Equal angle steel for sale
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Specifications of Equal Angle Steel
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2.Length:6m,9m,12m
3.Material:GBQ235B,Q345BorEquivalent;ASTMA36;EN10025,S235JR,S355JR;JISG3192,SS400;SS540.
 .
.
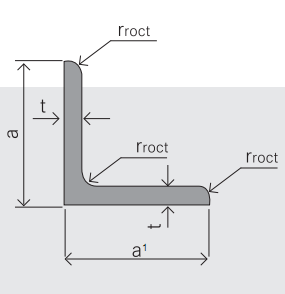
4.Sizes:
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES | |||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
25 | 25 | 2.5---3.0 | 6M/12M |
30 | 30 | 2.5---4.0 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 2.5 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 3.0---5.0 | 6M/12M |
40 | 40 | 3.0---6.0 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3.7---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
60 | 60 | 5.0---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
63 | 63 | 6.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
65 | 65 | 5.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
70 | 70 | 6.0---7.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
75 | 75 | 5.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
80 | 80 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
90 | 90 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
5. Material details:
Alloy No | Grade | Element (%) | |||||
C | Mn | S | P | Si | |||
Q235 | B | 0.12—0.20 | 0.3—0.7 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.3 | |
Alloy No | Grade | Yielding strength point( Mpa) | |||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | ||||
≥ | |||||||
Q235 | B | 235 | 225 | 215 | 205 | ||
Alloy No | Grade | Tensile strength (Mpa) | Elongation after fracture (%) | ||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | ||||
≥ | |||||||
Q235 | B | 375--500 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | |
Usage & Applications of Equal Anlge Steel
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.
- Q:Can steel angles be galvanized or coated for additional protection?
- Yes, steel angles can be galvanized or coated for additional protection. Galvanizing or coating provides a protective layer that helps prevent corrosion and extends the lifespan of the steel angle.
- Q:What are the different grades of steel used in manufacturing steel angles?
- There are several different grades of steel that are commonly used in manufacturing steel angles. These grades vary in terms of their composition, strength, and other properties, and are selected based on the specific requirements of the application. One commonly used grade is mild steel, also known as low carbon steel or A36 steel. This grade is widely available and commonly used due to its affordability and ease of machining. Mild steel angles are often used in general construction and fabrication projects. Another grade is high-strength low-alloy steel (HSLA), which contains small amounts of alloying elements such as copper, phosphorus, niobium, or vanadium. HSLA steels offer higher strength and improved corrosion resistance compared to mild steel, making them suitable for structural applications in heavy machinery or marine environments. There are also higher-strength steels, such as high-strength steel angles (HSS) or ultra-high-strength steel angles (UHSS). These grades are specifically designed to provide exceptional strength and durability, often used in demanding applications such as bridges, high-rise buildings, or automotive components. Stainless steel is another common grade used in manufacturing steel angles. With its excellent corrosion resistance, stainless steel angles are commonly used in food processing, chemical, or marine applications where resistance to rust and staining is crucial. The specific grade of steel used in manufacturing steel angles depends on factors such as load-bearing requirements, corrosion resistance, and cost considerations. Consulting with a structural engineer or steel supplier can help determine the most suitable grade for a particular application.
- Q:How do you determine the load capacity of a steel angle?
- The load capacity of a steel angle is determined by calculating its moment of inertia and considering factors such as material strength, dimensions, and the type of loading it will be subjected to. Additionally, engineering standards and codes provide guidelines for determining load capacities based on these calculations.
- Q:Can steel angles be used for structural support?
- Indeed, steel angles can serve as a means of providing structural support. Construction and engineering endeavors frequently employ steel angles in order to furnish structures with the necessary support and stability. Their application is particularly common in the construction of buildings, bridges, and various other forms of infrastructure. Steel angles possess strength and durability, rendering them suitable for bearing substantial loads and withstanding the forces of compression and tension. Furthermore, their L-shaped design facilitates effortless installation and connection to additional structural elements. By employing steel angles as beams, columns, braces, and other structural components, it is possible to endow a structure with both stability and strength.
- Q:Can steel angles be used in the construction of hospitals?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in the construction of hospitals. Steel angles are versatile and commonly used in various construction projects, including hospitals. They provide structural support, reinforcement, and are often used for framing, bracing, and connecting different components of a building. Steel angles offer strength, durability, and fire resistance, making them suitable for hospital construction where safety and stability are crucial.
- Q:How do you straighten a bent steel angle?
- In order to straighten a bent steel angle, a few tools and equipment will be necessary. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you effectively straighten the bent steel angle: 1. Prioritize safety: Make sure to wear the appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and safety goggles, to safeguard yourself against any potential hazards. 2. Evaluate the damage: Inspect the bent steel angle to gauge the extent of the bend. This will aid in determining the most suitable approach for straightening it. 3. Secure the angle: Firmly place the bent steel angle in a bench vise or clamp to ensure it remains stable. This will prevent any movement during the straightening process. 4. Apply heat (optional): If the bend is severe or the steel angle is hardened, heat may be required to increase its malleability. Utilize a blowtorch or heat gun to heat the bent area until it turns red-hot. 5. Utilize a hammer: With the bent steel angle securely held, gently tap the bent area in the opposite direction of the bend. Start from the outer edges and progressively work towards the center. Employ gradual force and avoid excessive striking, as it may result in further damage. 6. Monitor progress: Periodically release the angle from the vise or clamp to assess the progress. If necessary, reposition the steel angle in a different area within the vise to continue straightening. 7. Repeat if necessary: Depending on the severity of the bend, it may be necessary to repeat steps 4-6 multiple times to achieve the desired straightness. Exercise patience and take your time to prevent overcorrection or additional damage. 8. Test the angle: Once you believe the steel angle is straightened, cautiously remove it from the vise or clamp and test its straightness. Place it on a flat surface and inspect if it lies completely flat without any visible bends or wobbling. Remember, this process requires precision and caution. If you feel uncertain or uncomfortable handling this task, it is advisable to seek assistance from a professional or experienced metalworker who can help you safely and effectively straighten the bent steel angle.
- Q:What is the difference between galvanized steel angle and ordinary angle iron?
- Ordinary steel angle and cold galvanized steel angle per ton difference of about 500 yuan;
- Q:What are the design considerations for using steel angles in architectural applications?
- Some design considerations for using steel angles in architectural applications include structural stability, load-bearing capacity, aesthetic appeal, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation. Steel angles are commonly used to provide support, reinforcement, and stability to various architectural elements such as beams, columns, and frames. The selection of the appropriate size, thickness, and grade of steel angle is crucial to ensure the structural integrity and safety of the building. Additionally, architects may consider the visual impact of steel angles, as they can be exposed or concealed depending on the design intent. The corrosion resistance properties of the steel angles should also be taken into account, especially in applications where exposure to moisture or harsh environments is expected. Lastly, the ease of installation and compatibility with other building materials should be considered to streamline the construction process.
- Q:How do you determine the required length of a steel angle for a specific application?
- To determine the required length of a steel angle for a specific application, several factors need to be considered. 1. Load requirements: Begin by calculating the maximum load that the angle will need to bear. This includes both the weight of the object or structure it will support, as well as any additional live loads such as wind or snow. This load requirement will help determine the necessary strength and size of the angle. 2. Structural analysis: Perform a structural analysis of the intended application to determine the forces and stresses that will be placed on the steel angle. This analysis will help determine the required properties of the angle, such as its moment of inertia, section modulus, and bending capacity. 3. Material selection: Choose the appropriate steel material for the application based on its mechanical properties, such as yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility. Different grades of steel offer different levels of strength and durability, so selecting the right material is crucial for ensuring the angle can withstand the required loads. 4. Design codes and standards: Refer to applicable design codes and standards, such as those set by organizations like the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) or the Eurocode, to ensure compliance with industry regulations and guidelines. These codes provide specific formulas and procedures for calculating the required length and size of the angle based on the load and structural analysis. 5. Fabrication considerations: Consider any fabrication limitations or constraints that may affect the length of the steel angle. For example, standard lengths of steel angles may be available, so it may be necessary to select a length that is readily available or can be easily obtained through custom fabrication. 6. Consultation with professionals: If you are unsure about any aspect of determining the required length of a steel angle, it is advisable to consult with a structural engineer or a professional experienced in steel design. They can provide expert guidance and ensure that the angle is appropriately sized and designed for the specific application. By taking into account these factors and following a systematic approach, you can determine the required length of a steel angle that meets the specific requirements of your application.
- Q:Do steel angles require maintenance?
- Maintenance is necessary for steel angles. Despite being durable, steel can still rust and corrode, especially when exposed to moisture or harsh environments. To prevent these problems and prolong the lifespan of steel angles, regular maintenance is required. Common maintenance practices include checking for rust or damage, cleaning the surface to remove dirt and debris, and applying protective coatings or paints to prevent corrosion. Proper storage and handling also play a role in maintaining steel angles. It is crucial to follow manufacturer instructions and seek advice from experts to determine the specific maintenance needs for steel angles in various applications.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Equal angle steel for sale
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























