jisangle
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Specifications of GB Q235 Angle Steel
1. Standards: GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
3. Material:Material: GB Q235B, Q345B or Equivalent; ASTM A36; EN 10025, S235JR, S355JR; JIS G3192, SS400;
SS540.
4. Sizes:
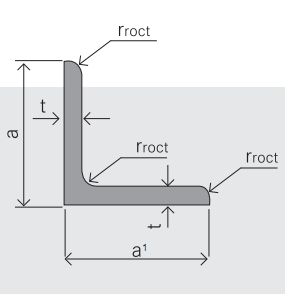
Sizes: 25mm-250mm | ||
a*t | ||
25*2.5-4.0 | 70*6.0-9.0 | 130*9.0-15 |
30*2.5-6.6 | 75*6.0-9.0 | 140*10-14 |
36*3.0-5.0 | 80*5.0-10 | 150*10-20 |
38*2.3-6.0 | 90*7.0-10 | 160*10-16 |
40*3.0-5.0 | 100*6.0-12 | 175*12-15 |
45*4.0-6.0 | 110*8.0-10 | 180*12-18 |
50*4.0-6.0 | 120*6.0-15 | 200*14-25 |
60*4.0-8.0 | 125*8.0-14 | 250*25 |
5. Material details:
Alloy No | Grade | Element (%) | |||||
C | Mn | S | P | Si | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Q235 | B | 0.12—0.20 | 0.3—0.7 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.3 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Alloy No | Grade | Yielding strength point( Mpa) | |||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | ||||
≥ | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Q235 | B | 235 | 225 | 215 | 205 | ||
Alloy No | Grade | Tensile strength (Mpa) | Elongation after fracture (%) | ||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
| ≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | |||
≥ | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Q235 | B | 375--500 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | |
Usage & Applications of GB Q235 Angle Steel
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.
Packaging & Delivery of GB Q235 Angle Steel
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: There will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
- Q:Are steel angles suitable for agricultural applications?
- Yes, steel angles are suitable for agricultural applications. They are commonly used in the construction of agricultural buildings, fences, and equipment due to their strength, durability, and versatility. Steel angles provide stability and support, making them ideal for various agricultural tasks such as framing structures, reinforcing corners, or creating sturdy connections.
- Q:How are steel angles protected during transportation and storage?
- To ensure the preservation and quality of steel angles during transportation and storage, various measures are taken. One commonly employed method involves the application of a protective coating or paint to the surfaces of the steel angles. This coating acts as a barrier, shielding the angles from moisture and preventing the occurrence of rust and corrosion. Moreover, plastic wrapping or tarp covering can be utilized to safeguard the angles against dirt, dust, and other contaminants. During transportation, the risk of shifting or falling is minimized by securing the steel angles in bundles or arranging them in a manner that reduces such hazards. Additionally, pallets or skids may be employed to facilitate handling and prevent direct contact with the ground. When stored, it is crucial to keep the steel angles in a well-ventilated and dry area in order to prevent the accumulation of moisture. Furthermore, proper labeling and handling instructions play a vital role in preventing mishandling or damage during transportation. This entails the use of appropriate lifting equipment and avoidance of rough handling that could potentially lead to bending or deformation. By implementing these protective measures, the integrity and quality of steel angles can be upheld throughout the transportation and storage processes, ensuring their readiness for use.
- Q:What are the different types of surface defects in steel angles?
- Steel angles can be affected by various types of surface defects, which can have negative effects on their appearance, strength, and overall quality. Common surface defects in steel angles include: 1. Scale: When steel is exposed to high temperatures during manufacturing or processing, a thin layer of iron oxide, known as scale, can form on its surface. Scale not only affects the appearance of the steel but can also lead to corrosion if not removed. 2. Pits: Small depressions or cavities on the steel surface, known as pits, can be caused by corrosion, improper handling, or manufacturing defects. Pits weaken the steel and reduce its overall strength. 3. Scratches: Grooves or marks on the steel surface caused by abrasion or contact with other objects are referred to as scratches. While scratches may not affect the structural integrity of the steel, they can impact its appearance and serve as potential starting points for corrosion. 4. Inclusions: Non-metallic particles or impurities that become trapped within the steel during the manufacturing process are called inclusions. Inclusions can weaken the steel, leading to reduced strength and potential failure under load. They can be caused by improper steelmaking techniques or the presence of foreign materials. 5. Laminations: Layers or sheets of metal that are improperly bonded together during the manufacturing process are known as laminations. Improper rolling or welding techniques can cause laminations to occur. Laminations weaken the steel, reducing its strength and potentially causing failure. 6. Corrosion: When steel is exposed to moisture and oxygen, a chemical reaction known as corrosion occurs, resulting in the formation of rust or other corrosion products on the steel surface. Corrosion weakens the steel and reduces its overall integrity. To ensure the quality and performance of steel angles, it is important to identify and address these surface defects. Regular inspection, proper handling, and appropriate surface treatment can help minimize the occurrence and impact of these defects.
- Q:Are steel angles fire resistant?
- Yes, steel angles are generally considered to be fire resistant. Steel is an inherently non-combustible material and has a high melting point, making it able to withstand high temperatures during a fire. Steel angles, which are L-shaped structural members, are commonly used in construction and engineering applications due to their strength and durability. In fire conditions, steel angles can maintain their structural integrity and resist deformation, which is crucial for the safety of a building or structure. However, it is important to note that the fire resistance of steel angles can be affected by factors such as the size and thickness of the angles, the type of fire protection measures applied, and the duration and intensity of the fire. Fire protection measures like fire-resistant coatings, fire barriers, and fireproofing materials can be used to enhance the fire resistance of steel angles and improve the overall fire safety of a structure.
- Q:What are the different types of surface finishes available for steel angles?
- There are several different types of surface finishes available for steel angles, each providing unique characteristics and benefits. 1. Mill Finish: This is the most basic and common type of surface finish for steel angles. It is essentially the raw, untreated surface of the steel, which may have some imperfections and roughness. Mill finish is often used for structural applications where aesthetics are not a priority. 2. Hot-Dip Galvanized: This surface finish involves immersing the steel angle in a bath of molten zinc, creating a protective coating that prevents corrosion. Hot-dip galvanized steel angles are highly resistant to rust and can be used in outdoor or corrosive environments. 3. Powder Coated: Powder coating is a process where a dry powder is electrostatically applied to the steel angle and then cured under heat. This creates a durable and attractive finish that provides excellent resistance to chipping, scratching, and fading. Powder coated steel angles are commonly used in architectural and decorative applications. 4. Painted: Steel angles can also be painted with various types of paint, such as epoxy, enamel, or acrylic. Paint provides a protective layer and can enhance the appearance of the steel angle. However, painted surfaces may be more susceptible to chipping and require periodic maintenance. 5. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel angles have a naturally smooth and polished surface due to their composition. They are highly resistant to corrosion and staining, making them suitable for applications in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine environments. 6. Shot Blasting: Shot blasting is a surface treatment process where steel angles are bombarded with small metallic or non-metallic particles at high velocity. This removes any rust, scale, or contaminants from the surface, resulting in a clean and roughened finish. Shot blasting prepares the steel angle for further coating or painting. These are just a few examples of the different types of surface finishes available for steel angles. The choice of finish depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as corrosion resistance, aesthetics, durability, and cost.
- Q:Are steel angles available in non-standard dimensions?
- Steel angles in non-standard dimensions can be obtained. Although standard steel angles are typically manufactured in specific sizes, such as 2x2 inches or 3x3 inches, there are manufacturers and suppliers capable of producing steel angles in custom sizes to fulfill specific project requirements. These custom sizes may involve varying leg lengths, thicknesses, or overall dimensions that are not commonly found in standard steel angles. Achieving the desired dimensions can be accomplished through processes like cutting, bending, and welding when fabricating custom steel angles. Nevertheless, it is important to consider that non-standard dimensions may result in additional time and cost for production compared to readily available standard sizes.
- Q:What are the common uses of unequal steel angles?
- Unequal steel angles are commonly used in construction, engineering, and fabrication projects. They are often used as structural supports, providing stability and strength in frameworks, buildings, and bridges. These angles are also used for creating bracing systems, reinforcing corner joints, and as components in machinery and equipment. Additionally, they are utilized in architectural designs for decorative purposes, adding aesthetic appeal to structures.
- Q:What are the different types of steel angle profiles?
- There are several different types of steel angle profiles, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types include: 1. Equal angle: This type of steel angle has equal sides and is typically used for structural purposes, such as supporting beams or framing. It provides equal strength and stability in both directions and is often used in construction and manufacturing industries. 2. Unequal angle: As the name suggests, this type of steel angle has unequal sides. It is commonly used in applications where more strength is required in one direction, such as supporting shelves or bracing components. Unequal angle profiles are also used in the construction of bridges and buildings. 3. L-shaped angle: This type of steel angle has one side that is longer than the other, forming an L shape. It is commonly used as a support or bracket in various applications, including furniture manufacturing, automotive industry, and construction. 4. Slotted angle: Slotted angle profiles have holes or slots along the length of the angle, allowing for easy attachment and adjustment of components. They are often used in shelving units, workbenches, and storage systems, providing flexibility and versatility in design. 5. Stainless steel angle: Stainless steel angles are made from corrosion-resistant steel, making them suitable for applications in environments where moisture and harsh chemicals are present. They are commonly used in food processing, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. 6. Galvanized angle: Galvanized steel angles are coated with a protective layer of zinc, which helps prevent corrosion and rusting. They are widely used in outdoor applications, such as fencing, signposts, and support structures, where exposure to weather elements is a concern. These are just a few examples of the different types of steel angle profiles available, each offering specific advantages and applications depending on the project requirements.
- Q:How do you cut steel angles to size?
- To cut steel angles to size, there are several methods you can use depending on the tools available to you. Here are a few common approaches: 1. Using an Angle Grinder: An angle grinder is a versatile tool that can be used to cut steel angles. Ensure you have a cutting disc suitable for metal cutting attached to the grinder. Measure and mark the desired length on the angle, then securely clamp it down. Using the grinder, carefully follow the marked line, applying even pressure to cut through the steel. Take necessary safety precautions, such as wearing protective eyewear and gloves, and be aware of any sparks produced during the cutting process. 2. Utilizing a Bandsaw: If you have access to a bandsaw, it can be an efficient tool for cutting steel angles. Ensure the bandsaw is equipped with a blade specifically designed for metal cutting. Securely clamp the angle, aligning the marked line with the blade's path. Start the bandsaw and slowly feed the angle into the blade, maintaining a steady pace to achieve a clean cut. 3. Using a Hacksaw: Although it may be a slower process, a hacksaw can also be used to cut steel angles. First, securely clamp the angle to a workbench or vise. Use a square to mark a straight cutting line on the angle, then carefully saw along the line. Apply steady pressure while sawing to maintain control and achieve a clean cut. Remember to use a blade suitable for cutting metal and take breaks if needed to avoid fatigue. Regardless of the method you choose, it is crucial to take safety precautions, such as wearing appropriate protective gear and ensuring the work area is clear and well-ventilated. Additionally, always double-check measurements and use proper techniques to achieve accurate cuts.
- Q:What are the different types of steel angles used in automotive manufacturing?
- Automotive manufacturing relies on a variety of steel angles that play a crucial role in designing and constructing automotive structures and parts. Some of the commonly utilized steel angles in this industry include: 1. Equal Angle: This type of steel angle consists of sides of equal length, forming a 90-degree angle. In automotive manufacturing, equal angles find applications in chassis frames, suspension components, and brackets. 2. Unequal Angle: As the name suggests, unequal angles have sides of unequal lengths, creating a 90-degree angle. Automotive manufacturers employ unequal angles to fabricate components with specific dimensions and angles, such as door frames, body reinforcements, and support structures. 3. L Angle: Also known as angle irons, L angles possess two sides of equal length that form a 90-degree angle. They are extensively used in automotive manufacturing for various purposes, including reinforcing panels, mounting brackets, and structural supports. 4. T Angle: Resembling the shape of the letter "T," T angles consist of one long side and one short side forming a 90-degree angle. In automotive manufacturing, T angles play a significant role in joining different components like body panels, fenders, and roof structures. 5. C Angle: Referred to as channel angles, C angles have a C-shaped cross-section. These angles offer structural strength and rigidity, making them suitable for applications such as frame rails, roll cages, and support beams in automotive manufacturing. 6. Z Angle: Z angles feature a Z-shaped cross-section, resembling the letter "Z." They are commonly employed in automotive manufacturing to join and reinforce components like door frames, roof structures, and body reinforcements. These examples merely scratch the surface of the numerous types of steel angles employed in automotive manufacturing. Each type serves a specific purpose and possesses unique properties, such as strength, stability, and flexibility, to meet the diverse requirements of automotive applications.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
jisangle
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords





























