Jewellery Induction Casting Crucible Galloni CG40(500),Graphite Melting Crucible
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5 Pieces pc
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 Pieces per Month pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Detailed Product Description
Jewellery Casting crucible CG-40 induction casting machine. Crucible capacity 500 G
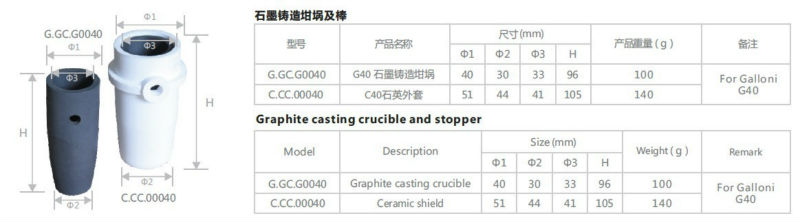
- Q:Does a graphite crucible react with any substances during use?
- During use, a graphite crucible does not undergo any reactions with substances. Graphite is chemically inactive and possesses a high melting point, rendering it perfect for high-temperature applications such as metal melting. It does not interact with the materials being melted or any other substances present within the crucible. This characteristic of graphite permits the secure and effective handling of diverse substances when carrying out processes like metal casting, glass melting, or chemical reactions.
- Q:Can graphite crucibles be used for alloy preparation?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for alloy preparation. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in metallurgy and foundry applications due to their high melting point, chemical resistance, and thermal conductivity. They can withstand high temperatures required for alloy preparation and are suitable for melting various metals and alloys. Graphite crucibles provide a stable and controlled environment for the melting process, allowing for precise alloy composition and homogeneity. Additionally, graphite crucibles have good thermal shock resistance, meaning they can handle rapid temperature changes without cracking or breaking. Therefore, graphite crucibles are a reliable choice for alloy preparation in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
- Q:How do you determine the appropriate crucible capacity for a specific application?
- When determining the suitable crucible capacity for a particular application, several factors must be taken into consideration. Firstly, the quantity of material that needs to be melted or heated in the crucible should be evaluated. This can be determined by considering either the volume or weight of the material. It is essential to select a crucible size that can accommodate the material adequately, avoiding both overflow and being too empty. These situations can negatively impact the heating efficiency and the final product's quality. Secondly, the required melting or heating temperature for the specific application needs to be considered. Different materials have varying melting points, and some may necessitate higher temperatures than others. The crucible should have the capacity to withstand and maintain the desired temperature without experiencing cracking or deformation. Moreover, the duration of the application needs to be taken into account. If the application requires an extended period of melting or heating, it is crucial to choose a crucible size that can hold the material for the required duration, eliminating the need for frequent refilling or emptying. This ensures a continuous and efficient operation. Additionally, the type of crucible material plays a significant role in determining the appropriate capacity. Various materials have different thermal conductivity and compatibility with specific substances. It is imperative to select a crucible material that is suitable for the specific application to prevent contamination or reactions between the crucible and the material being heated. Lastly, it is advisable to consult the manufacturer or supplier of the crucible for their recommendations. They possess the expertise and knowledge to guide you in selecting the appropriate crucible capacity based on your specific application requirements. By considering these factors and seeking expert advice, the appropriate crucible capacity for your specific application can be determined, ensuring optimal performance and desired results.
- Q:How do you prevent contamination of the melted material in a graphite crucible?
- To prevent contamination of the melted material in a graphite crucible, several measures can be taken. First, it is important to ensure that the crucible is clean and free from any previous residues or impurities. This can be achieved by thoroughly cleaning and preheating the crucible before use. Additionally, using crucible covers or lids can help prevent any external contaminants from entering the crucible during the melting process. It is also crucial to handle the crucible with clean and dry tools to avoid introducing any foreign substances. Finally, maintaining a controlled and clean environment during the melting process, such as keeping the work area free from dust or other potential contaminants, can further minimize the risk of contamination.
- Q:Can graphite crucibles be used for metal casting?
- Metal casting can indeed utilize graphite crucibles. Due to their elevated melting point and exceptional thermal conductivity, graphite is frequently employed as a crucible material in metal casting. It is especially well-suited for casting non-ferrous metals like gold, silver, copper, and aluminum. Graphite crucibles are capable of enduring high temperatures without experiencing cracking or deformation, making them ideal for melting and pouring molten metal. Moreover, graphite exhibits low chemical reactivity, preventing any adverse reactions with the metal being cast. This characteristic ensures the preservation of purity and quality in the final cast metal. However, it should be noted that graphite crucibles may not be suitable for casting certain metals with high melting points, such as steel, as they may not withstand the extreme temperatures required for melting these metals. In such instances, alternative materials such as clay or ceramic crucibles may prove more appropriate.
- Q:How is a graphite crucible manufactured?
- A graphite crucible is typically manufactured using a process called isostatic pressing. Isostatic pressing involves placing graphite powder into a mold and subjecting it to high pressure from all directions. This process ensures that the graphite particles are evenly compacted, resulting in a dense and homogeneous crucible. The first step in manufacturing a graphite crucible is to select the appropriate graphite material. High-quality graphite with a low ash content is typically chosen for its excellent thermal conductivity, high temperature resistance, and chemical stability. The graphite is then milled into a fine powder to ensure a consistent particle size. Next, the graphite powder is poured into a flexible rubber mold. The rubber mold is designed to withstand the high pressure that will be applied during the isostatic pressing process. The mold is carefully sealed to prevent any leakage of graphite powder. The sealed mold is then placed into a high-pressure vessel. Hydraulic pressure is applied from all directions, exerting uniform pressure on the graphite powder. This pressure compacts the graphite particles, eliminating any voids or porosity that may be present. The high pressure also helps to align the graphite particles, resulting in improved mechanical properties. Once the pressing process is complete, the mold is removed, leaving behind a green crucible. The green crucible is then subjected to a baking process called carbonization. During carbonization, the crucible is heated to temperatures of around 3000 degrees Celsius in an inert atmosphere. This process removes any volatile materials and further strengthens the crucible. After carbonization, the crucible undergoes a final machining process to achieve the desired dimensions and smooth surface finish. This may involve precision grinding, turning, or milling to ensure the crucible meets the required specifications. In conclusion, a graphite crucible is manufactured through a process called isostatic pressing, which involves compacting graphite powder under high pressure. This process, along with subsequent carbonization and machining, ensures the crucible has excellent thermal conductivity, high temperature resistance, and chemical stability.
- Q:Can graphite crucibles be used for electron beam melting processes?
- Graphite crucibles are indeed capable of being used in electron beam melting processes. They possess exceptional thermal conductivity, a high melting point, and commendable resistance to chemical attack, rendering them appropriate for high-temperature applications like electron beam melting. The remarkable thermal conductivity of graphite aids in the effective transfer of heat, thereby enabling uniform heating and melting of the material. Moreover, graphite crucibles exhibit excellent dimensional stability, a vital factor in ensuring precise control over the melting process. Consequently, graphite crucibles are widely favored in electron beam melting processes due to their advantageous attributes.
- Q:How does the thermal conductivity of the molten metal affect the performance of a crucible?
- The thermal conductivity of the molten metal affects the performance of a crucible by determining how efficiently heat is transferred from the molten metal to the crucible material. A higher thermal conductivity would allow for better heat transfer, resulting in more uniform heating and reduced risk of thermal stress or cracking in the crucible. On the other hand, a lower thermal conductivity could lead to uneven heating, hot spots, and potential damage to the crucible.
- Q:The difference between single graphite furnace graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer and double graphite furnace
- Flame atomizer: it consists of three parts: sprayer, premixing chamber and burner. Features: easy operation and good reproducibility.Graphite furnace atomic device is a type of system will be placed in the pipe wall, graphite platform, carbon sample holes or graphite crucible with electric heating to a high temperature to achieve atomization. Tubular graphite furnace is the most commonly used atomization device.The atomization program is divided into drying, ashing, atomization and high temperature purificationThe atomization efficiency is high: under the adjustable high temperature, the sample utilization rate is 100%High sensitivity: the detection limit is 10-6~10-14Small amount of sample: suitable for determination of refractory elements
- Q:Are graphite crucibles suitable for use in a vacuum environment?
- Graphite crucibles are indeed appropriate for utilization in a vacuum setting. Graphite, being an exceptionally stable substance, has the ability to endure elevated temperatures and corrosive surroundings. Consequently, it is extensively favored in various industrial applications, including those within vacuum environments. Notably, graphite crucibles possess outstanding thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock, both of which are crucial attributes for upholding temperature stability in a vacuum. Moreover, graphite exhibits low outgassing properties, signifying that it releases negligible amounts of gas or vapor when subjected to a vacuum. This further enhances its suitability for employment in such environments. All in all, graphite crucibles emerge as a dependable and efficient alternative for conducting experiments or processes in vacuum conditions.
We are always keeping enlarging production scale, perfecting management system, and improving office facilities to expand our markets both at home and abroad.We sincerely welcome clients at home and abroad to come for negotiations.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | Guangdong,China (Mainland) |
| Year Established | 2010 |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | North America South America Eastern Europe Southeast Asia Africa Oceania Mid East Eastern Asia Western Europe |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | 61% - 70% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | 1,000-3,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 10 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Jewellery Induction Casting Crucible Galloni CG40(500),Graphite Melting Crucible
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5 Pieces pc
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 Pieces per Month pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords





























