High Performance Ladle Slide Gate for Steel Industry 2015
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for High Performance Refractory Ladle Slide Gate
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Shape: | Plate | Material: | Alumina Block |
| SiO2 Content (%): | N/A | Al2O3 Content (%): | 80-90% | MgO Content (%): | N/A |
| CaO Content (%): | N/A | Refractoriness (Degree): | 1770°< Refractoriness< 2000° | CrO Content (%): | N/A |
| SiC Content (%): | N/A | Model Number: | CS80 | Brand Name: | |
| Product name: | High performance refractory ladle slide gate | Model No.: | cs80 | Brand name: | CMAX |
| Quality: | Al-C or Al-Zr-C | Service life: | 4-6 heats | Apparent porosity: | 7% Max |
| Bulk density:: | 3.1 MIN | C.C.S: | 120MPA | MOQ: | 100 pcs for trial |
| Delivery time: | 60 working days upon receipt of deposit |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Inner carton packing, outer wooden case suitable for long term sea shipping |
| Delivery Detail: | three months working days upon receipt of deposit |
Specifications
Surface flatness less than 0.05mm
High mechanical strength
Erosion resistance
Oxidation resistance
Thermal shock stability
Using the raw materials of tabular alumina, zirconia-corundum, carbon and other high-grade additives, after sintering to obtain characteristics of oxidation resistance, scour strength, erosion resistance, thermal shock resistance, shape stable and long service life, made our products the preferred materials for the large and medium-sized steel ladle, refining ladle, series of alloy steel ladle, and tundish. Our high performance sintering sliding gates include alumina carbon , Al2O3-ZrO2-C, etc, can meet the needs of different steel grade.
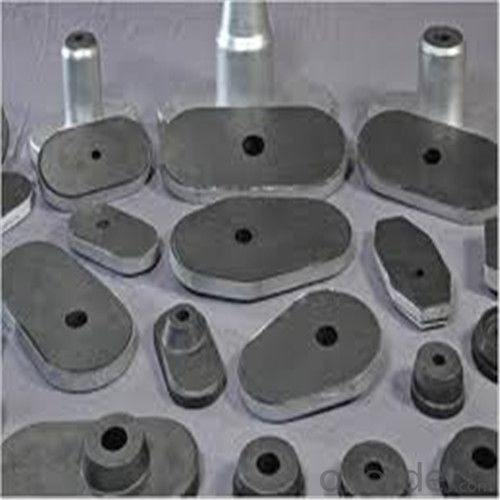
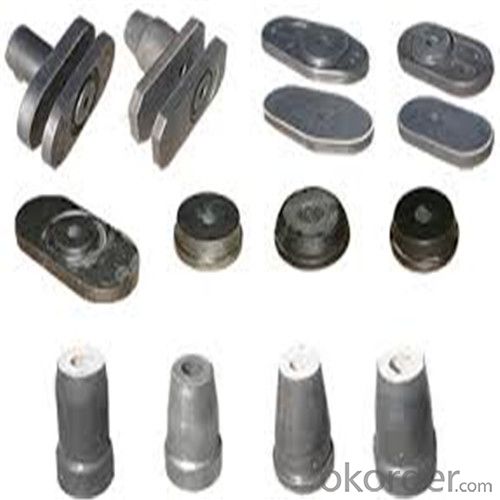
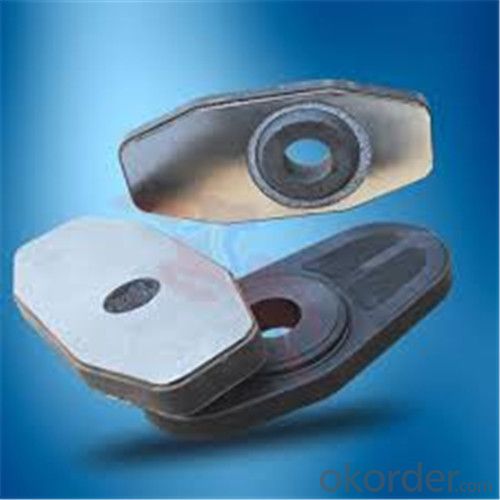


General Chemical Analysis for refractory ladle slide gate :
slide gate plate widely including Alumina carbon and Alumina Zirconia Carbon slide gate plate, MgO and MgO-spinel slide gate plate,nonoxides bonding slide gate plateand unburned slide gate plate.
Alumina -Zirconia-Carbon material
| Al-Zr-C Material | |||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) |
| 85 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
Composite type: Al-Zr-C for working line, outer Al-C material
| Al-Zr-C & Al-C Material | ||||||
| Al2O3 | C | ZrO2 | Apparent porosity | Bulk density | C.C.S | |
| (% minm) | (% minm) | (% minm) | (% max) | (gm./cc minm) | (MPa minm) | |
| Inner side (Working face) | 85 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 3.1 | 120 |
| Outside | 90 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |
Other Products:


About us


Sample is on your request.
Welcome to visit our factory~
- Q:What are the recommended installation techniques for monolithic refractories?
- The installation techniques for monolithic refractories depend on the specific type and application of the refractory material. However, there are general guidelines that can be followed for most installations of monolithic refractories. 1. Surface Preparation: Prior to installing monolithic refractories, it is essential to ensure that the surface is clean, dry, and free from loose particles or contaminants. This can be accomplished by removing any existing refractory materials, thoroughly cleaning the surface, and allowing it to completely dry. 2. Mixing: Monolithic refractories are typically supplied in either a dry or wet form, depending on the specific material. If the refractory is in a dry form, it must be mixed with water or a suitable liquid binder to achieve a workable consistency. It is important to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for the correct mixing ratio and duration to ensure proper bonding and setting of the refractory material. 3. Application: The technique for applying monolithic refractories can vary depending on the specific material and desired installation method. Some common techniques include troweling, gunning, ramming, and casting. - Troweling: This involves manually applying the refractory material with a trowel, typically used for thin linings or patching small areas. - Gunning: Gunning is a method of applying refractory material using a gunning machine or handheld gun. It is suitable for large areas or areas that are difficult to access. The refractory material is mixed with water or a liquid binder and sprayed onto the surface at a high velocity. - Ramming: Ramming involves compacting the refractory material into place using a ramming tool or pneumatic hammer. It is commonly used for forming furnace linings or repairing damaged areas. - Casting: Casting refers to pouring the refractory material into a mold to create a desired shape or lining. It is often used for complex shapes or large-sized components. 4. Curing and Drying: Once the refractory material is applied, it must be properly cured and dried to achieve its maximum strength and thermal properties. The curing and drying process may vary depending on the specific material, but typically involves controlled heating at a gradual rate to eliminate any remaining moisture and allow the refractory to set and harden properly. It is important to note that these are general guidelines, and it is always recommended to consult the manufacturer's instructions and specifications for the specific monolithic refractory material being used. Following the recommended installation techniques will help ensure the proper performance and longevity of the refractory lining.
- Q:How are monolithic refractories manufactured?
- Monolithic refractories are manufactured using a specific process that involves several steps. The first step is the selection and preparation of raw materials. These raw materials usually include aggregates, binders, and additives. Aggregates are chosen based on their chemical and physical properties, while binders are used to hold the aggregates together. Additives are included to enhance specific properties of the refractory material. Once the raw materials are selected, they are mixed together in precise proportions to create a homogeneous mixture. This mixture is then blended using various techniques such as dry or wet mixing, depending on the desired characteristics of the final product. After blending, the next step is shaping the refractory material. This can be done through several methods such as casting, gunning, ramming, or spraying. Each method is chosen based on the specific application and requirements of the refractory. Once the refractory material is shaped, it undergoes a curing process. This process involves drying the material at a controlled temperature to remove any excess moisture and allow for the development of desired properties. Finally, the cured refractory material is fired in a kiln at high temperatures. This firing process helps to further strengthen the refractory and enhance its resistance to heat and other harsh conditions. Overall, the manufacturing of monolithic refractories involves careful selection and preparation of raw materials, precise blending, shaping, curing, and firing processes. This ensures the production of high-quality refractory materials that can withstand the extreme conditions found in various industrial applications.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories improve the durability of furnace linings?
- Monolithic refractories improve the durability of furnace linings by providing a seamless and continuous structure that eliminates joints and weak points. This eliminates the risk of thermal shock and cracking, resulting in a longer lifespan for the furnace lining. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer better resistance to chemical attack, abrasion, and thermal stress, further enhancing the durability of the furnace lining.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories handle thermal expansion and contraction?
- Monolithic refractories handle thermal expansion and contraction by their ability to withstand high temperatures and adapt to changes in size without cracking or breaking. They are designed to have low thermal conductivity, which helps to minimize stress caused by thermal cycling. Additionally, they are often composed of materials with high refractoriness and high thermal shock resistance, allowing them to expand and contract with minimal damage.
- Q:How does the composition of monolithic refractories impact their performance?
- Determining the performance of monolithic refractories is heavily influenced by their composition. These refractories are unshaped materials used to line furnaces, kilns, and other high-temperature equipment. Their installation convenience and ability to conform to complex shapes make them preferable over traditional brick and mortar refractories. Various components, such as aggregates, binders, and additives, constitute the composition of monolithic refractories. These constituents significantly impact the physical, mechanical, and thermal properties of the refractory material. Aggregates, which are the primary component, provide structural integrity to monolithic refractories. Alumina, silica, magnesia, and carbon are among the materials used for aggregates. Each aggregate possesses unique properties that determine the refractory's resistance to heat, chemical attack, and mechanical stress. For instance, alumina aggregates offer excellent resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion, while carbon-based aggregates have high thermal conductivity and are preferred for this reason. The addition of binders enhances the strength and cohesion of the refractory. Common binders include clay, calcium aluminate cement, and colloidal silica. The choice of binder depends on the desired strength, workability, and setting time of the refractory material. Additives are incorporated into the composition to improve specific properties. They can enhance the refractory's resistance to thermal shock, abrasion, or chemical attack. Additives like zirconium oxide, silicon carbide, and graphite are frequently used to enhance the performance of monolithic refractories in specific applications. The proper combination and proportion of these constituents are vital for achieving the desired performance of monolithic refractories. The composition affects the refractory's thermal conductivity, thermal expansion, density, porosity, and chemical resistance. For example, a higher alumina content improves resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion, while a higher silica content enhances insulation properties. In conclusion, the performance of monolithic refractories is significantly impacted by their composition. Careful consideration must be given to the selection of aggregates, binders, and additives to achieve desired properties and ensure optimal performance in specific high-temperature applications.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories improve the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in improving the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production. These specialized materials are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, chemical reactions, and mechanical stresses, making them ideal for use in high-temperature industrial processes. One of the key ways in which monolithic refractories enhance performance is by providing a protective lining in furnaces, kilns, and other equipment used in iron and steel production. Due to their superior heat resistance, they protect the underlying structure from the intense heat and prevent any detrimental effects on the equipment. This results in reduced downtime, longer service life, and ultimately, increased overall efficiency. Monolithic refractories also ensure better thermal efficiency in the production process. By minimizing heat losses, these materials help to maintain a stable and uniform temperature distribution, thereby improving the energy efficiency of the system. This is particularly important in iron and steel production, where precise temperature control is crucial for achieving the desired metallurgical properties of the final product. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, erosion, and slag attacks. They act as a barrier between the molten metal and the refractory lining, preventing undesirable reactions and material degradation. This helps to maintain the integrity of the furnace lining, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Consequently, it leads to increased productivity and cost savings in the long run. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to be easily shaped, repaired, or replaced. Unlike traditional brick refractories, which require extensive labor and time-consuming installation, monolithic refractories can be applied in a more flexible and efficient manner. Their flexible nature allows for easy repair of damaged areas, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous production. In summary, the use of monolithic refractories significantly enhances the performance and efficiency of iron and steel production. These materials provide a protective lining, improve thermal efficiency, resist chemical corrosion, and offer easy installation and repair options. By optimizing the production process, monolithic refractories contribute to higher productivity, reduced downtime, and increased cost-effectiveness in the iron and steel industry.
- Q:What are the common failure mechanisms of monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories commonly fail due to thermal spalling, chemical attack, erosion, and mechanical stress. Thermal spalling arises from abrupt temperature changes, causing the refractory material to crack and break. This can result from thermal shock or cyclic heating and cooling. Chemical attack occurs when aggressive chemicals or gases interact with the refractory material, degrading its lining. This can lead to the formation of new compounds or the dissolution of the refractory material, weakening its structure and reducing its resistance to further chemical attack. Erosion is another prevalent failure mechanism, particularly in scenarios where the refractory lining is exposed to high-speed gas or liquid flows. The abrasive action of the medium can gradually erode the refractory material, causing thinning and eventual failure of the lining. Mechanical stress, such as thermal expansion or contraction mismatch, can also lead to failure in monolithic refractories. Rapid temperature changes can result in differential expansion or contraction, leading to the development of cracks and fractures in the lining. To mitigate these failure mechanisms, several techniques can be utilized. These include careful material selection based on operating conditions, meticulous design to minimize thermal gradients, application of protective coatings, and regular inspection and maintenance to promptly detect and address signs of failure or degradation.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories perform in rotary hearth furnace applications?
- Monolithic refractories are known for their excellent performance in rotary hearth furnace applications. These refractories are designed to withstand the extreme temperatures and harsh conditions found in rotary hearth furnaces, making them an ideal choice for this specific application. One of the main advantages of monolithic refractories is their ability to resist thermal shock. In a rotary hearth furnace, the material being processed is subjected to rapid heating and cooling cycles, which can cause significant thermal stress on the refractory lining. Monolithic refractories have high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion, allowing them to withstand these temperature fluctuations without cracking or spalling. Another key characteristic of monolithic refractories is their excellent abrasion resistance. In a rotary hearth furnace, the material being processed can contain abrasive particles that can erode the refractory lining over time. Monolithic refractories are formulated with high-quality aggregates and binders that offer superior resistance to abrasion, ensuring a longer service life for the lining. Furthermore, monolithic refractories have good chemical resistance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications in rotary hearth furnaces. They can withstand exposure to various chemical substances, such as molten metals, slags, and gases, without undergoing significant chemical reactions or degradation. This chemical stability ensures that the refractory lining remains intact and maintains its performance in the demanding environment of a rotary hearth furnace. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer excellent installation flexibility. Unlike traditional brick or tile refractories, which require complex installation procedures, monolithic refractories can be easily shaped and applied in-situ using various methods, such as gunning, casting, or ramming. This flexibility allows for quicker and more efficient lining repairs or replacements, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. In conclusion, monolithic refractories are highly reliable and efficient in rotary hearth furnace applications. Their ability to resist thermal shock, abrasion, and chemical attack, coupled with their easy installation, make them the preferred choice for lining materials in these demanding environments.
- Q:What are the key properties and characteristics of monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories, renowned for their ability to be shaped or installed in a single piece without joints, are a type of refractory material. They find their utility in high-temperature applications where traditional brick or tile refractories may not suffice. One noteworthy attribute of monolithic refractories lies in their superior thermal stability. They can withstand extreme temperatures without significant expansion or contraction, making them an ideal choice for furnaces, kilns, and other heat-intensive environments. This quality ensures the maintenance of their structural integrity and grants long-lasting performance. Another significant characteristic of monolithic refractories is their high resistance to thermal shock. They can endure abrupt temperature changes without cracking or spalling, a crucial aspect when the refractory material is exposed to alternating hot and cold conditions. The resistance to thermal shock ensures the refractory lining's longevity, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Monolithic refractories also demonstrate commendable mechanical strength, enabling them to withstand the mechanical stresses and loads imposed on them during usage. They possess excellent load-bearing capacity, resisting abrasion, erosion, and impact, making them suitable for applications where the refractory material faces mechanical wear or impact. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer the advantage of easy installation and repair. Unlike traditional refractories that necessitate skilled labor and time-consuming bricklaying techniques, monolithic refractories can be cast, gunned, or sprayed into place. This effortless installation expedites turnaround times and minimizes downtime during repairs or maintenance. Lastly, monolithic refractories exhibit commendable chemical resistance to various corrosive agents, such as acids, alkalis, and molten metals. This property renders them suitable for use in industries where the refractory material encounters aggressive chemical environments, including the steel, petrochemical, and glass industries. In summary, monolithic refractories possess excellent thermal stability, high resistance to thermal shock, good mechanical strength, effortless installation and repair, and commendable chemical resistance. These properties establish them as the preferred choice in high-temperature applications where durability, reliability, and performance are of utmost importance.
- Q:What are the main factors affecting the abrasion resistance of monolithic refractories?
- There are three key aspects that categorize the main factors influencing the abrasion resistance of monolithic refractories: material composition, microstructure, and service conditions. Firstly, the abrasion resistance of monolithic refractories is significantly determined by their material composition. The selection of raw materials, such as aggregates and binders, directly impacts the overall hardness, strength, and wear resistance of the refractories. For example, high-alumina refractories, which have a high proportion of alumina as their main component, demonstrate exceptional abrasion resistance due to the hardness and toughness of alumina. Conversely, refractories with a higher percentage of softer materials like clay or magnesia may exhibit lower abrasion resistance. Secondly, the microstructure of monolithic refractories plays a crucial role in their ability to endure abrasion. The arrangement and orientation of the aggregates, as well as the bond strength between the particles and the matrix, significantly contribute to their resistance against wear. An evenly distributed and interconnected network of aggregates can strengthen the refractories and enhance their resistance to abrasion. Additionally, a compact and well-sintered matrix can prevent abrasive particles from penetrating, thereby reducing wear. Lastly, the service conditions under which monolithic refractories operate are vital factors in determining their abrasion resistance. Variables such as temperature, atmosphere, and mechanical stress can greatly impact the wear behavior of refractories. High temperatures can cause thermal expansion and contraction, resulting in cracks and spalling, which accelerate abrasion. The presence of corrosive gases or chemicals can also deteriorate the microstructure of refractories, diminishing their wear resistance. Moreover, mechanical stress from impact or friction can lead to localized wear and damage the refractories. To conclude, the abrasion resistance of monolithic refractories is influenced by material composition, microstructure, and service conditions. By carefully selecting suitable raw materials, optimizing the microstructure, and considering specific service conditions, it is possible to enhance the abrasion resistance of monolithic refractories and improve their overall performance in high-wear applications.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
High Performance Ladle Slide Gate for Steel Industry 2015
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords































