Hot Rolled Steel I-Beam Q345
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Hot Rolled Steel I-Beam Q345
Standard: ASTM A36, EN10025, JIS, GB, etc.
Grade:S275, S355, SS400, Q235B, A36, Q345, etc
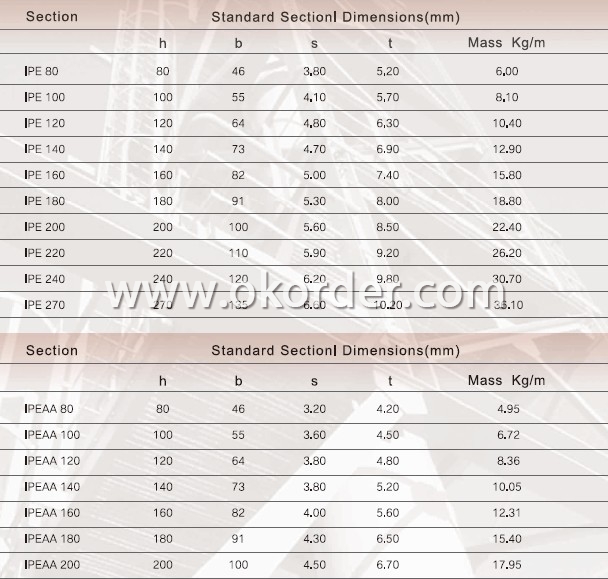
Sizes: 80MM-270MM
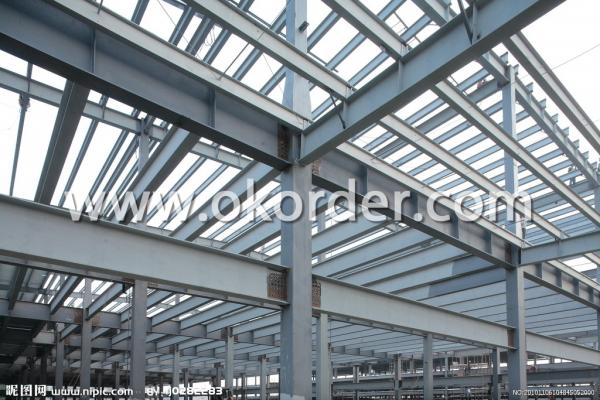
Applications of Hot Rolled Steel I Beam
Hot Rolled Steel I Beam is widely used in various building structures and engineering structures such as roof beams, bridges, transmission towers, hoisting machinery and transport machinery, ships, industrial furnaces, reaction tower, container frame and warehouse etc.

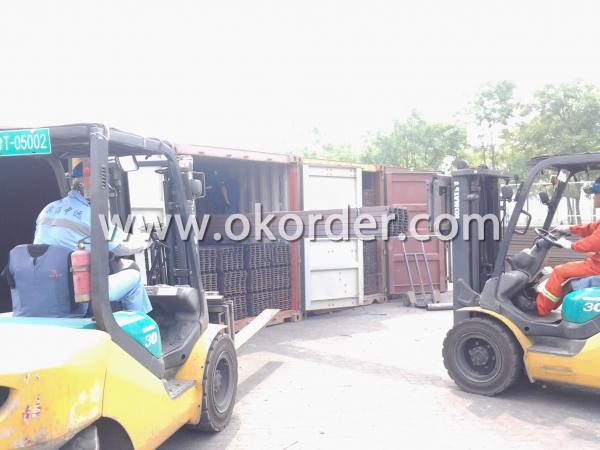
Package & Delivery Terms of Hot Rolled Steel I Beam
1. Package: All the hot rolled steel I beam will be tired by wire rod in bundles
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load
3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Shipment: In containers or in bulk cargo
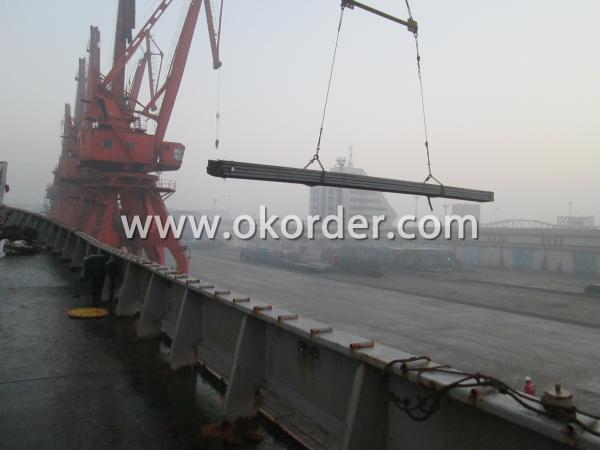


6. Delivery time: All the hot rolled steel I Beam will be at the port of the shipment within 45 days after receiving the L/C at sight ot the advance pyment by T/T
7. Payment: L/C at sight; 30% advance payment before production, 70% before shipment by T/T, etc.
Production flow of Hot Rolled Steel I Beam
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation
- Q:Can steel angles be used as lintels or supports for openings?
- Lintels or supports for openings, such as doors and windows, can be made using steel angles. In construction, steel angles are frequently utilized as structural elements because of their durability and strength. These angles offer the necessary structural support to withstand the weight above the opening. They are commonly installed horizontally, with one leg of the angle resting against the wall on each side. This allows the load from the structure above to be transferred to the steel angle, which then distributes the weight to the surrounding walls. Steel angles are a preferred option for lintels and supports because of their ability to bear heavy loads and resist bending and twisting forces.
- Q:What are the different types of steel angles used in engineering?
- Engineering incorporates a range of steel angle varieties that enjoy common usage. These angles are typically fashioned from hot-rolled steel and come in various sizes and dimensions to suit diverse applications. Within engineering, different steel angle types are employed, including: 1. Equal angles: These angles boast identical sides and are frequently utilized for structural purposes, like supporting beams or columns. They furnish stability and strength to the structure and are commonly employed in construction ventures. 2. Unequal angles: As the name suggests, unequal angles feature sides of differing lengths. These angles are often employed in situations where one side must be longer or shorter than the other, such as bracing or framing. 3. L-shaped angles: L-shaped angles possess one side longer than the other, forming an L shape. They are frequently used in construction to offer support and reinforcement, particularly for corners, joints, or connections. 4. Structural angles: Structural angles are specifically designed to bear heavy loads and confer structural stability. They are commonly deployed in constructing frame structures, bridges, or other load-bearing applications. 5. Stainless steel angles: Stainless steel angles are fabricated from stainless steel, which delivers excellent corrosion resistance and durability. These angles are often employed in environments where rust or corrosion may be a concern, such as marine applications or food processing facilities. 6. Galvanized steel angles: Galvanized steel angles are coated with a layer of zinc to provide corrosion resistance. These angles are commonly used in outdoor applications or environments where exposure to moisture or harsh conditions is expected. 7. Perforated steel angles: Perforated steel angles feature holes or perforations along their length, facilitating enhanced ventilation or drainage. These angles are frequently employed in situations where airflow or water drainage is required, such as in HVAC systems or outdoor structures. Overall, the selection of a steel angle hinges upon the specific requirements of an engineering project. Factors such as load-bearing capacity, resistance to corrosion, and aesthetic considerations play a crucial role in determining the appropriate type of steel angle for a particular application.
- Q:Are steel angles suitable for earthquake-resistant structures?
- Because of their high strength and ductility properties, steel angles are often used in earthquake-resistant structures. Their angular shape enables them to effectively withstand lateral forces resulting from seismic events. Steel angles have the capacity to absorb and disperse energy during earthquakes, making them suitable for withstanding the dynamic loads produced by ground movements. Moreover, connecting and joining steel angles is a straightforward process, which guarantees a high level of structural integrity and overall stability in buildings. These factors contribute to steel angles being a preferred option for earthquake-resistant structures, as they provide a dependable and long-lasting solution for minimizing the impact of seismic events.
- Q:What are the benefits of using hot-rolled steel angles?
- There are several benefits of using hot-rolled steel angles in various applications. Firstly, hot-rolled steel angles are known for their high strength and durability. The hot-rolling process involves heating the steel above its recrystallization temperature and then rolling it into the desired shape. This process results in a stronger steel angle compared to cold-rolled steel angles. The increased strength makes hot-rolled steel angles ideal for structural applications where load-bearing capacity is essential. Secondly, hot-rolled steel angles have excellent weldability. The high temperatures during the hot-rolling process refine the grain structure of the steel, making it easier to weld. This characteristic is particularly useful in construction projects where steel angles need to be joined together to form various structures. Additionally, hot-rolled steel angles have a smooth surface finish. The hot-rolling process eliminates surface defects and impurities, resulting in a clean and polished appearance. This makes hot-rolled steel angles aesthetically appealing and suitable for architectural and decorative applications. Furthermore, hot-rolled steel angles offer cost-effectiveness. The hot-rolling process is more efficient and cost-effective compared to other manufacturing methods, such as cold-rolling. This makes hot-rolled steel angles more affordable, which is advantageous for budget-conscious projects. Lastly, hot-rolled steel angles are readily available in a wide range of sizes and dimensions. This versatility allows for greater flexibility in design and construction applications. Whether it is for residential, commercial, or industrial projects, the availability of various sizes ensures that hot-rolled steel angles can be easily incorporated into any project. Overall, the benefits of using hot-rolled steel angles include high strength, excellent weldability, smooth surface finish, cost-effectiveness, and availability in various sizes. These qualities make hot-rolled steel angles a popular choice for a wide range of applications in various industries.
- Q:What is angle iron?
- Widely used in a variety of architectural and engineering structures, such as beams, bridges, towers, hoisting and conveying machinery, ships, industrial furnace, reaction tower, container rack and warehouse shelves, also used to protect column, wall parts easy to hit. Depending on the structure, a variety of different force components are needed, and they can also be used as connecting pieces between components.
- Q:What are the different methods for joining steel angles?
- There exist various techniques for connecting steel angles, each possessing its own advantages and applications. Welding, bolting, and utilizing adhesive or epoxy are among the most frequently employed methods. Welding is a favored approach for joining steel angles due to its capacity to establish a sturdy and enduring connection. The process involves melting the edges of the angles using a welding torch, allowing them to cool and solidify, thereby creating a bond between the two pieces. Depending on the project's specific requirements, welding can be executed using diverse techniques such as arc welding, MIG welding, or TIG welding. Bolting is another commonly utilized method for joining steel angles, whereby nuts and bolts are employed to secure the angles together. This technique permits easy disassembly and reassembly, making it suitable for scenarios that demand flexibility. Additionally, bolting does not require any heat or special equipment, rendering it a relatively straightforward and cost-effective option. Utilizing adhesive or epoxy represents a non-traditional technique for connecting steel angles. This method involves the application of a potent adhesive or epoxy onto the contact surfaces of the angles, which are subsequently pressed together. Particularly when employing high-strength adhesives designed for metal bonding, this approach can yield a robust and long-lasting bond. Adhesive bonding is often employed in situations where welding or bolting may prove impractical or undesirable, such as when dealing with thin or delicate materials. Ultimately, the selection of a joining method for steel angles depends on various factors, including the specific application, desired strength and durability, ease of installation, and the necessity for disassembly or flexibility. Consulting with an expert or engineer is recommended to determine the most suitable joining method for a particular project.
- Q:Can steel angles be used in telecommunications tower constructions?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in telecommunications tower constructions. Steel angles are commonly used in the construction of telecommunications towers due to their strength, durability, and ability to provide structural support. They can be utilized for various purposes such as bracing, cross arms, or mounting equipment, making them an essential component in telecommunications tower construction.
- Q:Can steel angles support heavy machinery or equipment?
- Yes, steel angles can support heavy machinery or equipment. Steel angles are commonly used in structural applications due to their high strength and durability. They provide excellent support and stability, making them suitable for handling heavy loads.
- Q:How do you calculate the buckling capacity of a steel angle?
- To calculate the buckling capacity of a steel angle, you need to consider several factors. Firstly, determine the effective length of the angle. This is the distance between points of rotation or points of restraint. Next, calculate the slenderness ratio, which is the effective length divided by the radius of gyration. The radius of gyration is a measure of how the steel angle's cross-sectional area is distributed around its centroid. Once you have the slenderness ratio, you can refer to design codes or standards, such as the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) Manual, to find the critical buckling stress or load for the given slenderness ratio. These codes provide tables or formulas to determine the critical buckling capacity based on the angle's dimensions and material properties. It is important to note that the buckling capacity of a steel angle depends on the boundary conditions, end fixity, and the method of buckling, whether it is flexural or torsional. Therefore, understanding the specific loading and boundary conditions is crucial in accurately calculating the buckling capacity.
- Q:What are the common uses of unequal steel angles?
- Unequal steel angles are commonly used in construction, engineering, and fabrication projects. They are often used as structural supports, providing stability and strength in frameworks, buildings, and bridges. These angles are also used for creating bracing systems, reinforcing corner joints, and as components in machinery and equipment. Additionally, they are utilized in architectural designs for decorative purposes, adding aesthetic appeal to structures.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Steel I-Beam Q345
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords




























