comparison to titanium. However, aluminum and titanium are known for their lightweight properties, making them preferable for applications where weight reduction is crucial. Ultimately, the choice between special steel, aluminum, or titanium depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the intended application.
- Q:How does special steel perform in cryogenic corrosion resistance?
- Special steels possess exceptional capabilities in terms of resisting corrosion in cryogenic environments. Unlike regular steels, which tend to become brittle and prone to corrosion when exposed to extremely low temperatures, special steels are specifically engineered to endure such conditions while maintaining their mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The remarkable performance of special steels in cryogenic settings can be primarily attributed to their composition and microstructure. These steels are typically infused with elements like nickel, molybdenum, and nitrogen, which significantly enhance their ability to withstand corrosion at low temperatures. Additionally, the microstructure of special steels is meticulously controlled, resulting in a fine grain size and a uniform distribution of alloying elements. This microstructure contributes to the steel's capacity to resist corrosion and retain its mechanical strength even in cryogenic temperatures. Furthermore, special steels undergo rigorous testing procedures to ensure their suitability for cryogenic applications. They are subjected to low-temperature impact tests, which evaluate their toughness and resistance to brittle fracture. These tests verify that the steel can endure the stresses and strains imposed by cryogenic conditions without experiencing failure. In conclusion, special steels exhibit exceptional resistance to cryogenic corrosion due to their distinct composition, microstructure, and comprehensive testing. They are the preferred choice for applications that demand reliable performance in extremely low temperatures, such as in the aerospace, energy, and scientific research industries.
- Q:How does special steel contribute to the oil and gas industry?
- Special steel plays a crucial role in the oil and gas industry by offering enhanced strength, durability, and corrosion resistance needed for various applications. It is used in the construction of pipelines, drilling equipment, storage tanks, and offshore platforms, ensuring reliable and safe operations in harsh environments. Additionally, special steel's high heat resistance enables it to withstand extreme temperatures in refining processes, while its resistance to cracking and wear ensures the longevity of critical components. Overall, special steel contributes significantly to the oil and gas industry by providing the necessary materials for efficient and secure exploration, production, and transportation of oil and gas resources.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Wire Coiled Deformed Bars of Building Metal
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords


































