Low Carbon Steel C10/C15/C22/C25 Round Bars
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 120000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Low Carbon Steel C10/C15/C22/C25 Round Bars
Product Description
1, Diameter: 8mm-250mm rounds
5mm-9mm rods
2, Length: 2m, 3m, 5.8m, 6m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black, Polished, Galvanized
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Products Show
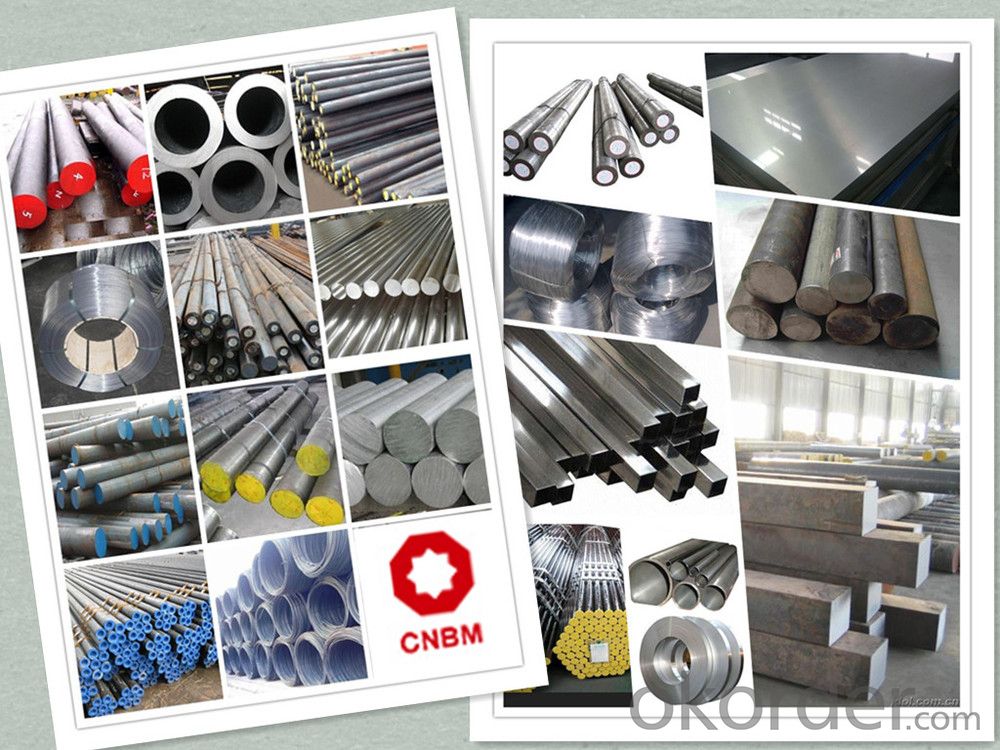

Product Overviews
| Product Name | Typical Grades | Diameter(mm) | Standard adopted |
| Carbon Steel | 20 (1020/S20C/C22) | Ø16-Ø300 |
GB/SAE/JIS/DIN
|
| 40 (1040/S40C/C40) | |||
| 45 (1045/S45C/C45) | |||
| Bearing Steel | GCr9 (51100/SUJ1) | Ø12-Ø250 | |
| GCr15 (52100/SUJ2/100Gr6) | |||
| GCr9SiMn (A485-Gr.1/SUJ3) | |||
Cr-Mo Steel | 20Cr (5120/SCr420H/20Cr4) | Ø12-Ø250 | |
| 40Cr (5140/SCr440/41Cr4) | |||
| 42CrMo(4140/SCM440/42CrMo4) | |||
| Gear Steel | 20CrNiMo | Ø16-Ø600 | |
| 20CrMn(5115/SMnC420/20MnCr5) | |||
| 20CrNiMo(8620/SNCM220/20CrMiMo2) |
Application
| Carbon Steel | Mold bottom, Plastic mold, Construction machinery parts Automobile parts, Security grills, Screens, Construction |
| Bearing Steel | Aerospace, Navigation, Nuclear energy, Chemical industry Electronic information, Petrochemical, Instrument and meter Transportation |
| Cr-Mo Steel | Mechanism & Fasteners gear, Stressed components for vehicles Engines and machines, Parts of larger cross-section |
| Gear Steel | All kinds of gears, Statically and dynamically stressed component for vehicles Engines and machine, Larger cross-section parts, Crankshafts |
Work Shop
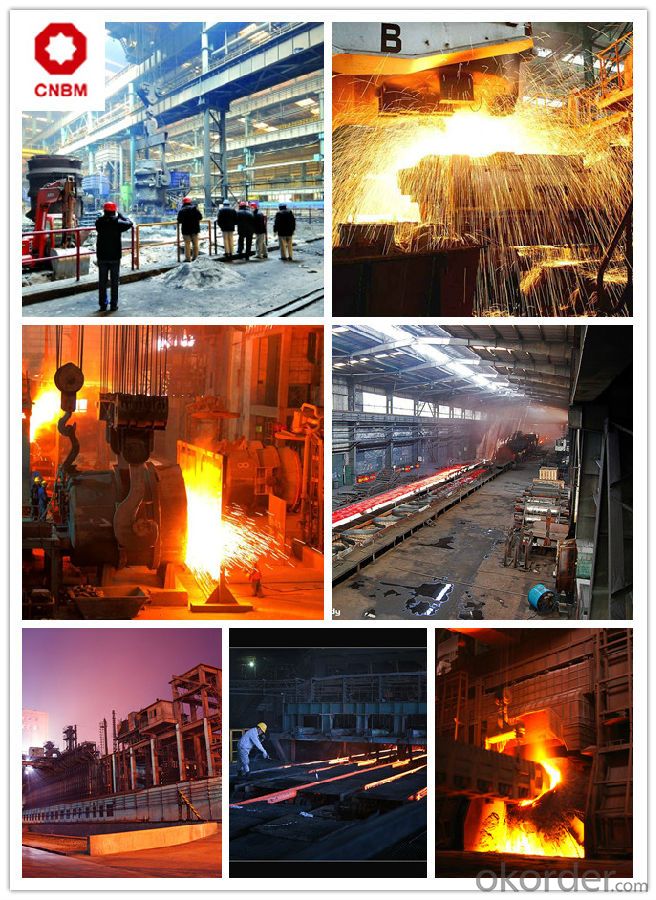

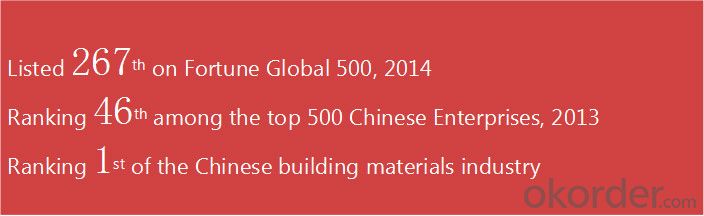
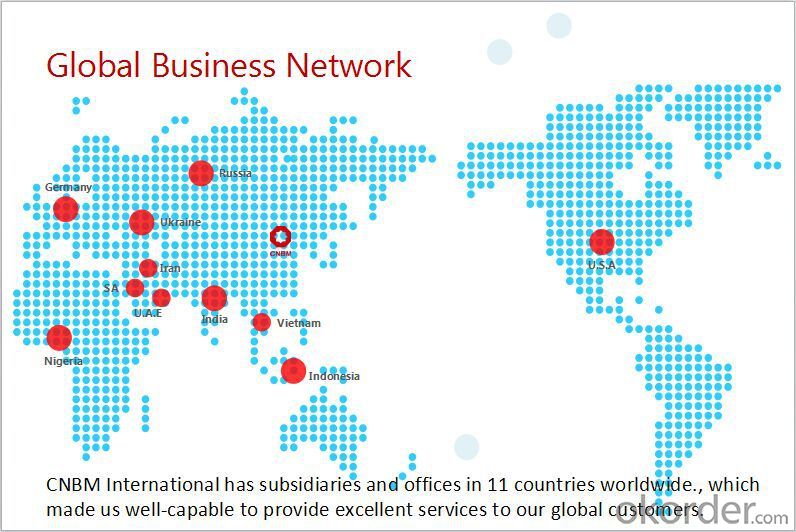
Company Information
FAQ
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
Packaging & Delivery
1, Packaging: seaworthy package or as required
2, Delivery: 35-45 days or based on quantity

- Q:How do you calculate the fatigue strength of a steel round bar?
- The fatigue strength of a steel round bar can be calculated using various methods, such as the stress-life (S-N) curve approach or the strain-life (ε-N) curve approach. 1. Stress-Life (S-N) Curve Approach: This method involves plotting the stress amplitude (S) against the number of cycles to failure (N) on a log-log scale. The S-N curve is obtained by subjecting multiple specimens of the steel round bar to different stress levels and measuring the number of cycles to failure for each stress level. The fatigue strength of the steel round bar can be determined by identifying the stress level at which the desired number of cycles to failure is achieved, typically referred to as the endurance limit. 2. Strain-Life (ε-N) Curve Approach: This method involves plotting the strain amplitude (ε) against the number of cycles to failure (N) on a log-log scale. Similar to the S-N curve approach, multiple specimens of the steel round bar are subjected to different strain levels, and the number of cycles to failure is measured. The strain-life curve can then be used to determine the fatigue strength by identifying the strain level corresponding to the desired number of cycles to failure. It is important to note that calculating the fatigue strength of a steel round bar requires conducting fatigue tests on representative specimens under controlled conditions. These tests involve subjecting the specimens to cyclic loading, typically in the form of tension-compression cycles, and recording the number of cycles to failure. The obtained data is then used to construct the S-N curve or the ε-N curve, which provides valuable information about the fatigue behavior and strength of the steel round bar.
- Q:What is the hardness of a steel round bar?
- The hardness of a steel round bar may differ depending on the type of steel and the manufacturing process utilized. To measure the hardness of steel, the Rockwell hardness scale is commonly employed. This scale determines the depth of indentation caused by a specific load on a diamond or steel ball. Steel round bars generally exhibit hardness values ranging from approximately 20 to 60 Rockwell C (HRC), with higher values indicating greater hardness. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that the hardness of a steel round bar can also be affected by factors such as heat treatment, alloying elements, and any applied surface treatments. Consequently, it is imperative to refer to the manufacturer or supplier's specified hardness specifications to accurately ascertain the hardness of a steel round bar.
- Q:What is the maximum weight that can be lifted using a steel round bar as a lifting rod?
- The maximum weight that can be lifted using a steel round bar as a lifting rod depends on several factors such as the diameter and length of the bar, the material composition and quality of the steel, and the lifting technique employed. Steel round bars have different load-bearing capacities based on their dimensions and grade. The load-bearing capacity of a steel bar can be calculated using engineering principles and formulas specific to the material and geometry of the bar. To determine the maximum weight that can be lifted with a particular steel round bar, it is necessary to consider its ultimate tensile strength (UTS), yield strength, and factor of safety. The UTS represents the maximum stress a material can withstand before failure, while the yield strength is the stress at which permanent deformation occurs. The factor of safety is a design parameter that accounts for uncertainties and ensures structural integrity. It is crucial to consult engineering references, standards, or professionals to obtain accurate and reliable information regarding the load-bearing capacity of a specific steel round bar. They can provide the necessary calculations, taking into account the diameter, length, and material properties of the bar, as well as the intended lifting application and safety requirements. In summary, the maximum weight that can be lifted using a steel round bar as a lifting rod depends on various factors and cannot be determined without considering the specific characteristics of the bar and the lifting scenario. Consulting engineering resources or experts is essential to ensure safe and accurate calculations.
- Q:What are the different types of steel round bar surface treatments for improved hardness?
- There are several different types of steel round bar surface treatments that can be used to improve hardness. These treatments are designed to enhance the strength and durability of the steel, making it more resistant to wear and tear. Some of the common surface treatments for improved hardness include: 1. Heat Treatment: This is a widely used method where the steel round bar is heated to a specific temperature and then cooled rapidly to alter its microstructure. This process can increase the hardness of the steel, making it suitable for applications that require high strength and toughness. 2. Nitriding: Nitriding involves exposing the steel round bar to a nitrogen-rich environment at high temperatures. This treatment forms a hard layer of nitrides on the surface of the steel, enhancing its hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue life. 3. Carbonitriding: Similar to nitriding, carbonitriding involves introducing both carbon and nitrogen into the steel round bar's surface. This treatment creates a hard and wear-resistant layer while maintaining a tough core. Carbonitriding is commonly used for applications that require a combination of hardness and toughness. 4. Induction Hardening: In this process, the steel round bar is heated through electromagnetic induction and then rapidly cooled. This treatment selectively hardens the surface of the steel, leaving the core relatively unaffected. Induction hardening is effective in improving the hardness and wear resistance of specific areas, such as gears or shafts. 5. Chroming: Chrome plating is a surface treatment method where a layer of chromium is deposited onto the steel round bar's surface. This treatment provides excellent hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance. Chroming is commonly used for applications exposed to harsh environments or for parts that require a smooth and hard surface. 6. Shot Peening: Shot peening involves bombarding the steel round bar's surface with tiny metal or ceramic particles at high speed. This treatment induces compressive stress, which improves the material's hardness, fatigue strength, and resistance to crack initiation and propagation. It is important to note that the choice of surface treatment for improved hardness depends on the specific requirements of the application, the type of steel used, and the desired mechanical properties. Consulting with a materials engineer or specialist is recommended to determine the most suitable treatment for a particular steel round bar.
- Q:What is the difference between a hot rolled and a precision ground steel round bar?
- The manufacturing processes and resulting surface finishes of a hot rolled steel round bar and a precision ground steel round bar are the primary factors that differentiate them. Hot rolled steel round bars are created by heating the steel billet or ingot to high temperatures and passing it through a series of rollers to achieve the desired shape and size. This method yields a rougher surface finish with visible mill-scale or oxide layers. Additionally, the hot rolling process allows for variations in size and shape, making it a cost-effective choice for producing steel round bars in large quantities. On the other hand, precision ground steel round bars undergo a more refined and controlled manufacturing process. After the initial hot rolling, the bar is ground to achieve a smooth and consistent surface finish. Precision grinding eliminates the mill-scale and oxide layers, resulting in a more polished appearance. This process also ensures tight dimensional tolerance and improved straightness of the round bar. The selection between a hot rolled and a precision ground steel round bar depends on the specific application requirements. Hot rolled round bars are commonly used in applications where surface finish is not crucial, such as structural components, machinery parts, or construction materials. In contrast, precision ground steel round bars are employed in applications that demand a smooth surface finish, precise dimensions, and tight tolerances, such as in the production of precision tools, machinery components, or in industries like aerospace or automotive. In conclusion, the key distinction between a hot rolled and a precision ground steel round bar lies in their manufacturing processes and resulting surface finishes. Hot rolled round bars offer cost-effectiveness and versatility, while precision ground round bars provide a smoother surface finish, tighter tolerances, and improved dimensional accuracy for more demanding applications.
- Q:What are the different grades of steel used for round bars?
- There are several different grades of steel that are commonly used for round bars. These grades vary in their composition and properties, making them suitable for different applications. Some of the most common grades of steel used for round bars include: 1. Mild Steel (Low Carbon Steel): This is the most basic and widely used grade of steel. It has a low carbon content, which makes it easy to work with and relatively inexpensive. Mild steel round bars are commonly used in construction, automotive, and general engineering applications. 2. Carbon Steel: This grade of steel contains higher levels of carbon than mild steel, giving it improved strength and hardness. Carbon steel round bars are often used in high-stress applications, such as structural components, axles, and shafts. 3. Alloy Steel: Alloy steel round bars are made by adding various alloying elements, such as chromium, nickel, or molybdenum, to the base steel. This enhances the strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance of the material. Alloy steel round bars are commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and machinery industries. 4. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is a corrosion-resistant grade of steel that contains high levels of chromium. It is known for its excellent strength, durability, and resistance to rust and staining. Stainless steel round bars are widely used in the food industry, marine applications, and architectural components. 5. Tool Steel: Tool steel round bars are specifically designed to have high hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance. They are commonly used in the manufacturing of cutting tools, dies, and molds. These are just a few examples of the different grades of steel used for round bars. Each grade offers unique properties and characteristics, allowing for a wide range of applications across various industries.
- Q:What is the difference between a forged and a peeled steel round bar?
- A forged steel round bar and a peeled steel round bar are both types of steel bars used in various industries for different applications. However, there are distinct differences between the two in terms of their manufacturing processes and physical characteristics. A forged steel round bar is made by heating a solid steel billet to a high temperature and then applying pressure to shape it into the desired form. This process involves the use of machinery, such as hammers or presses, to shape the steel and create the round bar. The forging process imparts strength and durability to the steel, making it suitable for applications that require high strength and resistance to wear and tear. On the other hand, a peeled steel round bar is produced through a different manufacturing process known as peeling or turning. In this process, a solid steel bar is rotated against a cutting tool, which removes the outer layer of the bar, resulting in a smooth and precise surface finish. Peeling removes any surface defects or imperfections present in the original bar, improving its dimensional accuracy and surface quality. In terms of physical characteristics, forged steel round bars typically have a rougher surface texture due to the nature of the forging process. This rough texture can provide enhanced grip or adhesion when used in certain applications. Additionally, forged bars often have a denser and more uniform internal grain structure, which contributes to their superior mechanical properties. Peeled steel round bars, on the other hand, possess a smooth and shiny surface finish as a result of the peeling process. This smooth surface makes peeled bars suitable for applications that require aesthetic appeal or require a low coefficient of friction. However, the peeling process may result in a slight reduction in the overall diameter of the bar. In summary, the main difference between a forged and a peeled steel round bar lies in their manufacturing processes and resulting physical characteristics. Forged bars are created through the application of pressure, resulting in a rougher surface texture and superior mechanical properties. Peeled bars, on the other hand, are produced by removing the outer layer of a steel bar, resulting in a smooth surface finish and improved dimensional accuracy. The choice between these two types of bars ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application at hand.
- Q:How can stainless steel rounds occur? Is it a quality problem?
- Cracks caused by surface folding, cracks and steel surface of 15 degrees to 75 degrees angle, about 1.5 ~ 3.5mm, tail vortex shape, slightly decarburization on both sides, decarburization layer 0.15 ~ 0.25mm, crack in the presence of oxide scales. Its macro shape is in the surface of the round steel along the rolling direction into a straight line or zigzag, continuous or intermittent appear in the partial or full length of steel. This shows that this is a folding process in the process of rolling steel. Main reasons of folding is finished before the workpiece with a handleonapot; secondly, in the process of rolling each pass from the handle, flash, serious scratch, damage, and roll ring groove wear etc., can make the product surface folding; in addition, such as the serious defect of blank, if cleaning may also be caused by improper finished folding. Therefore, the main measures to reduce or avoid folding appear: pass through reasonable design, accurate estimation of the spread, precisely adjust the position of roller groove, reduce or eliminate the finished product before rolling the handle, flash, scratches and other defects; the serious defects of the blank surface carefully cleaned.
- Q:What are the advantages of using tin-alloy steel round bars?
- Tin-alloy steel round bars offer several benefits in various industries: 1. Corrosion Resistance: Due to the presence of tin, these bars have exceptional resistance to corrosion. They are suitable for industries exposed to moisture, chemicals, or harsh environments like marine, automotive, and construction. 2. Enhanced Machinability: Tin-alloy steel round bars are known for their superior machinability. The addition of tin makes them easier to cut, drill, and shape, reducing tool wear and increasing productivity during machining. 3. Strength and Durability: By alloying tin with steel, these bars become stronger and more durable. They have higher tensile strength and hardness compared to regular steel bars, making them resistant to wear, deformation, and fatigue. This ensures longevity and suitability for heavy-duty applications. 4. Efficient Heat Transfer: Tin-alloy steel round bars exhibit excellent thermal conductivity. They are ideal for applications that require efficient heat transfer, such as heat exchangers, radiators, and engine components. 5. Reduced Friction: Compared to regular steel bars, tin-alloy steel round bars have a lower friction coefficient. This makes them suitable for applications where minimizing friction is crucial, like bearings, shafts, and gears. It results in reduced energy consumption and increased operational efficiency. 6. Cost-Effective Alternative: Tin-alloy steel round bars offer a cost-effective alternative to pricier materials like stainless steel or brass. They provide similar performance characteristics at a lower price point, making them a viable choice for various applications without compromising on quality. In conclusion, the advantages of using tin-alloy steel round bars include corrosion resistance, improved machinability, strength and durability, efficient heat transfer, reduced friction, and cost-effectiveness. These properties make them versatile and reliable for diverse applications across different industries.
- Q:How do you calculate the maximum allowable stress for a steel round bar?
- To calculate the maximum allowable stress for a steel round bar, you need to determine the material's yield strength and apply a safety factor. The formula is: Maximum Allowable Stress = Yield Strength / Safety Factor. The safety factor typically depends on the application and industry standards.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Low Carbon Steel C10/C15/C22/C25 Round Bars
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 120000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products


































