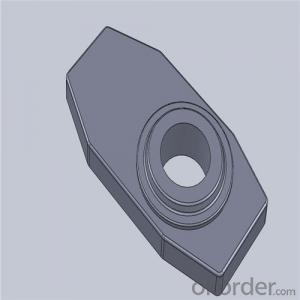
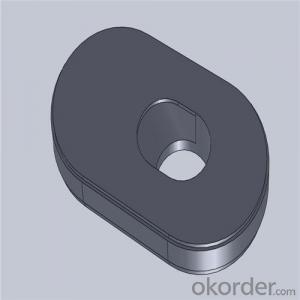
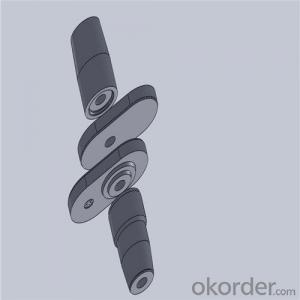
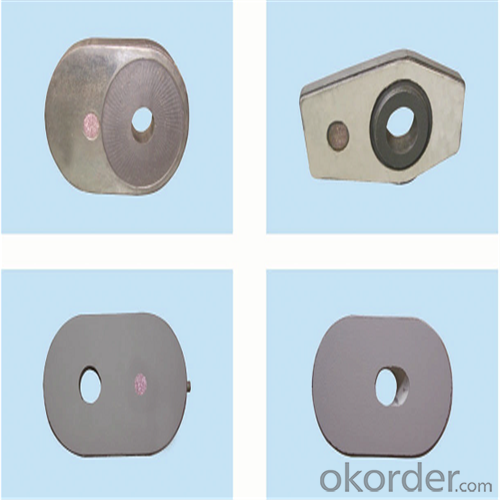
High Performance&Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate Steel
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
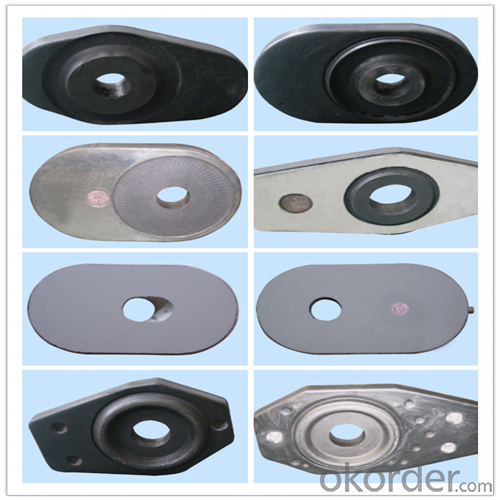

| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |


Other Products

About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q:What are the key properties of ramming mixes used for monolithic refractory installations?
- The key properties of ramming mixes used for monolithic refractory installations are: 1. High thermal stability: Ramming mixes should possess high thermal stability to withstand the extreme temperatures and thermal cycling in refractory applications. This property ensures that the ramming mix remains intact and does not undergo significant structural changes under varying thermal conditions. 2. High density: Ramming mixes need to have a high density to provide good resistance against thermal conductivity. This property helps in minimizing heat loss and maintaining the desired temperature in the refractory lining. 3. Low porosity: Low porosity is essential for ramming mixes as it helps in reducing the penetration of molten metals or slag into the refractory lining. This property enhances the overall durability and longevity of the refractory installation. 4. Good mechanical strength: Ramming mixes should possess good mechanical strength to withstand the stresses and loads encountered during installation, as well as during the operation of the refractory lining. This property ensures that the ramming mix can resist any physical or mechanical damage, such as cracking or spalling. 5. Chemical resistance: Ramming mixes should exhibit excellent resistance to chemical attack from molten metals, slag, or corrosive gases. This property is crucial for protecting the refractory lining from chemical reactions and degradation, which can compromise its performance and lifespan. 6. Easy installation and workability: Ramming mixes should have good workability, allowing for easy installation and compaction. This property ensures that the mix can be easily shaped and rammed into place without excessive effort or time, facilitating efficient and effective refractory installations. 7. Controlled setting time: Ramming mixes should have a controlled setting time to allow sufficient time for proper placement and consolidation. This property ensures that the mix remains workable during installation but sets and hardens within a reasonable time frame, allowing for timely completion of the refractory lining. In summary, the key properties of ramming mixes used for monolithic refractory installations include high thermal stability, high density, low porosity, good mechanical strength, chemical resistance, easy installation and workability, and controlled setting time. These properties collectively contribute to the overall performance, durability, and longevity of the refractory lining in various high-temperature applications.
