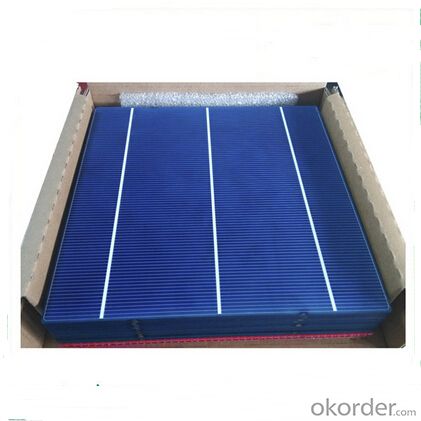
Polycrystalline Solar Cell High Quality 17.2-17.4
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Solar Cells:
solar cells, when struck by photons of light from the sun, generates an electrical current which can then be used to power DC or AC electrical loads.
A solar cell is made of silicon. Computer chips are made of this same material. Basically, when light strikes the surface of a solar cell some of it is absorbed into the silicon. This light energy bumps the electrons loose and causes energy to flow
Solar cells is made by solar wafer, it has three categories of solar cell right now, monocrystalline polycrystalline and thin film,These cells are entirely based around the concept of PN junction, which is the critical part of solar module, it is the part that can convert the light energy into electricity, the thickness is from 180um to 200um, with even busbars to conduct electricity, textured cell can decrease diffuse reflection; they are often electrically connected and encapsulated as a module. Photovoltaic modules often have a sheet of glass on the front (sun up) side, allowing light to pass while protecting semiconductor wafers from abrasion and impact due to wind-driven debris, rain, hail, etc. Solar cells are also usually connected in series in modules, creating an additive voltage. Connecting cells in parallel will yield a higher current;With high quality and stable quality. Our Cells can greatly improve the performance of Solar Modules.
Features:
High efficiencies up to 16.4%
Proven long term mechanical stability of silicone
Make of highly purified poly silicone
Three bus bars for reduced series resistance and improved module and cell efficiency
Blue anti-reflecting coating ensures improved light absorption and increased efficiency
Acid texturization offers a uniform appearance and virtually invisible crystal structure
Excellent low light behavior for improved energy yield
Specifications
Efficiency cell (%) | Maximum power Pmpp(w) | Peak voltage Vmp(V) | Peak current Imp (A) | Open-circuit Voltage Voc(V) | Short-circuit current Isc(A) |
17.2-17.4 | 4.19 | 0.524 | 8.008 | 0.629 | 8.500 |
17.0-17.2 | 4.14 | 0.523 | 7.957 | 0.628 | 8.454 |
16.8-17.0 | 4.09 | 0.520 | 7.883 | 0.627 | 8.362 |
16.6-16.8 | 4.04 | 0.518 | 7.832 | 0.626 | 8.315 |
16.4-16.6 | 3.99 | 0.516 | 7.779 | 0.623 | 8.265 |
16.2-16.4 | 3.94 | 0.514 | 7.772 | 0.620 | 8.210 |
16.0-16.2 | 3.89 | 0.511 | 7.668 | 0.618 | 8.158 |
Solar Cells Advantage:
• High efficiency and stable performance in photovoltaic conversion.
• Advanced diffusion technique ensuring the homogeneity of energy conversion efficiency of the cell.
• Advanced PECVD film forming, providing a dark blue silicon nitride anti-reflection film of homogenous color and attractive appearance.
• High quality metal paste for back surface and electrode, ensuring good conductivity, high pulling strength and ease of soldering.
• High precision patterning using screen printing, ensuring accurate busbar location for ease with automatic soldering a laser cutting.

FAQ
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
①What price for each watt?
It depends on the efficiency of the solar cell, quantity, delivery date and payment terms.
②How long can we receive the product after purchase?
In the purchase of product within three working days, We will arrange the factory delivery as soon as possible. The pecific time of receiving is related to the state and position of customers.Commonly 7 to 10 working days can be served.
③Can you provide the peripheral products of the solar panels, such as the battery, controller, and inverter? If so, can you tell me how do they match each other?
Yes, we can, we have two companies for solar region, one is CNBM International, the other is CNBM engineering Co.
We can provide you not only the solar module but also the off grid solar system, we can also provide you service with on grid plant.
④What is your warranty of solar cell?
Our product can promise lower than 0.3% open box crack, we support claim after opening the box if it has crackm color difference or sth, the buyer should give pictures immediately, we can not accept the claim after the solar cell has assembled to solar panel.
• Timeliness of delivery
• ⑤How do you pack your products?
We have rich experience on how to pack the solar cell to make sure the safety on shipment, we could use wooden box or pallet as buyer's preference.
A solar cell is an electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect. Solar cells are forms of solar modules, themselves coupled into even bigger units known as solar panels or chopped into chips . Just like the cells in a battery, the cells in a solar panel are designed to generate electricity; but where a battery's cells make electricity from chemicals, a solar panel's cells generate power by capturing sunlight instead. They are sometimes called photovoltaic (PV) cells because they use sunlight to make electricity.
In contrast, a solar thermal collector supplies heat by absorbing sunlight, for the purpose of either direct heating or indirect electrical power generation from heat. A "photo electrolytic cell", on the other hand, refers either to a type of photovoltaic cell, or to a device that splits water directly into hydrogen and oxygen using only solar illumination.
In general, a solar cell that includes both solar and nonsolar sources of light (such as photons from incandescent bulbs) is termed a photovoltaic cell. Fundamentally, the device needs to fulfill only two functions: photo generation of charge carriers in a light-absorbing material, and separation of the charge carriers to a conductive contact that will transmit the electricity. This conversion is called the photovoltaic effect, and the field of research related to solar cells is known as photovoltaics.
There is more about the different types of solar cell here. The nominal output voltage of a solar panel is usually 12 Volts, and they may be used singly or wired together into an array. The number and size required is determined by the available light and the amount of energy required.
We can think of light as being made of tiny particles called photons, so a beam of sunlight is like a bright yellow fire hose shooting trillions upon trillions of photons our way. Stick a solar cell in its path and it catches these energetic photons and converts them into a flow of electrons—an electric current. Each cell generates a few volts of electricity, so a solar panel's job is to combine the energy produced by many cells to make a useful amount of electric current and voltage.
Virtually all of today's solar cells are made from slices of silicon, although as we'll see shortly, a variety of other materials can be used as well. When sunlight shines on a solar cell, the energy it carries blasts electrons out of the silicon. These can be forced to flow around an electric circuit and power anything that runs on electricity. That's a pretty simplified explanation!
Historically solar cells have been used in situations where electrical power from the grid is unavailable, such as in remote area power systems, Earth orbiting satellites, consumer systems, e.g. handheld calculators or wrist watches, remote radio-telephones and water pumping applications.
Solar cells are regarded as one of the key technologies towards a sustainable energy supply.
- Q:What is the future of solar cells?
- The future of solar cells looks promising, as advancements in technology continue to improve their efficiency, affordability, and versatility. With ongoing research and development, we can expect to see solar cells become even more efficient in converting sunlight into electricity, allowing for greater energy production. Additionally, innovations in materials and manufacturing techniques may lead to more cost-effective production methods, making solar cells more accessible to a wider range of consumers. Furthermore, integration of solar cells into various surfaces and structures, such as windows, clothing, and vehicles, will likely expand their applications and increase their adoption. Overall, the future of solar cells appears to be characterized by higher efficiency, lower costs, and increased integration, leading to a greater contribution to our global energy needs.
- Q:Is the Photovoltaic cell panel good to save the energy?
- The Photovoltaic cell panel is actually very much developed for saving the energy. After several years of research and development, the third generation solar cells (including various semiconducting properties at the molecular level of the material) has already being used.
- Q:Can solar cells be used in combination with batteries?
- Yes, solar cells can be used in combination with batteries. Solar cells convert sunlight into electrical energy, which can be used to charge batteries. This allows for the storage of excess solar energy during the day and the use of that stored energy during nighttime or when sunlight is not available.
- Q:Can solar cells be used to power irrigation systems?
- Yes, solar cells can be used to power irrigation systems. By converting sunlight into electricity, solar cells can effectively provide a sustainable and renewable energy source to operate irrigation systems, reducing reliance on traditional power sources and promoting eco-friendly practices.
- Q:Can solar cells be used for powering submarines?
- Yes, solar cells can be used for powering submarines to some extent. However, due to limitations in surface area and the amount of sunlight that can penetrate the water, solar power alone is not sufficient to power submarines for long durations or at great depths. Submarines typically rely on a combination of diesel-electric engines and rechargeable batteries for propulsion and power generation.
- Q:What is the environmental impact of solar cells?
- The environmental impact of solar cells is generally considered to be low. While the production process does generate some greenhouse gas emissions and requires the use of certain materials, such as silicon and metals, the overall emissions and resource consumption are significantly lower compared to fossil fuel-based energy sources. Additionally, solar cells do not generate air or water pollution during operation, making them a cleaner and more sustainable option for generating electricity.
- Q:Can solar cells be used in powering electric boats?
- Yes, solar cells can be used to power electric boats. Solar panels can be installed on the boat's surface to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, which can then be used to power the boat's electric motor and other electrical systems. This enables the boat to operate without relying on traditional fuel sources, making it a more environmentally friendly and sustainable option.
- Q:Can solar cells be used in healthcare facilities?
- Yes, solar cells can be used in healthcare facilities. They can be employed to generate electricity, which can power medical equipment, lighting, and other essential systems in healthcare facilities. Solar energy can help reduce reliance on the conventional power grid, providing a sustainable and cost-effective source of electricity for healthcare facilities, especially in remote or off-grid areas. Additionally, solar cells can contribute to reducing carbon emissions and promoting environmental sustainability in the healthcare sector.
- Q:Can solar cells be used in traffic management systems?
- Yes, solar cells can be used in traffic management systems. Solar cells are a renewable and sustainable source of energy that can provide power for traffic lights, road signs, surveillance cameras, and other equipment used in traffic management systems. By relying on solar energy, these systems can reduce their carbon footprint and decrease dependency on grid electricity.
- Q:Can solar cells be used in powering remote weather stations?
- Yes, solar cells can be used to power remote weather stations. Solar cells convert sunlight into electricity, making them an ideal and sustainable power source for remote locations where access to traditional power grids may be challenging. The abundance of sunlight in many regions allows solar cells to efficiently generate electricity, providing a reliable source of power for remote weather stations.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Polycrystalline Solar Cell High Quality 17.2-17.4
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords