Z31 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Z31 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
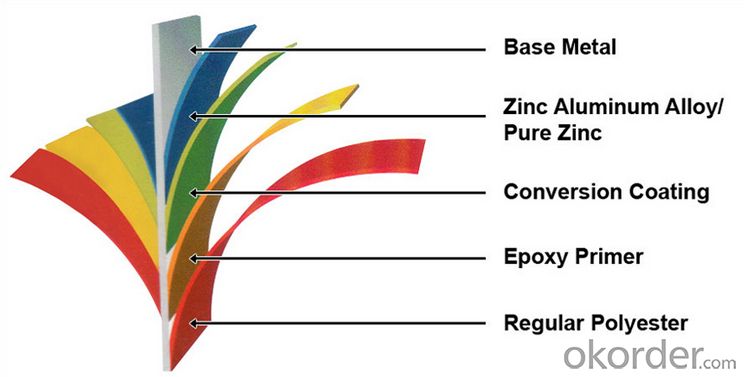
Description of Z31 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
PPGI is made by cold rolled steel sheet and galvanized steel sheets as baseplate, through the surface pretreatment (degreasing, cleaning, chemical conversion processing), coated by the method of continuous coatings (roller coating method),
and after roasting and cooling. Zinc coating: Z60, Z80, Z100, Z120, Z180, Z275, G30, G60, G90
Alu-zinc coating: AZ60, AZ80, AZ100, AZ120, AZ180, G30, G60, G90
Main Feature of Z31 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1) Excellent corrosion resistance: The zinc layer provides a good protection of Pre-painted Galvanizeed Steel Sheet.
2) High heat resistance: The reflective surface of the material aids in efficiently reflecting the sunlight away and in turn reducing the amount of heat transmitted. The thermal reflectivity converts into energy savings.
3) Aesthetics: Pre-Painted Galvanized steel sheet is available in plethora of patterns and multiple sizes as per the requirements that given by our customers.
4) Versatility: can be used in the various areas.Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock, with inner coil sleeve.
Applications of Z31 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture:barn; etc.
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; etc. 
Specifications of Z31 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
| Classified symbol | Yield Point Minimum N/mm2 | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | ||||
| N/mm2 | Nominal Thickness mm (t) | |||||||
| JIS | Yogic | 0.25-0.4 | 0.4-0.6 | 0.6-1.0 | 1.0-1.6 | |||
| G3312 | specification | |||||||
| CGCC | CGCC | -205 | -270 | -20 | -21 | -24 | -24 | Commercial |
| CGCD | CGCD | --- | 270 | --- | 27 | 31 | 32 | Drawing |
| --- | CG340 | 245 | 340 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Structural |
| CGC400 | CG400 | 295 | 400 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC440 | CG440 | 335 | 440 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | Structural |
| CGC490 | CG490 | 365 | 490 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | Structural |
| CGC570 | CG570 | 560 | 570 | --- | --- | --- | --- | Structural |
| ASTM Designation | Yield Point Minimum | Tensile Strength Minimum | Elongation Minimum % | Application | Q/BQB 445-2004(China standard) | ASM A653/A653M | JISG 3312 | |
| ksi(MPa) | ksi(MPa) | TDC51D+Z | (CS TYPE A+Z) | CGCC | ||||
| A653(M)-99 CS TYPE A,B,C | --- | --- | --- | Commercial | TDC52D+Z | CGCD | ||
| A653(M)-99 FS | --- | --- | --- | Lock Forming | TS250GD+Z | (G250+Z) | - | |
| A653(M)-99 DS | --- | --- | --- | Drawing | TS300GS+Z | (G300+Z) | CGC 400 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade33(230) | 33(230) | 45(310) | 20 | Structural | TS350GD+Z | (G350+Z) | CGC490 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade37(255) | 37(255) | 52(360) | 18 | Structural | TS550GD+Z | (G550+Z) | CGC570 | |
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade40(275) | 40(275) | 55(380) | 16 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade50(345) | 50(345) | 65(450) | 12 | Structural | ||||
| A653(M)-99 SS Grade80(550) | 80(550) | 82(570) | --- | Structural | ||||
FAQ of Z31 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. How Can I Visit There?
Our company is located in Tianjin City, China, near Beijing. You can fly to Tianjin Airport Directly. All our clients, from home or aboard, are warmly welcome to visit us!
2. How Can I Get Some Sample?
We are honored to offer you sample.
3. Why choose CNBM?
1, ISO, BV, CE, SGS approved.
2, Competitive price and quality.
3, Efficient service team online for 24 hours.
4, Smooth production ability(50000tons/month) .
5, quick delivery and standard exporting package.
6, Flexible payment with T/T, L/C, Paypal, Kunlun bank, etc .
- Q:How are steel billets used in the production of beams and columns?
- Steel billets are used as a raw material in the production of beams and columns. They are heated and then passed through a series of rolling mills to be shaped into the desired beam or column profiles. The billets provide the necessary strength and durability required for structural applications, ensuring the final products can withstand heavy loads and provide support in construction projects.
- Q:What are the main applications of steel billets in the aerospace industry?
- Steel billets possess exceptional strength, durability, and thermal properties, making them an indispensable component in the aerospace industry. Their numerous applications include the production of aircraft structural components, engine parts, fasteners and connectors, as well as hydraulic and pneumatic systems. A primary application of steel billets in the aerospace industry is seen in the manufacturing of aircraft structural components. These billets are commonly utilized to produce critical parts such as landing gear, wing spars, fuselage frames, and engine mounts. These components provide the necessary strength and stability required for safe and efficient flight. Furthermore, steel billets find use in the aerospace industry for the production of engine components. Their high heat resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures make them ideal for manufacturing turbine blades, shafts, and other critical parts within jet engines. These components must endure intense heat and pressure, and steel billets offer the required properties for reliable and efficient engine performance. Additionally, steel billets play a vital role in the aerospace industry by being applied in the production of fasteners and connectors. These components are crucial for securely joining various parts of an aircraft, ensuring structural integrity and safety during flight. Steel billets are employed to manufacture high-strength bolts, screws, and other fasteners, providing the necessary strength and reliability for aerospace applications. Moreover, steel billets are frequently used in the aerospace industry for the manufacture of hydraulic and pneumatic systems. These systems are responsible for controlling the movement of the aircraft, landing gear operation, and other critical functions. Steel billets are utilized to produce hydraulic cylinders, valves, and tubes, offering the required strength and resistance to withstand high pressures and extreme conditions. In conclusion, the aerospace industry heavily relies on steel billets for various applications, including aircraft structural components, engine parts, fasteners and connectors, as well as hydraulic and pneumatic systems. The exceptional strength, durability, and thermal properties of steel billets ensure the safety, efficiency, and reliability of aerospace operations.
- Q:How are steel billets used in the production of steel cables?
- Steel billets are used in the production of steel cables by being heated and then passed through a series of rollers to shape them into thin, long strands. These strands are then twisted together to form the cables, which are used for various applications such as suspension bridges, elevators, and construction projects. The high strength and durability of steel billets make them ideal for producing strong and reliable steel cables.
- Q:What are the main challenges in the recycling of steel billets?
- The recycling of steel billets, which are semi-finished steel products, poses several challenges. The main challenges in the recycling of steel billets include: 1. Contamination: Steel billets can become contaminated with various materials during their use, such as oil, grease, paint, or other metals. Removing these contaminants and ensuring the purity of the recycled steel can be a complex and costly process. 2. Sorting and segregation: Steel billets come in different grades and sizes, and they need to be sorted and segregated accordingly for effective recycling. This requires advanced sorting technologies and manual labor to ensure the right billets are recycled in the appropriate manner. 3. Energy consumption: The recycling of steel billets involves melting and reprocessing the steel, requiring significant energy inputs. This energy consumption can be a challenge as it contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and increases the overall environmental impact of the recycling process. 4. Infrastructure and logistics: The collection, transport, and processing of steel billets require a well-developed infrastructure and logistics network. The lack of adequate facilities or transportation can hinder the efficient recycling of steel billets. 5. Economic viability: The economic viability of recycling steel billets can be a challenge, especially when the cost of recycling exceeds the value of the recycled material. This can discourage recycling efforts and lead to a higher reliance on primary steel production. 6. Consumer awareness and participation: Educating consumers about the importance of recycling steel billets and encouraging their participation in recycling programs is crucial. Lack of awareness and apathy towards recycling can hinder the collection of steel billets for recycling purposes. 7. International trade barriers: In some cases, trade barriers and import/export restrictions can affect the recycling of steel billets. These barriers can limit the flow of recycled steel billets across different countries, impacting the overall recycling capacity and market dynamics. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort between industries, governments, and consumers. Investments in research and development, technology advancements, and policy support can help overcome these challenges and promote the sustainable recycling of steel billets.
- Q:What is the standard tolerance for steel billet dimensions?
- The standard tolerance for steel billet dimensions can vary depending on the specific industry and application. However, commonly accepted tolerances for steel billet dimensions typically range from +/- 0.5% to +/- 2% of the specified dimensions.
- Q:What are the different types of cleaning methods used for steel billets?
- Steel billets can be cleaned using several methods, each with specific requirements and desired results. Here are some commonly used cleaning methods for steel billets: 1. Acid cleaning: To eliminate rust, scale, and grease, acid solutions are applied. This method effectively removes tough stains and corrosion, but it necessitates careful handling and proper disposal of acidic waste. 2. Shot blasting: High-speed projectiles are used to impact the surface of steel billets, removing rust, scale, and other impurities and leaving a polished finish. Shot blasting is often employed for large-scale cleaning and can be automated for efficiency. 3. Pickling: Steel billets are submerged in an acid solution, typically hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, to eliminate oxide layers and impurities, resulting in a clean and corrosion-resistant surface. 4. Ultrasonic cleaning: By agitating a cleaning solution with high-frequency sound waves, microscopic bubbles are created, aiding in the removal of dirt, grease, and contaminants from the steel billet's surface. This method is particularly effective for fine particles and hard-to-reach areas. 5. Electrolytic cleaning: A direct electric current is used to attract surface impurities from the steel billets. Immersed in an electrolyte solution, the billets undergo cleaning as the impurities adhere to an electrode. 6. Chemical cleaning: Specialized chemicals are employed to dissolve or react with surface contaminants like rust, oil, or paint. The choice of chemicals depends on the type of contaminant and the desired outcome. Chemical cleaning effectively removes both organic and inorganic substances from steel billets. In conclusion, these various cleaning methods offer diverse approaches to achieve a clean and polished surface for steel billets, ensuring their quality and suitability for further processing or applications.
- Q:Can steel billets be used for structural applications?
- Structural applications can indeed utilize steel billets. Steel billets are produced through continuous casting or hot rolling, resulting in semi-finished products with a rectangular cross-section. These billets serve as raw material for the production of various shapes and forms, including structural components. Steel billets possess multiple properties that make them suitable for structural applications. Firstly, steel is renowned for its strength and durability, enabling it to withstand heavy loads and resist deformation. Consequently, steel billets are a reliable choice for constructing buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects. In addition, steel billets can be easily fabricated into different shapes and sizes to meet specific structural requirements. Techniques such as hot rolling, forging, and extrusion can further process them to produce beams, columns, bars, and other structural elements. Furthermore, steel billets offer excellent weldability, facilitating the joining of individual components to create larger structures. This feature makes them an ideal material for construction projects that commonly involve prefabrication and on-site assembly. Overall, steel billets are widely employed in structural applications due to their high strength, versatility in fabrication, and exceptional mechanical properties.
- Q:What are the different types of surface finish defects found in steel billets?
- Steel billets can contain various types of surface finish defects, which can arise from the manufacturing process or from handling and transportation. Common defects include scale, pitting, scratches, roll marks, lamination, decarburization, and surface irregularities. Scale refers to the rough, flaky oxide layer that forms on the billet surface during heating and rolling. It can be removed through different surface cleaning methods. Pitting is the formation of small depressions or craters on the billet surface, caused by factors like corrosion, improper handling, or contamination during processing. Pitting weakens the steel and compromises its integrity. Scratches are visible marks or lines on the billet surface, occurring during handling, transportation, or processing. They can be superficial or deep, with deep scratches potentially requiring further inspection or treatment. Roll marks are impressions or patterns left on the billet surface by the rolling process. They result from improper alignment or wear and tear of the rolling equipment. While they affect the billet's aesthetic appearance, they generally don't impact its structural integrity. Lamination refers to the separation of layers or flakes within the billet, caused by inadequate bonding during manufacturing or excessive rolling. Lamination weakens the steel and compromises its performance. Decarburization is the loss of carbon from the billet surface due to exposure to high temperatures or oxidizing environments. It reduces the steel's hardness and strength. Surface irregularities encompass any distortion or unevenness on the billet surface, such as dents, bulges, or uneven textures. They can be caused by factors like improper handling, machining, or defects in the manufacturing process. It's worth noting that the severity and impact of these surface finish defects can vary. Some defects may have minimal effect on the steel's performance and be purely cosmetic, while others may necessitate further inspection or treatment to ensure the billet's structural integrity.
- Q:What are the different sizes and shapes of steel billets?
- Steel billets come in various sizes and shapes, including square, rectangular, and round. The sizes can range from small billets measuring a few inches to larger ones measuring several feet in length and width. The specific size and shape of a steel billet depend on its intended use and manufacturing requirements.
- Q:How are steel billets different from steel ingots?
- Steel billets and steel ingots, although both semi-finished steel products, vary in their shape, size, and manufacturing process. To begin with, the shape of steel billets and steel ingots differs. Steel billets generally have a square or rectangular shape, with dimensions determined by production requirements. Conversely, steel ingots possess a more irregular shape, often resembling a large block or loaf. The mold used for casting determines the shape of the ingot. Furthermore, the size of steel billets and steel ingots also varies. Billets are typically smaller in size compared to ingots. They are produced with smaller cross-sectional areas and lengths, making them suitable for further processing. In contrast, steel ingots are larger and heavier, as they are cast in molds capable of accommodating a greater volume of molten steel. Finally, the manufacturing process for steel billets and steel ingots differs. Steel billets are typically produced through continuous casting, a process in which molten steel is poured into a water-cooled mold to solidify into the desired shape. This method allows for controlled and efficient production of billets. On the other hand, steel ingots are generally produced through casting in open or closed molds, where the molten steel is poured and left to solidify. This process tends to be slower and less precise compared to continuous casting. In conclusion, steel billets and steel ingots differ in terms of their shape, size, and manufacturing process. Billets are square or rectangular in shape, smaller in size, and produced through continuous casting, whereas ingots possess an irregular shape, larger in size, and are produced through casting in molds. Both products serve as crucial raw materials for the production of various steel products.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Z31 BMP Rolled Steel Coil Construction Roofing Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords

































