Titanium Billet Turbo Compressor Wheel Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Titanium Billet Turbo Compressor Wheel Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
Specification
Steel billet(ingot) by cogging or breakdown of semi-finished products, is the raw material of all kinds of steel mill. Billet section of square, round, flat, rectangular and abnormity of several kinds of, mainly related to the shape of rolled products.
CNBM Q235,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi Billets Steel
Hot Rolled Steel Billets/ Mild Steel Bar/ Billet Steel
Specification (see below)
Standard: GB/JIS/ASTM
Size: 50*50mm-180*180mm
Length: 3-12mtrs or Customised
Steel material: Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
Technique: Hot rolled
FOB Unit Ton Price $250-350 and Usually I will quote you CFR price.
MOQ: Usually 1000-10000MT/size
Shipment:By Container,Bulk Vessel
Packaging Details: bundles with steel strips or as customers's requirements
Delivery time: Usually within 30 days after the deposit/LC
Inspection:Third party inspection before loading.
Technical data
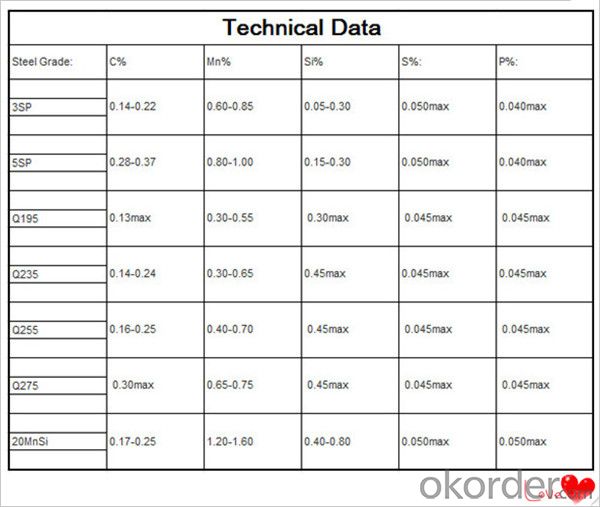
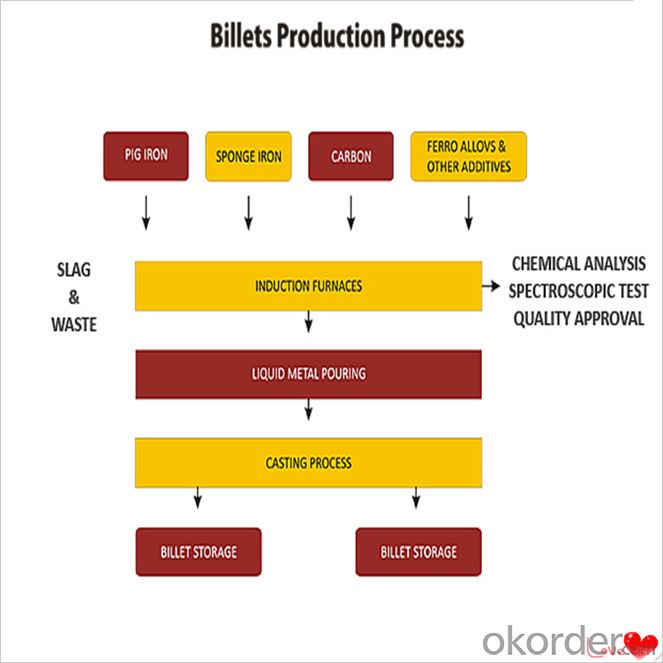
Feature Steel Billet
Rectangular billet continuous casting billet and mainly general carbon steel, low carbon low silicon cold-rolled material, high quality carbon structural steel, high strength low alloy steel, special steel, etc.
The billet is mainly divided into two kinds from the shape:
Slab: cross section width and height of the ratio of the larger, mainly used for rolling plate.
Billet: equal cross section width and height, or a huge difference, mainly used for rolling steel, wire rod. ,
Steel billets have distinct characteristics as compared with already furnished steel bars and products. Billets have a specific grain structure, which enables the metal to be processed more intricately. Steel billets are also known for their malleability and ductility, especially when exposed to varying temperatures during shaping and molding.
Packaging & Shipping
1. Packaging:
1) Small size: in bundles
2)Big size: in bulk
3)in plastic packing or as per customer requirement
2. Delivery time:
1) Normal size: within 7days send from warehouse directly
2) Special size: with 25-30days customer made for you
3. Trade terms:FOB/CFR/CIF
4. Shippment:
1) length:≤5.8m loaded in 20FT Container with 25-27tons
2) length:≤11.8m loaded in 40FT Container with 25-27tons
3) lengnth:≥12m shipped by bulk vessel, FILO terms
Steel Billet Images
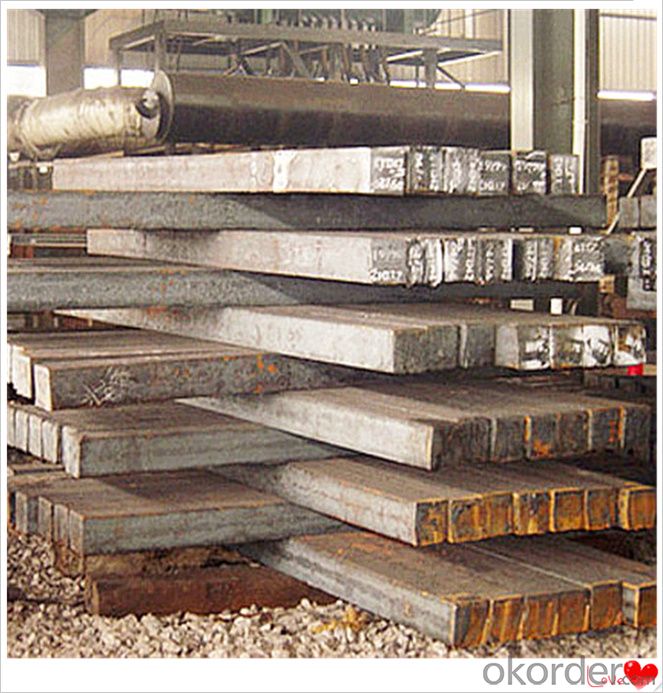
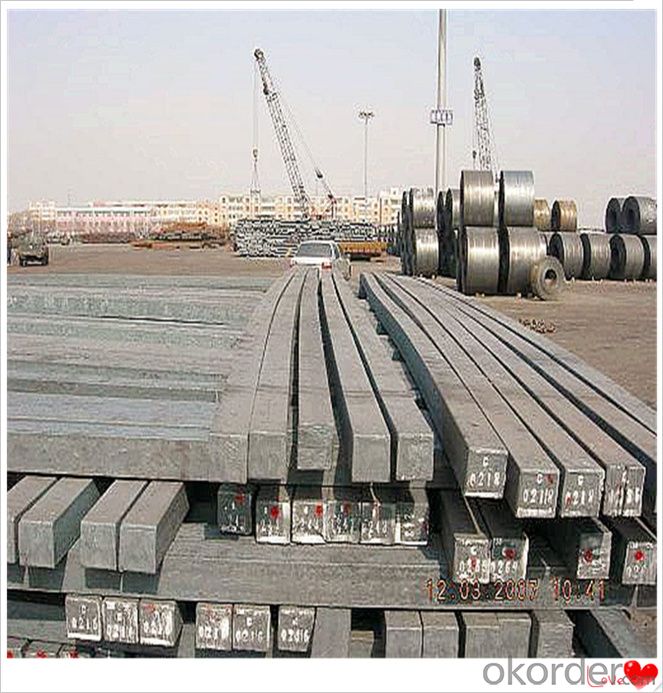






Processing
Usage-Billet Steel
Used for the plant, the bridge,shipment building high-rise building construction,lifting and transportation machinery, equipment manufracturing base building the support foundation pile manufacturing.
Billets, or ingots (as they sometimes referred to), are not of practical use until they have been formed into more functional shapes and sizes. While they have already been put in the furnace, they still require a series of shaping and molding procedures such as hot and cold working, milling and cutting before they are sold in hardware stores, or used for different applications. The unformed billets, however, can be used in striking currency such as coins and as reserves, similar to gold bars.
FAQ-Billet Steel
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1) How about your company?
A world class manufacturer & supplier of castings forging in carbon steel and alloy steel,is one of the large-scale professional investment casting production bases in China,consisting of both casting foundry forging and machining factory. Annually more than 8000 tons Precision casting and forging parts are exported to markets in Europe,America and Japan. OEM casting and forging service available according to customer’s requirements.
2) How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
3) How long can we receive the product after purchase?
In the purchase of product within three working days, We will arrange the factory delivery as soon as possible. The pecific time of receiving is related to the state and position of customers.Commonly 7 to 10 working days can be served.
4)Do you have your own QC department?
Yes, we have, our QC department will inspect the goods during the process of mass production and after completion of production.
hot sale!!! Cast Steel Grades/ mild steel bar/ billet steel
(1): High quality steel with reasonable price.
(2): Wide excellent experiences with after-sale service.
(3): Every process will be checked by responsible QC which insures every product's quality.
(4): Professional packing teams which keep every packing safely.
(5): Trial order can be done in one week.
(6): Samples can be provided as your requirements.
- Q:Can steel billets be used in the production of consumer electronics?
- No, steel billets are primarily used in the production of construction materials and machinery, rather than consumer electronics which typically require more specialized materials such as semiconductors, plastics, and alloys.
- Q:What are the challenges faced in steel billet manufacturing?
- There are several challenges faced in steel billet manufacturing. One of the main challenges is achieving consistent quality and uniformity in the billets. Steel billets need to have a specific chemical composition and physical properties to meet the requirements of the end products they will be used for. However, variations in raw materials, such as iron ore and scrap metal, can affect the quality of the billets. Maintaining consistent quality throughout the production process is crucial but can be difficult due to the variable nature of the raw materials. Another challenge is ensuring the proper heat treatment of the billets. Heat treatment is necessary to enhance the mechanical properties of the steel billets, but it requires precise control of temperature, time, and cooling rates. Any deviation from the recommended heat treatment process can result in inconsistent mechanical properties, leading to a decrease in the overall quality of the billets. In addition, the production of steel billets involves complex and energy-intensive processes. The manufacturing facilities need to have advanced equipment and technology to handle the high temperatures required for melting and casting the steel. The continuous casting process, which is commonly used for billet production, also requires precise control of various parameters, such as casting speed and cooling rates. Maintaining the equipment and ensuring its proper functioning can be a challenge in itself. Moreover, environmental concerns pose challenges in steel billet manufacturing. The process generates significant emissions of greenhouse gases, particulate matter, and other pollutants. Strict environmental regulations and the need to reduce the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process require steel producers to invest in energy-efficient technologies and implement sustainable practices. Lastly, the market demand for steel billets can be volatile, leading to challenges in production planning and inventory management. Fluctuations in demand can result in overproduction or stockouts, which can impact the overall efficiency and profitability of the manufacturing process. Overall, steel billet manufacturing faces challenges in maintaining consistent quality, achieving proper heat treatment, managing energy-intensive processes, addressing environmental concerns, and adapting to market dynamics. Overcoming these challenges requires continuous improvement, investment in technology, and adherence to stringent quality standards.
- Q:What is the typical composition of a steel billet?
- The specific grade and intended use of a steel billet can cause its typical composition to vary. Nevertheless, in general, a steel billet primarily consists of iron, carbon, and additional alloying elements. Steel's main constituent is iron, which typically accounts for about 98% of its composition. This element provides the material with structural strength and durability. Carbon, the second most significant element, usually ranges from 0.02% to 2.1% and plays a vital role in determining the steel's hardness and strength. Besides iron and carbon, steel billets often incorporate various alloying elements to enhance specific properties. These elements may include manganese, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, and others. Each element contributes to different characteristics, such as corrosion resistance, heat resistance, toughness, or machinability. Moreover, steel billets are frequently produced through processes like continuous casting or hot rolling, which can introduce small amounts of impurities. These impurities, such as sulfur, phosphorus, and oxygen, are typically maintained at very low levels to preserve the desired quality of the steel. In conclusion, the typical composition of a steel billet comprises a combination of iron, carbon, alloying elements, and minor impurities. These components are carefully regulated to achieve the desired mechanical properties and performance for a wide range of applications in industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
- Q:What are the main challenges in the storage of steel billets?
- The main challenges in the storage of steel billets include maintaining proper environmental conditions, managing space efficiently, ensuring safety measures, preventing corrosion, and minimizing material damage. Firstly, the storage area should be maintained at a controlled temperature and humidity to prevent the steel billets from being exposed to extreme weather conditions, which could lead to rusting, oxidation, or other forms of corrosion. Adequate ventilation is also necessary to prevent the buildup of moisture that could affect the quality of the billets. Secondly, managing space efficiently is crucial in steel billet storage. Billets are often stored in large quantities, so proper organization and stacking methods must be employed to maximize the storage capacity and facilitate easy access to individual billets when needed. Implementing effective inventory management systems can help prevent unnecessary handling and potential damage. Safety measures are another significant challenge in steel billet storage. Due to their heavy weight and potential for sharp edges, it is essential to ensure proper handling and storage procedures to avoid accidents or injuries. Adequate training for personnel and the use of appropriate lifting equipment are necessary to maintain a safe working environment. Corrosion prevention is a critical concern in steel billet storage. Applying protective coatings, such as oil or rust inhibitors, can help shield the billets from moisture and prevent oxidation. Regular inspections and maintenance routines are also necessary to identify and address any signs of corrosion promptly. Lastly, minimizing material damage is crucial in steel billet storage. Proper handling techniques, such as avoiding dropping or dragging the billets, should be followed to prevent deformation or surface damage. Using suitable packaging or padding materials during transportation and storage can also help protect the billets from scratches or other physical impacts. In conclusion, the main challenges in the storage of steel billets revolve around maintaining proper environmental conditions, efficient space management, ensuring safety measures, preventing corrosion, and minimizing material damage. By addressing these challenges effectively, the longevity and quality of the steel billets can be preserved, resulting in enhanced operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Q:What are the different types of steel billets?
- There are several different types of steel billets, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types include: 1. Carbon Steel Billets: These are the most widely used type of steel billets and are made from iron and carbon. Carbon steel billets are known for their high strength and durability, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including construction, automotive, and machinery manufacturing. 2. Alloy Steel Billets: These billets are made by adding various alloying elements to carbon steel, such as chromium, nickel, or manganese. Alloy steel billets offer enhanced properties such as increased strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. They are often used in industries that require high-performance materials, such as aerospace, oil and gas, and power generation. 3. Stainless Steel Billets: Stainless steel billets are made with a high content of chromium, which provides excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation. They are commonly used in applications where hygiene, durability, and aesthetic appearance are crucial, such as food processing, medical equipment, and architectural structures. 4. Tool Steel Billets: Tool steel billets are specially designed to have high hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance. They are commonly used to make cutting tools, molds, and dies for various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, and construction. 5. Electrical Steel Billets: Electrical steel billets are made from low carbon steel with specific magnetic properties. They are used in the manufacturing of electrical equipment, such as transformers, motors, and generators, where low energy loss and high magnetic permeability are vital. 6. High-speed Steel Billets: High-speed steel billets are alloyed with elements like tungsten, molybdenum, and cobalt, which enable them to retain their hardness and strength at high temperatures. They are widely used to make cutting tools that need to withstand high-speed cutting operations, such as drills, milling cutters, and taps. These are just a few examples of the different types of steel billets available. The choice of steel billet depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as strength, durability, corrosion resistance, or special properties needed for particular industries.
- Q:How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of railway equipment?
- Steel billets play a crucial role in the production of railway equipment. These semi-finished steel products serve as vital raw materials for manufacturing railway components like rails, wheels, axles, and structural parts. To initiate the manufacturing process, the steel billets undergo heating in a furnace until they reach the desired temperature for hot rolling. This heating procedure enhances the malleability and ductility of the steel, facilitating its shaping into the desired railway equipment components. Once the steel billets attain the appropriate temperature, they are then passed through a series of rolling mills. This stage subjects the billets to immense pressure, causing them to elongate and change shape. Known as hot rolling, this process is pivotal in transforming the steel billets into long, slender sections like rails or axles. Following the hot rolling stage, the railway components undergo further processing to achieve the desired shape and specifications. For instance, rails may undergo head hardening to enhance their wear resistance and strength. Similarly, wheels and axles may undergo additional heat treatment processes to improve their mechanical properties and durability. It is essential to note that the quality of the steel billets utilized in the manufacturing process significantly affects the overall quality of the railway equipment. The steel employed should possess specific characteristics such as high strength, toughness, and resistance to wear and fatigue, ensuring the safety and reliability of the final products. To summarize, steel billets are an indispensable component in the manufacturing process of railway equipment. Through hot rolling and subsequent processing, these billets are transformed into various components that form the backbone of rail systems. The quality of the steel billets directly impacts the performance and longevity of the final railway equipment, making them a critical element in the industry.
- Q:What are the challenges faced in the production of steel billets?
