Steel Heavy Rail GB2585-81 with High Quality
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specificaions of Steel Heavy Rail GB2585-81 with High Quality:
Production Standard: GB2585-81
Material: 50Mn, U71Mn
Grade | Element(%) | ||||
C | Mn | S | P | Si | |
50Mn | 0.48—0.56 | 0.70—1.00 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | 0.17-0.37 |
U71Mn | 0.65—0.76 | 1.10—1.40 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 | 0.15-0.35 |
Sizes: 38kg, 43kg, 45kg, 50kg, 60kg
Length: 10m, 12m, 12.5m or as the requriement of the clients
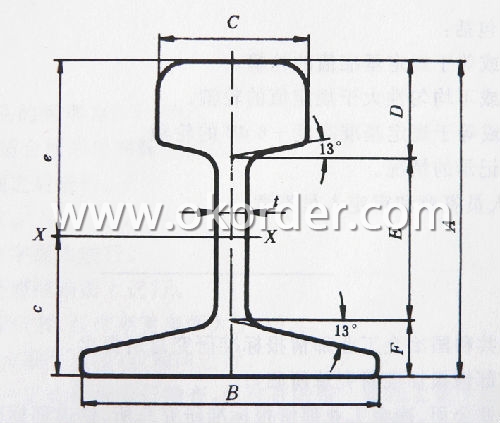
Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
Payment terms: 30% advance payment by T/T, 70% payment against the copy of the B/L; 100% L/C at sight, etc.
Usage & Applications of Steel Heavy Rail GB2585-81 with High Quality:
Heavy Steel Rail is suitable for the laying of main trunk line of the curves and the orbit of the tunnel, can also be used for tower crane and other crane track.
For example: railway, subway, transportation track, express, curve way, tunnel way.
Packaging & Delivery of Steel Heavy Rail GB2585-81 with High Quality:
1. Packing: it is nude packed in bundles by steel wire rod
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load
3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Delivered by container or bulk vessel
6. Delivery Time: All the Ms Heavy Steel Rail will be transpoted at the port of Tianjin, China within 30 days after receiving the advance payment by T/T or the orginal L/C at sight.
Production flow of Steel Heavy Rail GB2585-81 with High Quality:
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation
FAQ:
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
A1: All products offered byOKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: How do we guarantee the quality of our products?
A2: We have established an advanced quality management system which conducts strict quality tests at every step, from raw materials to the final product. At the same time, we provide extensive follow-up service assurances as required.
Q3: How soon can we receive the product after purchase?
A3: Within three days of placing an order, we will begin production. The specific shipping date is dependent upon international and government factors, but is typically 7 to 10 workdays.
Images:


- Q:How are steel rails protected against fire?
- Steel rails are protected against fire through the use of fire-resistant coatings and insulating materials such as fireproof paint or intumescent coatings. These coatings help to prevent the steel from reaching high temperatures during a fire, thereby maintaining its structural integrity and preventing any potential damage. Additionally, fire detection and suppression systems are often installed along rail tracks to quickly identify and extinguish any fire incidents, ensuring the safety of the rail infrastructure.
- Q:What are the potential risks of using steel rails?
- There are several potential risks associated with using steel rails. One major risk is the potential for corrosion. Steel is susceptible to rusting, especially when exposed to moisture and certain environmental conditions. Corrosion can weaken the rails, making them more prone to damage and breakage. This poses a significant safety hazard as it can lead to derailments and accidents. Another risk is the potential for fatigue failure. Steel rails experience constant stress and strain from the weight and movement of trains. Over time, this can lead to the development of cracks and fractures in the rails, known as fatigue failure. If not detected and repaired in a timely manner, these cracks can grow and eventually cause catastrophic failures. Furthermore, steel rails are also subject to wear and tear from the constant friction between the train wheels and the rail surface. This can result in the formation of grooves and flat spots on the rails, which can affect the train's stability and increase the risk of derailment. Additionally, steel rails can be vulnerable to temperature variations. Extreme heat or cold can cause the rails to expand or contract, leading to buckling or misalignment. This can compromise the overall integrity of the track and pose risks to train operations. Lastly, although not directly related to the physical properties of steel rails, there is also a risk associated with the financial cost of maintaining and replacing them. Steel rails require regular inspections, maintenance, and eventual replacement as they reach the end of their lifespan. These expenses can be significant for railway operators, and failure to adequately invest in maintenance can increase the likelihood of accidents and disruptions. Overall, while steel rails have been a reliable and widely used material for railway tracks, it is important to acknowledge and manage the potential risks associated with their use to ensure safe and efficient train operations.
- Q:What are the different types of steel rail sleepers?
- There are several different types of steel rail sleepers, including the conventional rail sleeper, the concrete sleeper with steel inserts, the steel channel sleeper, and the steel lattice sleeper.
- Q:Can steel rails be used in high-temperature environments?
- Yes, steel rails can be used in high-temperature environments. Steel has a high melting point and excellent heat resistance properties, making it suitable for applications in which extreme temperatures are present.
- Q:What are the safety precautions for working with steel rails?
- When working with steel rails, it is important to follow several safety precautions to ensure the well-being of workers and prevent accidents. Here are some key safety measures to consider: 1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear the appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, hard hats, steel-toed boots, gloves, and high-visibility clothing. This will protect against potential hazards, such as sharp edges, flying debris, or falling objects. 2. Training and Competency: Ensure that all workers are adequately trained and competent in handling steel rails. Provide proper training on safe lifting techniques, use of equipment, and awareness of potential hazards. Only authorized and trained personnel should be allowed to work with steel rails. 3. Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly inspect the steel rails for any defects or damage. Look for cracks, bends, loose fasteners, or other signs of wear and tear. Immediately report any issues to the appropriate personnel and remove damaged rails from service until they can be properly repaired or replaced. 4. Manual Handling Techniques: When lifting or moving steel rails, always use proper lifting techniques. Bend at the knees, not the waist, and lift with the legs, not the back. Avoid twisting or jerking motions that could strain muscles or cause injury. If the rails are too heavy to lift manually, use appropriate lifting equipment, such as cranes or forklifts. 5. Secure Storage and Transportation: Store steel rails in a designated area away from pedestrian traffic or other work activities. Ensure that rails are properly secured to prevent them from rolling or falling. When transporting rails, use appropriate equipment and secure them with straps or chains to prevent shifting or falling during transit. 6. Fall Protection: If working at heights or on elevated surfaces, use appropriate fall protection measures, such as guardrails, safety harnesses, or safety nets. Ensure that workers are trained in fall protection techniques and that equipment is regularly inspected, maintained, and used correctly. 7. Communication and Signage: Clearly mark areas where steel rails are being handled or stored with appropriate signage. This will alert workers and visitors to potential hazards and remind them to follow safety precautions. Additionally, maintain open communication between workers, supervisors, and management to address any safety concerns or issues promptly. By implementing these safety precautions, the risk of accidents and injuries when working with steel rails can be significantly reduced. It is crucial to prioritize safety and ensure that all workers are aware of and follow these precautions to maintain a safe working environment.
- Q:Can steel rails be replaced without disrupting train services?
- Train services can continue without interruption even when steel rails need to be replaced. This procedure, known as rail renewal or rail replacement, is carefully carried out by railways following specific maintenance schedules and procedures to ensure efficiency and safety. Typically, rail replacement involves removing old steel rails and installing new ones. This can be done during scheduled maintenance periods when train services are reduced or temporarily halted. Alternatively, rail replacement can take place on weekends or during overnight hours when there is less train activity. To minimize disruption, railway authorities plan rail replacement projects well in advance, taking into account factors such as train schedules, passenger volume, and the availability of alternative transportation options. They collaborate closely with train operators to coordinate the replacement process and minimize the impact on passenger services. Rail replacement is a complex task that goes beyond simply replacing steel rails. It also involves ensuring that the new rails are accurately aligned and securely fastened. Skilled workers and specialized equipment are typically employed to guarantee precise and efficient replacement. By carefully planning and executing rail replacement projects, disruptions to train services can be minimized, allowing passengers to continue traveling safely and efficiently.
- Q:How are steel rails protected against corrosion caused by water and moisture?
- Corrosion prevention or corrosion control is employed to safeguard steel rails from the detrimental effects of water and moisture. Various methods are utilized to ensure the durability and longevity of these rails. One prevalent approach involves the use of protective coatings, such as paint or epoxy. These coatings create a barrier between the steel surface and the surrounding environment, effectively preventing direct contact with water and moisture. Additionally, they seal any existing cracks or imperfections in the rail, further reducing the possibility of corrosion. Another method employed is galvanization, wherein a layer of zinc is applied to the steel rail through either a hot-dip galvanizing process or electroplating. The zinc acts as a sacrificial anode, corroding instead of the steel. This sacrificial process effectively prevents corrosion by sacrificing the zinc coating, rather than the rail itself. Regular maintenance and inspection are also crucial in safeguarding steel rails against corrosion. Periodic inspections are carried out to detect any signs of corrosion or damage, enabling timely repairs or replacement of affected sections. Additionally, routine cleaning and removal of debris from the rail surface help prevent moisture accumulation, thereby reducing the risk of corrosion. Moreover, proper drainage systems are implemented to ensure that water and moisture do not accumulate on or around the steel rails. This prevents prolonged exposure to moisture, which can accelerate the corrosion process. In conclusion, protective coatings, galvanization, regular maintenance, and proper drainage systems are employed to protect steel rails from corrosion caused by water and moisture. These measures minimize contact between the steel surface and corrosive elements, ensuring the long-term integrity and functionality of the rails.
- Q:Can steel rails be used in conjunction with other rail materials?
- Yes, steel rails can be used in conjunction with other rail materials. In fact, it is quite common to have sections of railroad tracks that incorporate different rail materials based on specific requirements such as weight, durability, or cost. This allows for a more efficient and cost-effective rail infrastructure system.
- Q:How are steel rails affected by changes in track curvature?
- Steel rails are affected by changes in track curvature because they experience increased stress and wear. As the curvature of the track increases, the rails are subjected to higher lateral forces and bending moments. This can lead to increased rail wear, fatigue, and even failure if the curvature is too severe. Therefore, proper maintenance and monitoring of track curvature is crucial to ensure the safety and longevity of steel rails.
- Q:What are the different types of steel rail tunnels?
- There are several types of steel rail tunnels, including bored tunnels, cut-and-cover tunnels, immersed tube tunnels, and shield tunnels.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Steel Heavy Rail GB2585-81 with High Quality
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products




