- Q:What are the main factors affecting the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories?
- The thermal expansion of monolithic refractories is influenced by various factors. These factors comprise the type of refractory material, the temperature range, the chemical composition, and the physical structure of the refractory. To begin with, the thermal expansion behavior of a refractory is significantly determined by its type of material. Different types of refractories, such as alumina-based, silica-based, and magnesia-based refractories, possess varying coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE). For instance, alumina-based refractories generally exhibit a lower CTE in comparison to silica-based refractories. Consequently, the choice of refractory material holds great influence over its thermal expansion characteristics. Secondly, the thermal expansion of a refractory is affected by the temperature range to which it is exposed. As the temperature rises, the refractory material expands due to the absorption of thermal energy. However, different refractories demonstrate different expansion behaviors depending on temperature. Some refractories may exhibit a linear or near-linear expansion with temperature, while others may display non-linear or step-wise expansion. Hence, the temperature range of operation is a critical factor in determining the suitability of a refractory for a specific application. The chemical composition of the refractory also has an impact on its thermal expansion. The presence of various chemical elements and compounds in the refractory material can influence its expansion behavior. For instance, the addition of specific oxides, like magnesia or zirconia, can modify the CTE of the refractory. Similarly, impurities or variations in the chemical composition can introduce discrepancies in expansion characteristics among refractories of the same type. Lastly, the physical structure of the refractory, encompassing factors such as porosity, density, and microstructure, can influence thermal expansion. The existence of open or closed pores within the refractory can affect its ability to expand uniformly under thermal stress. The density of the refractory also plays a role, as denser refractories tend to have lower thermal expansion. Moreover, the microstructure, including grain size and orientation, can impact the overall expansion behavior of the refractory. To conclude, the primary factors influencing the thermal expansion of monolithic refractories include the type of refractory material, temperature range, chemical composition, and physical structure. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is crucial in selecting the appropriate refractory for a specific application to ensure optimal performance and durability.
- Q:How does the choice of monolithic refractory impact the overall cost of iron and steel production?
- The choice of monolithic refractory can significantly impact the overall cost of iron and steel production. Monolithic refractories are used to line the furnaces and other high-temperature areas in the production process, providing insulation and protection against extreme heat and chemical erosion. The cost of monolithic refractories varies depending on their composition, quality, and performance properties. Opting for high-quality monolithic refractories can increase their initial cost but can result in longer refractory lifespan, reduced downtime for repairs, and improved productivity. On the other hand, choosing lower-quality or inadequate refractories may save costs initially but can lead to frequent replacements, increased downtime, and decreased production efficiency. Additionally, monolithic refractories play a crucial role in energy efficiency. Using refractories with better insulation properties can help to reduce heat loss, leading to lower energy consumption and cost savings in the long run. Therefore, the selection of the right monolithic refractory is crucial in iron and steel production, as it directly impacts the overall cost by influencing refractory lifespan, productivity, maintenance, energy consumption, and overall operational efficiency.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories withstand high temperatures and thermal shocks?
