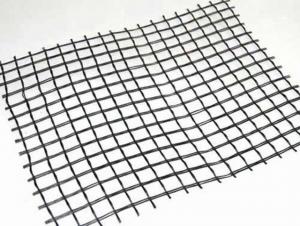
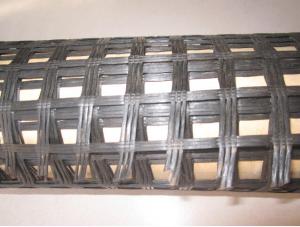
Woven & Knitted Biaxial Plastics Geogrid BX1200 BX1100
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Type:
1) Woven & knitted: use various fiber types (e.g. monofilament, multi-filament, split extruded film) in different combinations.
2)Non-woven: staple or continuous fiber that are heat treated or needle punched to “fix” fiber relative to each other.
Functions:
Major functions: Separation, filtration, drainage, reinforcement, protection, and liquid barrier
1) Filtration
The filtration layer of the dykes, river canal, seacoast, concrete slope, retaining walls. At the same time of preventing the clay granule from passing, it allows the water and the gas pass through freely.
2) Separation
The isolation of the railway dregs and the roadbed, roadbed and the soft base, surface of the airdrome and parking lot and the groundsill, different dam materials. It isolates the soil and the gravel of two kinds of different granule pathway from the groundsill or other buildings.
3 )Adding muscle:
The highway, railway, soil-stone dam, breakwater, airport, backfill soil of retaining wall, slope protection, etc in which distributes the earth stress, prevents the side-displacement of the earth body and improves the earth body stability.
4 )Protection
It prevents the bank from being washed out, protects the bank and the bottom, prevents the water and soil from being washed away.
Specigication:
Quality per unit area(g/m2) | 120g | 160g | 200g | 240g | 280g | 340g | 400g |
After the breaking strength(KN/m)≥ | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 100 |
Zonal breaking strength(KN/m)≥ | 15 | 22 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 56 | 70 |
Latitude and longitude to the elongation at break(%)≤ | 25 | ||||||
Trapezoidal tear strength (longitudinal)(KN)≥ | 0.2 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.48 | 0.6 | 0.72 |
Bursting Strength(KN)≥ | 1.6 | 2.4 | 3.2 | 4.0 | 4.8 | 6.0 | 7. |
Vertical permeability coefficient(cs/m) | 10-1~10-4 | ||||||
Equivalent aperture(O95mm) | 0.07-0.5 | ||||||
Deviation permit(%) | ±10 | ||||||
- Q:What are the factors that affect the performance of geogrids under cyclic loading?
- The factors that affect the performance of geogrids under cyclic loading include the type and quality of the geogrid material, the design and installation of the geogrid, the magnitude and frequency of the cyclic loading, the soil properties and conditions, and the duration of the cyclic loading.
- Q:How do geogrids improve the performance of reinforced soil slopes in seismic areas?
- Geogrids improve the performance of reinforced soil slopes in seismic areas by providing additional stability and strength to the soil structure. They work by distributing and transferring the forces generated during an earthquake throughout the soil mass, reducing the risk of slope failure. Geogrids also enhance the overall tensile strength of the soil, preventing excessive deformation and maintaining the integrity of the slope.
- Q:What is a geogrid?
- A geogrid is a type of synthetic material made from polymers, typically used in civil engineering and construction applications. It is a grid-like structure with open spaces that allow for soil or aggregate to interlock with the grid, providing reinforcement and stability to the ground. Geogrids are commonly used to enhance the strength and load-bearing capacity of soil, preventing soil erosion and improving the performance of structures such as retaining walls, roads, and embankments.
- Q:Are geogrids suitable for use in ground reinforcement for solar farms?
- Yes, geogrids are suitable for use in ground reinforcement for solar farms. Geogrids offer excellent soil stabilization and reinforcement properties, enhancing the load-bearing capacity of the ground and preventing soil erosion. They can effectively distribute the weight of solar panels and equipment, reducing the risk of settlement and ensuring long-term stability. Additionally, geogrids are easy to install, cost-effective, and provide long-lasting performance, making them a suitable choice for ground reinforcement in solar farms.
- Q:Are there any limitations or disadvantages of using geogrids?
- Yes, there are limitations and disadvantages of using geogrids. Some of the limitations include the need for proper installation and maintenance, as improper installation can reduce their effectiveness. Additionally, geogrids may not be suitable for all soil types and conditions, and their performance can vary depending on the specific application. Disadvantages of using geogrids include the potential for high material and installation costs compared to alternative soil stabilization methods. Furthermore, geogrids may not provide long-term stability in highly dynamic or extreme environmental conditions.
- Q:How do geogrids improve the load distribution in foundations?
- Geogrids improve load distribution in foundations by effectively spreading the load over a larger surface area. This is achieved through their high tensile strength and stiffness, which allows them to distribute and transfer the load from the foundation to a wider soil area, reducing stress concentration points. By doing so, geogrids help prevent differential settlement and soil failure, enhancing the overall stability and performance of the foundation.
- Q:Can geogrids be used in ground reinforcement for military installations?
- Yes, geogrids can be used in ground reinforcement for military installations. Geogrids are often employed in various civil engineering applications, including military projects, to enhance soil stability, provide load-bearing support, and improve overall ground reinforcement. They are effective in reinforcing and stabilizing soil, which is essential for military installations that require durable and resilient foundations to withstand heavy equipment, traffic, and potential ground disturbances. Geogrids can also assist in reducing soil erosion, enhancing slope stability, and minimizing the risk of ground movement or settlement, making them a valuable tool in military construction and infrastructure projects.
- Q:What are the potential drawbacks of using geogrids?
- One potential drawback of using geogrids is their high initial cost compared to traditional construction materials. Additionally, geogrids require skilled installation and may have limited availability in certain regions. There is also a risk of improper installation or maintenance, which can lead to reduced effectiveness or failure of the geogrids. Moreover, the long-term durability of geogrids is still being studied, and their performance can be influenced by factors such as UV radiation and chemical exposure.
- Q:What is the tensile strength of a geogrid?
- The tensile strength of a geogrid refers to its ability to withstand pulling forces without breaking. It is typically measured in units of force per unit of width, such as kilonewtons per meter (kN/m). The specific tensile strength of a geogrid can vary depending on its material composition and design.
- Q:Where is the geogrid used?
- For subgrade reinforcement, the particulate filler and each grid locked together, to form a stable plane, prevent filler subsidence, and the vertical load or scattered areas with adverse geographical conditions can use multi-layer reinforcement; 2 shop on the dam and embankment can increase its stability, reduce the area for 3; Pavement Reinforcement, grid and pavement material mix, can effectively disperse the load transfer, avoid cracks; 4 can bear impact load; 5 can withstand higher cyclic load; 6, shorten the construction cycle; 7 in harsh environmental conditions, but also to the construction; 8 can prevent frost caused by pavement subsidence and crack;
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Woven & Knitted Biaxial Plastics Geogrid BX1200 BX1100
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords