Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for instruction building
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Item specifice
Product Description:
Specifications of Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for instruction building
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
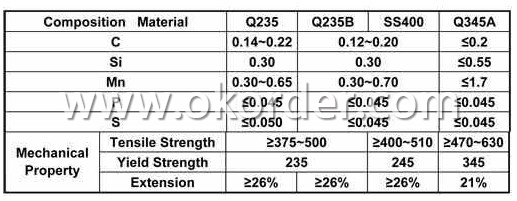
2. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request3.Material:GBQ235B,Q345BorEquivalent;ASTMA36;EN10025,S235JR,S355JR;JISG3192,SS400;SS540.
4. Payment terms:
1).100% irrevocable L/C at sight.
2).35% T/T prepaid and the balance against the copy of B/L.
3).35% T/T prepaid and the balance against L/C
5.Sizes:
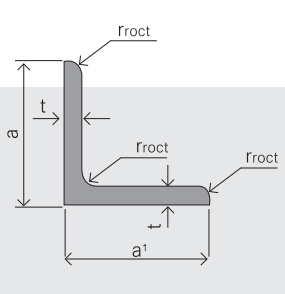
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
50 | 50 | 3.7---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
60 | 60 | 5.0---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
63 | 63 | 6.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
65 | 65 | 5.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
70 | 70 | 6.0---7.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
75 | 75 | 5.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
80 | 80 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
6. Material details:
Usage & Applications Hot Rolled Angle Steel
According to the needs of different structures, Angle can compose to different force support component, and also can be the connections between components. It is widely used in various building structures and engineering structures such as roof beams, bridges, transmission towers, hoisting machinery and transport machinery, ships, industrial furnaces, reaction tower, container frame and warehouse etc.
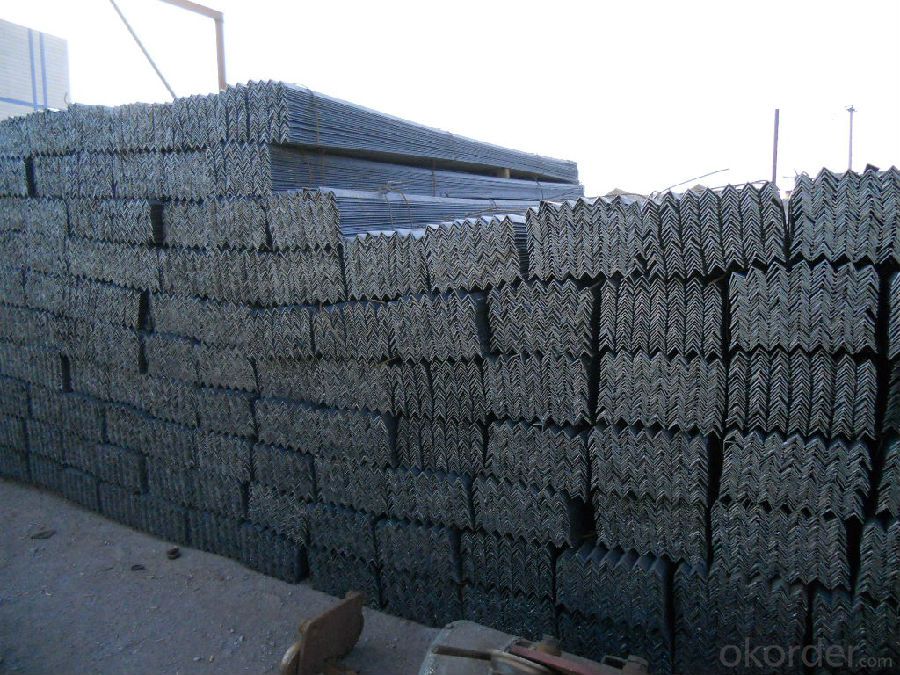
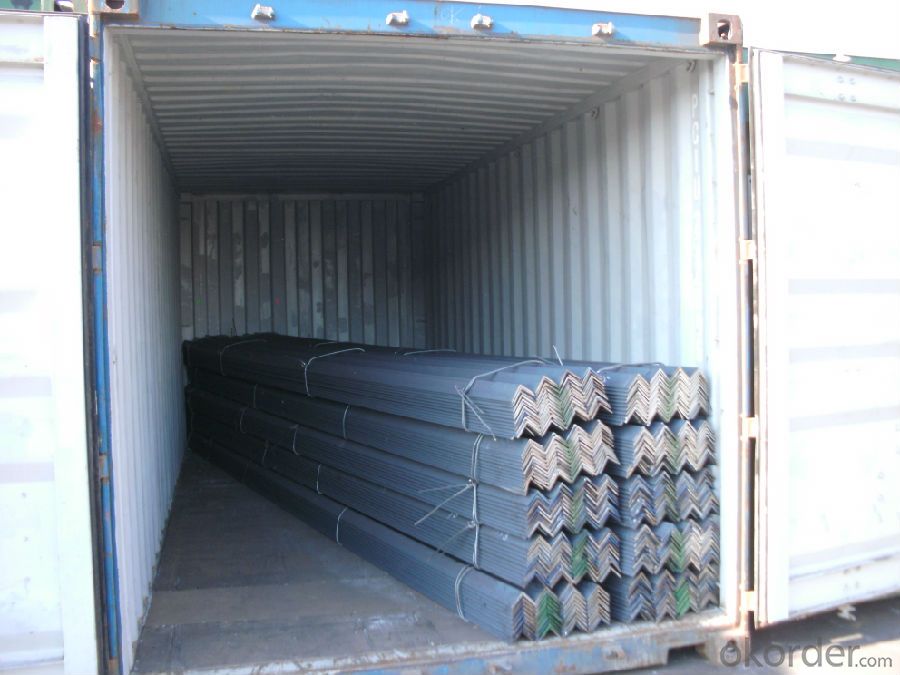


Packaging & Delivery of Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for instruction building
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 30MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
- Q:What are the limitations of using steel angles?
- One limitation of using steel angles is their susceptibility to corrosion. Without proper maintenance and protective coatings, steel angles can rust over time, compromising their structural integrity. Additionally, steel angles have weight limitations and may not be suitable for heavy load-bearing applications. Finally, steel angles are limited in terms of design flexibility compared to other materials, as they are typically available in standard sizes and shapes.
- Q:Can steel angles be used for modular construction?
- Absolutely, modular construction can make use of steel angles. Steel angles are widely utilized in the construction industry due to their robustness, adaptability, and cost-efficiency. When it comes to modular construction, steel angles find application in constructing frameworks, supporting structures, and establishing connections between modules. By providing stability and ensuring structural integrity, they guarantee the durability and safety of the modular units. Moreover, steel angles can be effortlessly fabricated and tailored to meet the precise design prerequisites of modular construction ventures. In summary, steel angles are a practical and frequently employed material in modular construction, owing to their multitude of advantages and suitability for the construction process.
- Q:What are the different specifications for steel angles?
- Steel angles, also referred to as angle irons or L-shaped bars, are utilized as versatile structural components in various industries. Their distinguishing feature is their L-shaped cross-section, which consists of two legs of either equal or unequal lengths. The dimensions of steel angles are determined by their leg lengths (L1 and L2) and thickness (T). The leg lengths can range from equal angles (L1 = L2) to unequal angles (L1 ≠ L2), with common leg lengths falling between 20mm and 200mm, and thicknesses typically ranging from 3mm to 20mm. In terms of material composition, steel angles are predominantly made from carbon steel, prized for its strength and durability. The choice of carbon steel grade employed is dependent on the specific application and the desired mechanical properties. Common grades include A36, A572, and A588. To ensure quality and consistency, steel angles are manufactured in adherence to various standards. These standards, such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), EN (European Norms), and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards), establish guidelines for the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and tolerances of steel angles. Steel angles can possess different surface finishes to accommodate diverse applications and meet aesthetic requirements. Popular finishes include hot-dip galvanized, painted, or left as a mill finish (raw steel). Galvanized angles are coated with a layer of zinc for enhanced corrosion protection, while painted angles provide an additional layer of protection and can be customized in terms of color. To ensure conformity with required standards and suitability for structural applications, steel angles are subject to specific tolerances. These tolerances define acceptable deviations from the specified dimensions and can vary based on the manufacturing standard and the particular dimensions of the angle. In conclusion, the specifications for steel angles encompass dimensions (leg lengths and thickness), material composition (carbon steel grades), manufacturing standards (ASTM, EN, JIS), surface finish (galvanized, painted, mill finish), and tolerances. These specifications facilitate the selection of the appropriate steel angle for a given application, guaranteeing structural integrity and optimal performance.
- Q:What are the common loadings or forces that steel angles are designed to withstand?
- Steel angles are widely utilized in different structural applications because of their versatility and strength. These angles are engineered to endure various loadings or forces, depending on the specific application. Some typical loadings that steel angles are engineered to tolerate include: 1. Compression: Steel angles have the ability to withstand compressive forces, which are forces that tend to compress or squeeze the material. They are frequently employed in columns or supports to bear the weight of a structure or to resist crushing loads. 2. Tension: Steel angles can also endure tensile forces, which are forces that stretch or pull the material. They are commonly used in tension members, like roof trusses or bridge supports, to resist pulling or stretching loads. 3. Bending: Steel angles are designed to resist bending forces, which occur when a material is subjected to a combination of tension and compression. They are commonly used in beams or braces to provide structural stability and prevent excessive deflection or bending. 4. Shear: Steel angles have the capacity to withstand shear forces, which occur when one section of a material is pushed in one direction and another section is pushed in the opposite direction. They are frequently employed in connections or joints to transfer loads between structural members and resist shearing forces. 5. Lateral loads: Steel angles are also engineered to withstand lateral loads, which are forces that act horizontally on a structure. These loads can be caused by wind, earthquakes, or other external factors. Steel angles are often utilized in bracing systems to provide lateral stability and prevent the structure from overturning or collapsing. It is important to note that the specific loadings and forces that steel angles are engineered to withstand may vary depending on the size, shape, and grade of the angle, as well as the specific design requirements of the application. Therefore, it is crucial to consult the appropriate design codes and engineering guidelines to ensure the proper selection and application of steel angles in a given structural design.
- Q:What are the common sizes of steel angles?
- The sizes of steel angles can differ based on the industry and specific project requirements. However, there are several standard sizes that are commonly utilized. In the United States, the most readily accessible steel angles are available in widths of 1/2 inch, 1 inch, 1-1/2 inches, and 2 inches. Typically, these angles have thicknesses ranging from 1/8 inch to 1/4 inch. Furthermore, larger and smaller angles can also be found for specialized applications. These specialized angles may include wider angles measuring up to 8 inches or more, or thinner angles with thicknesses as low as 1/16 inch. It is important to acknowledge that these sizes might vary in different countries or regions, and suppliers may have their own specific range of sizes. Thus, it is advisable to consult with local suppliers or manufacturers to determine the most prevalent sizes of steel angles in a particular area.
- Q:Angle iron specifications 125 * 80 * 101 m multiple
- The angle iron can be made up of different force components according to the different structure, and can also be used as the connecting piece between the components. Widely used in a variety of architectural and engineering structures, such as beams, bridges, towers, hoisting and conveying machinery, ships, industrial furnace, reaction tower, container frame, cable bracket, power piping, busbar support installation, and warehouse shelves.
- Q:How are steel angles defined?
- Steel angles are defined based on the length of their legs, thickness, and their shape, which is typically L-shaped. These angles are commonly used in construction and engineering applications for structural support and framing purposes.
- Q:Can steel angles be used as framing members in buildings?
- Yes, steel angles can be used as framing members in buildings. Steel angles are commonly used in structural applications due to their strength, durability, and versatility. They provide excellent support and stability, making them suitable for framing various building elements such as walls, floors, and roofs.
- Q:What is the typical density of steel angles?
- Steel angles can have varying densities depending on the particular steel type and grade employed. On average, their density falls within the range of 7.7 to 8.1 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), or equivalently 7700 to 8100 kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). In comparison to other substances, steel angles possess a notably high density, imparting strength and durability for a multitude of structural and construction purposes.
- Q:What does 50*50*5 angle mean?
- 50*50*5 angle means: the outer section of angle steel is 50mmx50mm, and the angle steel is 5mm.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled unequal Angle Steel for instruction building
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords



