- There are several challenges faced in the production of steel billets. Some of the major challenges include ensuring consistent quality and composition of the billets, managing the high temperatures involved in the production process, minimizing energy consumption, and meeting environmental regulations. Additionally, maintaining the proper size and shape of the billets throughout the production process is crucial, as any deviations can lead to subsequent processing issues. Overall, the production of steel billets requires careful monitoring, control, and adherence to strict standards to overcome these challenges.
- Q:What are the different types of casting processes used for shaping steel billets?
- There are several different types of casting processes used for shaping steel billets. These processes include: 1. Continuous Casting: This is the most commonly used method for casting steel billets. In this process, molten steel is poured into a water-cooled mold that is continuously moving. As the steel solidifies, it is continuously pulled out of the mold, resulting in a continuous billet. This process is efficient and allows for high production rates. 2. Centrifugal Casting: In this process, molten steel is poured into a rotating mold. The centrifugal force generated by the rotation distributes the molten metal evenly along the mold walls, resulting in a cylindrical billet. This method is used to produce high-quality and defect-free billets. 3. Ingot Casting: This is a traditional method of casting steel billets. In this process, molten steel is poured into a mold and allowed to solidify. The solidified steel, known as an ingot, is then removed from the mold and further processed to obtain the desired shape of the billet. Ingot casting allows for flexibility in terms of billet shape and size. 4. Sand Casting: This process is used for producing large and complex steel billets. It involves creating a mold using a mixture of sand and a binder material. Molten steel is then poured into the mold, and once it solidifies, the mold is removed to reveal the billet. Sand casting allows for the production of custom-shaped billets but is a slower and less precise process compared to others. 5. Investment Casting: Also known as lost-wax casting, this process is suitable for complex and intricate shapes. In investment casting, a wax pattern of the desired billet shape is created. The wax pattern is then coated with a ceramic shell, and the wax is melted out, leaving behind a hollow mold. Molten steel is poured into the mold, and once it solidifies, the ceramic shell is broken to retrieve the billet. Each of these casting processes has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of process depends on factors such as the desired billet shape, size, production volume, and quality requirements.
- Q:What are the different types of surface finish defects found in steel billets?
- There are several types of surface finish defects that can be found in steel billets. These defects can occur during the manufacturing process or as a result of handling and transportation. Some common types of surface finish defects in steel billets include: 1. Scale: Scale is a type of oxide layer that forms on the surface of steel billets during the heating and rolling process. It appears as a rough, flaky layer that can vary in thickness. Scale can be removed through various surface cleaning methods. 2. Pitting: Pitting is the formation of small, localized depressions or craters on the surface of the steel billet. It can be caused by various factors such as corrosion, improper handling, or contamination during processing. Pitting can weaken the steel and compromise its integrity. 3. Scratches: Scratches are visible marks or lines on the surface of the steel billet. They can occur during handling, transportation, or processing. Scratches can be superficial or deep, depending on the severity. Deep scratches may require further inspection or surface treatment. 4. Roll marks: Roll marks are impressions or patterns left on the surface of the steel billet by the rolling process. These marks can be caused by improper alignment or wear and tear of the rolling equipment. Roll marks can affect the aesthetic appearance of the billet but generally do not impact its structural integrity. 5. Lamination: Lamination is the separation of layers or flakes within the steel billet. It can be caused by inadequate bonding during the manufacturing process or as a result of excessive rolling. Lamination can weaken the steel and compromise its performance. 6. Decarburization: Decarburization is the loss of carbon from the surface of the steel billet. It occurs when the billet is exposed to high temperatures or oxidizing environments. Decarburization can lead to reduced hardness and strength of the steel. 7. Surface irregularities: Surface irregularities refer to any distortion or unevenness on the surface of the steel billet. These can include dents, bulges, or uneven textures. Surface irregularities can be caused by various factors such as improper handling, machining, or defects in the manufacturing process. It is important to note that these surface finish defects can vary in severity and impact on the steel billet. Some defects may be cosmetic and have minimal effect on the performance of the steel, while others may require further inspection or treatment to ensure the structural integrity of the billet.
- Q:Are steel billets used in the manufacturing of oil and gas pipelines?
- Yes, steel billets are commonly used in the manufacturing of oil and gas pipelines. These billets are typically formed into seamless or welded pipes, which are then used to transport oil and gas over long distances. The high strength and durability of steel make it an ideal material for withstanding the harsh conditions encountered in the oil and gas industry.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Titanium Billet Turbo Compressor Wheel Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords

































