Equal Angle steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Specifications of Equal Angle
1. Standards: GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2. Length:6m,9m,12m
3. Material:Material: GB Q235B, Q345B or Equivalent; ASTM A36; EN 10025, S235JR, S355JR; JIS G3192, SS400;
SS540.
4. Sizes:
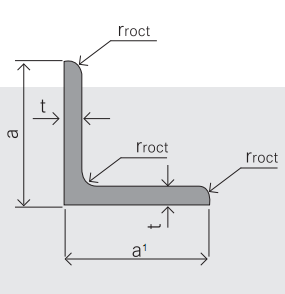
Sizes: 25mm-250mm | ||
a*t | ||
25*2.5-4.0 | 70*6.0-9.0 | 130*9.0-15 |
30*2.5-6.6 | 75*6.0-9.0 | 140*10-14 |
36*3.0-5.0 | 80*5.0-10 | 150*10-20 |
38*2.3-6.0 | 90*7.0-10 | 160*10-16 |
40*3.0-5.0 | 100*6.0-12 | 175*12-15 |
45*4.0-6.0 | 110*8.0-10 | 180*12-18 |
50*4.0-6.0 | 120*6.0-15 | 200*14-25 |
60*4.0-8.0 | 125*8.0-14 | 250*25 |
5. Chemical data: %
C | Mn | S | P | Si |
0.14-0.22 | 0.30-0.65 | ≤0.050 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.30 |
Usage & Applications of Equal Angle
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.
- Q:Are steel angles suitable for manufacturing structural beams?
- Yes, steel angles are suitable for manufacturing structural beams. Steel angles are versatile and commonly used in construction for their strength, durability, and ability to support heavy loads. They can be easily welded or bolted together to form beams of various lengths and sizes, making them a popular choice in structural engineering.
- Q:Can steel angles be used for electrical conduits or cable trays?
- No, steel angles are not typically used for electrical conduits or cable trays. These applications usually require specialized materials and designs that are specifically engineered for electrical installations to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Q:How do steel angles perform under cyclic or alternating loading conditions?
- Steel angles generally perform well under cyclic or alternating loading conditions. Due to their structural shape and material properties, steel angles have good resistance to fatigue and can withstand repeated loading without significant loss of strength or deformation. Their high strength and stiffness make them suitable for applications that involve cyclic loading, such as in construction and engineering structures. Additionally, steel angles have the advantage of being relatively easy to fabricate and install, making them a popular choice in various industries.
- Q:How do steel angles contribute to the resiliency of a structure?
- Steel angles contribute to the resiliency of a structure in several ways. Firstly, they provide additional structural support and stability by distributing the load across different members. Steel angles are often used as reinforcements or braces in construction projects, allowing for the transmission of forces and preventing excessive deflection or deformation. This helps to resist the impact of external forces such as wind, earthquakes, or heavy loads, enhancing the structure's overall resilience. Moreover, steel angles are highly durable and corrosion-resistant, which further adds to the resiliency of a structure. Steel, as a material, has exceptional strength and longevity, making it ideal for withstanding harsh environmental conditions and potential structural failures. This durability ensures that the structure can withstand the test of time, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements and improving its overall resilience. Additionally, steel angles offer flexibility in design and construction, allowing for efficient load transfer and optimized structural configurations. They can be easily customized and fabricated to meet specific project requirements, ensuring that the structure can be tailored to withstand various dynamic and static loads. This adaptability enhances the resiliency of the structure by enabling it to adapt to changing conditions or future modifications. Overall, steel angles play a crucial role in enhancing the resiliency of a structure by providing additional support, durability, and flexibility. Their ability to distribute loads, resist external forces, and withstand harsh conditions ensures that the structure can withstand unexpected events and maintain its integrity, making steel angles an essential component in resilient construction practices.
- Q:Can steel angles be used for mezzanine floors?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for mezzanine floors. Steel angles are commonly used as structural supports in construction, and they provide strength and stability to mezzanine floors. They can be used to create the framework and support the decking materials of the mezzanine floor, ensuring its durability and safety.
- Q:Can steel angles be used for support columns?
- Indeed, support columns can utilize steel angles. In construction, steel angles are widely employed as structural elements, serving to offer support and stability for diverse building components. Their robustness, longevity, and load-bearing capacity make them particularly fitting for use as support columns. By virtue of their ability to be tailored and manufactured to meet specific structural needs, steel angles prove to be an excellent option for sustaining heavy loads or providing vertical support in different building applications. Furthermore, steel angles offer flexibility in terms of size, shape, and connection alternatives, enabling tailored column designs that effectively distribute loads and guarantee structural soundness. In summary, steel angles are a dependable and extensively utilized choice for support columns in various construction undertakings.
- Q:How do you inspect and measure the dimensions of a steel angle?
- To inspect and measure the dimensions of a steel angle, you can follow the following steps: 1. Gather the necessary tools: You will need a measuring tape or ruler, a protractor, and a square. 2. Start by examining the length of the steel angle. Place one end of the measuring tape or ruler at one end of the angle and extend it to the opposite end. Ensure that the measuring tape is straight and aligned with the edge of the angle. Read the measurement in inches or millimeters to determine the length. 3. Next, measure the width or thickness of the angle. Place the measuring tape or ruler perpendicular to the length of the angle, and measure the distance between the two parallel sides. This will provide you with the width measurement. 4. To measure the height or depth of the angle, place the measuring tape or ruler perpendicular to the width measurement. Again, ensure that the measuring tape is aligned with the edge of the angle and measure the distance between the two sides. This will provide you with the height measurement. 5. To ensure that the angle is accurately 90 degrees, use a square. Place the square against one side of the angle and ensure that it is aligned with the adjacent side. Check if the corner of the angle fits perfectly within the square. If it does, the angle is indeed 90 degrees. If not, it may be necessary to adjust or correct the angle. 6. Lastly, if you need to measure the angle of the steel angle, you can use a protractor. Align one side of the protractor with one side of the steel angle and see where the other side intersects with the protractor scale. Read the angle measurement to determine the exact angle. By following these steps and using the appropriate tools, you can effectively inspect and measure the dimensions of a steel angle.
- Q:Are steel angles resistant to corrosion?
- Yes, steel angles are generally resistant to corrosion. Steel angles are commonly made from carbon steel or stainless steel, both of which have inherent corrosion-resistant properties. Carbon steel angles have a protective layer of iron oxide, known as rust, which forms on their surface when exposed to oxygen and moisture. This rust layer acts as a barrier, preventing further corrosion of the underlying metal. Stainless steel angles, on the other hand, contain a minimum of 10.5% chromium, which forms a thin, transparent oxide layer on the surface. This oxide layer, called a passive film, provides excellent corrosion resistance, making stainless steel angles highly resistant to rust and other forms of corrosion. However, it is important to note that steel angles can still corrode under certain conditions, such as prolonged exposure to high levels of moisture or corrosive chemicals. Regular maintenance and proper cleaning can help extend the lifespan of steel angles and enhance their corrosion resistance.
- Q:What are the different tolerances for steel angles?
- The different tolerances for steel angles depend on the specific manufacturing standards and specifications. Generally, the tolerances for steel angles are determined by the governing bodies or organizations that set industry standards, such as the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The tolerances for steel angles can vary based on factors such as the angle's dimensions, shape, and intended application. These tolerances ensure that the angles meet the required dimensional and geometric specifications, allowing them to be used effectively in various structural or engineering applications. Some common tolerances for steel angles include: 1. Dimensional Tolerances: These tolerances define the allowable variations in length, width, and thickness of the angle. For example, a 90-degree angle might have a tolerance of +/- 1/8 inch in its leg length or a maximum deviation of 2 degrees from the specified angle. 2. Straightness Tolerances: This tolerance measures the allowable deviation from a straight line along the length of the angle. It ensures that the angle does not have excessive bends or twists, which may affect its structural integrity. 3. Surface Finish Tolerances: These tolerances specify the acceptable variations in the surface finish of the angle, such as roughness or surface irregularities. They ensure that the angle meets the required aesthetic and functional standards. 4. Squareness Tolerances: Squareness tolerance measures the maximum allowable deviation from a perfect right angle for angles that are specified to be 90 degrees. It ensures that the angle maintains its intended shape and can be properly joined or connected to other components. 5. Weight Tolerances: These tolerances define the acceptable variations in the weight of the steel angle. They ensure that the angle meets the specified weight requirements, which may be crucial in applications where weight distribution plays a role. It is important to note that the specific tolerances for steel angles may vary depending on the region, industry, or project requirements. Therefore, it is essential to consult the relevant standards or specifications to determine the appropriate tolerances for a specific steel angle.
- Q:How do you measure the dimensions of a steel angle?
- To measure the dimensions of a steel angle, you can use a measuring tape or ruler to determine the length of the two sides that form the angle. Additionally, you can measure the thickness of the steel angle using a caliper or a micrometer.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Equal Angle steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords


























