HR Square Bar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50Tons m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500 tons per month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of HR Square Bar:
-Standard: GB,
-Grade: Q195 or equivalent.
-Chemical Composition:
|
Standard |
Grade |
Element (%) | ||||
|
GB |
Q195 |
C |
Mn |
S |
P |
Si |
|
0.06~0.12 |
0.25~0.50 |
≤0.050 |
≤0.045 |
≤0.30 | ||
Measures of HR Square Bar (small measures):
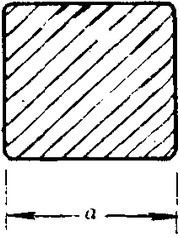
(Section of HR Square Bar)
-Length of a side and Theoretical weight of Square Bar.
|
Length of a side(mm) |
Theoretical weight(kg/m) |
Length of a side(mm) |
Theoretical weight(kg/m) |
|
7 |
0.385 |
22 |
3.80 |
|
8 |
0.502 |
24 |
4.52 |
|
9 |
0.636 |
25 |
4.91 |
|
10 |
0.785 |
26 |
5.30 |
|
11 |
0.950 |
28 |
6.15 |
|
12 |
1.13 |
30 |
7.06 |
|
13 |
1.33 |
32 |
8.04 |
|
14 |
1.54 |
34 |
9.07 |
|
15 |
1.77 |
36 |
10.17 |
|
16 |
2.01 |
38 |
11.24 |
|
17 |
2.27 |
40 |
12.56 |
|
18 |
2.54 |
42 |
13.85 |
|
19 |
2.82 |
45 |
15.90 |
|
20 |
3.14 |
48 |
18.09 |
|
21 |
3.46 |
50 |
19.63 |
Notes:
1, The theoretical weights in the list, base on the density of 7.85 g/cm3.
2, Formula for theoretical weight of Square bar: (length of a side)2 * 0.00785
3, The numbers with *mean that they are not regular or we don’t offer them.
-Regular length of Square Bar:
|
Steel |
Length of a side (mm) |
Length of steel (m) |
|
Normal steel |
< 25 |
4~10 |
|
> 25 |
3~9 | |
|
Steel of high quality |
All measure |
2~6 |
|
Tool steel >75 |
1~6 |
Usage/Applications of HR Square Bar:
-The Square Bar is normally used as structure steel.
-Row material for other structure steel like steel angles, channels, I-beams, H-beams, etc…
Packaging & Delivery of HR Square Bar:
-Packing Detail: The products can be packed in bundles by steel wires.
-Marks: We make tag marks and color marks. The tag marks with white background and red company logo will be tied up to each bundle of the products. The information is usually including basic information of products and company and other information requested by customers. As for color marks, we will paint both ends of bundles to make sure that it will be more convenient for customers to distinguish them from other products.
-Delivery Detail: 30~45 working days after receive buyer’s T.T. or L/C.
Transportation:
-The products can be delivered by bulk vessel or by container. As for container, products with the length of 6m will be loaded in 20’ container, with 9m or 12m, in 40’ container.
-The maximum quantity of loading of container is 25 tons.
-The products are usually transported to the nearest port from the production place.
Photos of HR Square Bar:


We sincerely welcome partners around the world to establish business cooperation with us on the basis of mutual trust, benefit and development.
- Q:Can a steel square be used for checking the flatness of a floor joist?
- Using a steel square to check the flatness of a floor joist? Not possible. A steel square is specifically crafted for measuring right angles and establishing perpendicular lines. It does not possess the capability or appropriateness for assessing the flatness of a floor joist. To properly gauge the flatness of a floor joist, one must employ a straight edge or a level that is capable of spanning the length of the joist and delivering precise measurements of any deviations from a level surface.
- Q:What are the different markings on a steel square used for?
- A steel square, also known as a framing square or carpenter's square, is a versatile tool commonly used in woodworking, construction, and other trades. It consists of two arms, typically made of steel, that meet at a 90-degree angle. The arms are marked with various measurements and markings, each serving a specific purpose. 1. Degree Scale: One of the most prominent markings on a steel square is the degree scale, which allows users to measure and mark angles other than 90 degrees. This scale is useful for tasks such as cutting rafters, stair stringers, or other angled cuts. 2. Inch Scale: The inch scale is typically marked along one or both arms of the square. It allows for precise measurements in inches, making it handy for measuring and marking lengths or widths of materials. 3. Rafter Tables: Many steel squares have rafter tables printed on one of the arms. These tables provide measurements and angles for common rafter cuts, hip and valley rafter cuts, and other roofing-related calculations. They help carpenters and roofers determine the proper angles and lengths of rafters needed for a particular roof design. 4. Octagon Scale: Some steel squares feature an octagon scale, which is used for marking out octagonal shapes. This scale provides the necessary angles and lengths required to construct an octagon, making it useful for projects like building gazebos or other eight-sided structures. 5. Protractor: Many steel squares have a protractor or angle finder built into one of the arms. This allows users to measure and mark angles accurately, especially when trying to replicate or transfer an existing angle. 6. Center Finding Scale: Some steel squares include a center finding scale that helps users locate the center point of a board or material. This scale is useful for tasks such as drilling holes or marking the midpoint for symmetrical cuts. Overall, the different markings on a steel square serve to enhance its versatility and functionality. They allow users to accurately measure angles, mark dimensions, and perform various calculations, making the tool an essential companion for carpenters, woodworkers, and construction professionals.
- Q:Can a steel square be used for checking the alignment of machinery?
- Indeed, the alignment of machinery can be assessed using a steel square. A steel square, commonly employed in carpentry and metalworking, is a versatile tool utilized for measuring right angles and inspecting the alignment of diverse components. It comprises a lengthy metal blade and a shorter metal tongue that intersect at a 90-degree angle. To ascertain the alignment of machinery, one can position a steel square against distinct parts of the machine to establish their perpendicularity or parallelism. For instance, it can be employed to verify if the table of a milling machine is at a right angle to the spindle or if a drill press table runs parallel to the drill bit. By applying the square to various surfaces, it offers a visual indication of any misalignment or need for adjustment. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that although a steel square can be handy for initial alignment checks, it may not deliver the level of precision required for exceptionally precise machinery alignment. In such instances, specialized alignment tools like dial indicators or laser alignment systems may be indispensable. Moreover, it is always advisable to consult the manufacturer's guidelines or seek professional assistance to ensure the appropriate procedures for machinery alignment.
- Q:Can a steel square be used for measuring the height of a flag?
- Yes, a steel square can be used for measuring the height of a flag. A steel square is a versatile measuring tool that can be used for various purposes including measuring angles, distances, and heights. To measure the height of a flag, one can hold the steel square vertically against the flagpole and align it with the top of the flag. By reading the measurement scale on the square, the height of the flag can be determined accurately. However, it is important to ensure that the steel square is held perpendicular to the ground and that the flag is not swaying or moving excessively to obtain an accurate measurement.
- Q:How do you use a steel square to find the length of a board?
- To use a steel square to find the length of a board, you align the long edge of the square with one end of the board and extend it along the length. Then, you read the measurement markings on the square to determine the length of the board.
- Q:Can a steel square be used for measuring circular objects?
- Using a steel square is not an option when it comes to measuring circular objects. This particular tool, also referred to as a carpenter's square or a framing square, is specifically designed for measuring and marking right angles. Its structure includes a lengthy straight edge and a shorter edge that is perpendicular, forming the shape of an "L." While it can serve various functions in carpentry and woodworking, it is not well-suited for measuring curves or circular objects. In order to accurately measure such objects, tools like a compass, a tape measure, or a set of calipers would be more suitable.
- Q:How is a steel square different from a carpenter's square?
- Both construction and woodworking employ measuring tools such as steel squares and carpenter's squares, but they possess distinct characteristics. To begin with, the manner in which these squares are constructed and the materials used diverge. The steel square, as its name suggests, is fashioned entirely from steel, rendering it heavier and more resilient. Conversely, a carpenter's square typically consists of wood, supplemented with a metal edge or lip to guarantee precision. Regarding design, a steel square boasts a lengthier body with a broader base and an L-shaped structure incorporating two arms that intersect at a right angle. One arm serves as a measuring device, while the shorter arm aids in achieving accurate cuts or angles. Conversely, a carpenter's square, also referred to as a try square, possesses a shorter body with a right-angled shape, rendering it suitable for assessing corner precision and marking 90-degree angles. Another distinction lies in functionality. The steel square exhibits greater versatility, facilitating measurement, angle marking, and cut line layout. It often includes supplementary features like a level, protractor, and scribe, making it an exhaustive tool for diverse construction endeavors. Conversely, a carpenter's square principally serves the purpose of verifying right angles and ensuring squareness in woodworking projects. Carpenters and cabinetmakers commonly employ it for layout tasks, aligning joinery, and verifying the accuracy of cuts and joints. In summary, while both steel squares and carpenter's squares fulfill analogous objectives, their disparities reside in their construction, design, and functionality. Steel squares excel in durability and versatility, whereas carpenter's squares represent simpler tools primarily employed for assessing right angles and guaranteeing precision in woodworking projects.
- Q:Can a steel square be used for baseboard installation?
- Baseboard installation can be facilitated using a steel square. A steel square, also referred to as a framing square or a carpenter's square, is a multifunctional tool commonly utilized in woodworking and construction projects. Constructed from durable steel, this tool features a 90-degree angle and a ruler along its edge. The utilization of a steel square can greatly benefit baseboard installation. It aids in achieving precise and accurate cuts on the baseboard material, as well as measuring and marking angles for corners and joints. The 90-degree angle of the steel square is particularly advantageous for marking and cutting baseboards that necessitate perfect fitting into corners or against walls. Moreover, a steel square can be employed to assess the levelness and squareness of the baseboards during the installation process. By placing the square against both the baseboard and the wall, it is effortless to determine if the baseboard is straight and properly aligned. In conclusion, although alternative tools are available for baseboard installation, a steel square is a dependable and versatile choice that can be effectively employed in this task.
- Q:How do you use a steel square to mark out mortise and tenon joints?
- For marking out mortise and tenon joints with a steel square, the following steps should be followed: 1. Choose the appropriate size of the steel square for your project. Smaller squares are more convenient for smaller joints, while larger squares are suitable for larger joints. 2. Determine the dimensions of your mortise and tenon joint. Measure the tenon's width and thickness, as well as the mortise's depth and width. 3. Use the steel square to mark the tenon's width on the end of the wood piece that will form the tenon. Place the square against the wood's edge and draw a line that matches the tenon's width. Repeat this step on all sides of the tenon piece. 4. Next, mark the tenon's thickness on the face of the tenon piece. Align the square with the wood's end and draw lines on both sides, indicating the tenon's thickness. Repeat this step on all sides of the tenon piece. 5. Once the tenon is marked, position it against the wood piece that will receive the mortise. Align the tenon with the corresponding edge of the receiving piece and use the square to mark the tenon's outline on the receiving piece. This will show where the mortise will be cut. 6. To mark the mortise's width and depth, align the square with the tenon's outline lines on the receiving piece. Draw lines along the sides of the square to indicate the mortise's width and depth. Repeat this step on all sides of the receiving piece. 7. Finally, use a chisel or mortising machine to cut out the mortise and shape the tenon according to the markings made with the steel square. Ensure a snug fit between the tenon and mortise for a strong and precise joint. By utilizing a steel square for marking out mortise and tenon joints, accurate and consistent measurements can be achieved, resulting in well-fitting and durable joints.
- Q:Can a steel square be used for checking the squareness of a table saw sled?
- A table saw sled's squareness can be assessed by employing a steel square. This tool is extensively utilized for angle measurements and inspections, guaranteeing reliable accuracy. To examine the squareness of the sled, position the steel square flush against the fence of the sled. Then, align the sled with the table saw blade and verify if the square is perpendicular to the blade. If the square perfectly aligns with the blade, the sled is square. However, if any gaps or misalignments are detected, the sled can be adjusted to ensure proper squareness.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | Renqiu, China |
| Year Established | 1996 |
| Annual Output Value | Above US$ 30 Million |
| Main Markets | Mid East; Southeast Aisa |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Tianjin; |
| Export Percentage | 20% - 30% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | 11-20 People |
| Language Spoken: | English; Chinese |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | Above 70,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | 1 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | Average |
Send your message to us
HR Square Bar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50Tons m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500 tons per month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords



