- Monolithic refractories are able to withstand high temperatures and thermal shocks due to their unique composition and design. These refractories are made from a single piece or structure, hence the term "monolithic". This structural integrity allows them to resist the extreme heat and sudden temperature changes experienced in high-temperature applications. One key factor that enables monolithic refractories to withstand high temperatures is the use of high-quality raw materials. These materials are carefully selected for their ability to withstand heat and thermal stress. Common components include silica, alumina, magnesia, and other refractory minerals with high melting points. Additionally, the manufacturing process plays a crucial role in enhancing the thermal resistance of monolithic refractories. The raw materials are mixed with binders, such as clay or cement, to form a homogenous mixture. This mixture is then shaped and installed in its final position, either by pouring or gunning, depending on the application. The binder ensures that the refractory maintains its shape and integrity during thermal cycling. Furthermore, monolithic refractories possess excellent thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion properties. This means that they can efficiently transfer and dissipate heat, minimizing the risk of thermal stress and cracking. The low thermal expansion also reduces the likelihood of spalling or delamination, which is crucial for withstanding thermal shocks. Another factor contributing to the high-temperature resistance of monolithic refractories is their ability to form a protective layer or slag at the surface. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing the refractory from direct contact with corrosive materials or aggressive atmospheres. It helps to improve the refractory's longevity and resistance to thermal shocks. Overall, the combination of high-quality raw materials, careful manufacturing techniques, and beneficial thermal properties enables monolithic refractories to withstand high temperatures and thermal shocks. These refractories are widely used in various industries, including steel, cement, glass, and petrochemical, where they serve as reliable linings in furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature equipment.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories contribute to the safety of iron and steel operations?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing the safety of iron and steel operations. These refractories are made of a single, continuous material, which offers several benefits that contribute to the overall safety of the operations. Firstly, monolithic refractories provide excellent thermal insulation. They are designed to withstand high temperatures, preventing heat transfer to the surrounding environment. This insulation property helps in maintaining a safe working temperature for the operators, reducing the risk of burns or other heat-related injuries. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have high resistance to chemical attack. In iron and steel operations, various chemicals and molten metals are used, which can be corrosive and hazardous. The use of monolithic refractories as lining materials creates a protective barrier that resists the corrosive effects of these substances, preventing leaks and potential accidents. Another safety benefit is the ability of monolithic refractories to withstand mechanical stress. Steelmaking processes involve heavy machinery and equipment, which can exert significant pressure on the refractory linings. Monolithic refractories have excellent mechanical strength, which enables them to withstand these stresses and maintain their integrity. This prevents the risk of sudden failure or collapse, reducing the possibility of accidents and injuries due to falling debris. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and repair. They can be applied as a castable or gunning material, allowing for quick and efficient lining of furnaces, ladles, and other equipment. This ease of installation reduces downtime during maintenance or repairs, minimizing the risk of accidents caused by delayed or prolonged shutdowns. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute to the safety of iron and steel operations through their excellent thermal insulation, resistance to chemical attack, ability to withstand mechanical stress, and ease of installation and repair. By providing a protective barrier, these refractories help in preventing injuries, maintaining a safe working environment, and minimizing the potential hazards associated with high temperatures, corrosive substances, and mechanical failures.
- Q:What are the challenges in recycling monolithic refractories?
- One of the main challenges in recycling monolithic refractories is their composition. Monolithic refractories are typically made from a combination of different minerals, binders, and additives, which can make the separation and recovery of individual components difficult. Additionally, the high temperatures at which monolithic refractories are used can cause chemical reactions and physical changes that affect their recyclability. Furthermore, the presence of contaminants, such as metal oxides or impurities from the manufacturing process, can also pose challenges in the recycling process. Overall, developing efficient and cost-effective recycling methods for monolithic refractories requires addressing these challenges and finding innovative solutions.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories resist erosion from molten metals and slags?
- Monolithic refractories resist erosion from molten metals and slags through several mechanisms. Firstly, they have a high melting point, which allows them to withstand the high temperatures of molten metals and slags without any significant degradation. Secondly, they have a dense and compact structure, which reduces the penetration of molten metals and slags into their surface. Additionally, monolithic refractories often contain additives such as antioxidants or slag resistance agents, which further enhance their resistance to erosion.
- Q:What are the advantages of using monolithic refractories in electric arc furnaces?
- Using monolithic refractories in electric arc furnaces offers several advantages. Firstly, their excellent thermal shock resistance allows them to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or deteriorating. This ensures the longevity and efficiency of the furnace. Secondly, monolithic refractories have superior corrosion resistance. They are specifically designed to resist chemical attack from aggressive slag compositions, providing long-lasting protection against corrosion. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer great flexibility in terms of installation. Unlike brick linings, they can be easily applied as a liquid or paste, allowing for faster and more efficient installation. This reduces downtime during maintenance or repairs and allows for customized linings to be easily created. Moreover, monolithic refractories have excellent thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat transfer within the furnace. This results in optimal energy use and minimized heat losses, leading to reduced operating costs and increased productivity. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have a high refractoriness, meaning they can withstand extremely high temperatures without deformation or failure. This is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of electric arc furnaces. In conclusion, the advantages of monolithic refractories in electric arc furnaces include their thermal shock resistance, corrosion resistance, ease of installation, high thermal conductivity, and exceptional refractoriness. These properties contribute to improved furnace performance, increased productivity, reduced operating costs, and extended furnace life.
- Q:How are monolithic refractories installed and repaired in iron and steel applications?
- To ensure optimal performance and longevity in iron and steel applications, specific procedures are employed for the installation and repair of monolithic refractories. The installation process typically involves the following steps: 1. Proper surface preparation is crucial. This entails removing loose material, dirt, and dust to create a smooth and clean substrate that facilitates good adherence of the refractory material. 2. The refractory material, supplied as dry powders or granules, is mixed with water or a specific bonding agent according to the manufacturer's instructions to achieve the desired properties. 3. The mixed refractory material is then applied to the prepared surface using techniques such as troweling, spraying, or casting, depending on the installation requirements and the type of monolithic refractory. 4. Curing is necessary to maximize the strength and durability of the refractory material. The curing process can involve air drying, heat treatment, or a combination of both, in accordance with the specific refractory material's recommendations. When it comes to repairing monolithic refractories in iron and steel applications, the following steps are generally followed: 1. Thorough assessment of the damaged area or component is conducted to determine the extent of the damage and the appropriate repair method. 2. The damaged monolithic refractory material is carefully removed using suitable tools and techniques while ensuring the underlying substrate remains intact. 3. Similar to the installation process, the surface where the repair will take place is cleaned and prepared by removing any loose material, dirt, and dust. 4. The repair material, typically the same or similar to the original monolithic refractory, is mixed and applied to the damaged area. The application method may vary depending on the nature of the repair and the specific requirements of the refractory material. 5. The repaired area is properly cured and inspected to ensure the quality and effectiveness of the repair, following the manufacturer's guidelines for curing and post-repair inspection procedures. In conclusion, the meticulous execution of surface preparation, proper mixing and application of refractory material, and appropriate curing procedures are essential for the installation and repair of monolithic refractories in iron and steel applications. These steps guarantee reliable and durable refractory linings, which are vital for the efficient operation of iron and steel processes.
- Q:How are monolithic refractories different from traditional refractories?
- Monolithic refractories differ from traditional refractories in terms of their composition, installation method, and performance characteristics. To begin with, monolithic refractories consist of only one material, as their name suggests, while traditional refractories are typically comprised of multiple materials. This singular composition of monolithic refractories allows for greater control over their properties and performance. Moreover, the installation process for monolithic refractories differs from that of traditional refractories. Traditional refractories are typically installed in the form of bricks or precast shapes, which are assembled together to create the desired lining. In contrast, monolithic refractories are provided in a ready-to-use form, such as a dry mix or suspension, which is then poured, sprayed, or gunned into place. This facilitates a faster and more efficient installation of monolithic refractories. Lastly, monolithic refractories offer superior performance characteristics compared to traditional refractories. They possess improved thermal shock resistance, higher hot strength, and enhanced resistance to chemical attacks. Furthermore, they can be more easily repaired or patched compared to traditional refractories, which often necessitate the replacement of entire bricks or shapes. In conclusion, the key distinctions between monolithic refractories and traditional refractories lie in their composition, installation method, and performance characteristics. Monolithic refractories provide better control over properties, simpler installation, and superior performance, making them the preferred choice in numerous industrial applications.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
High Performance&Temperature Ladle Sliding Gate Steel
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords