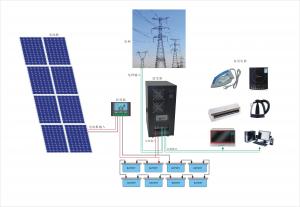
CNBM On Grid System 9000W with Certificate UL TUV CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Item specifice
CNBM On Grid System 9000W with Certificate UL TUV CE
Product description
They range from small residential and commercial rooftop systems to large utility-scale solar power stations. Unlike stand-alone power systems, a grid-connected system rarely includes an integrated battery solution, as they are still very expensive. When conditions are right, the grid-connected PV system supplies the excess power, beyond consumption by the connected load, to the utility grid.
Connection of the photovoltaic power system can be done only through an interconnection agreement between the consumer and the utility company. The agreement details the various safety standards to be followed during the connection.[4]
Electrical connections are made in series to achieve a desired output voltage and/or in parallel to provide a desired current capability. The conducting wires that take the current off the modules may contain silver, copper or other non-magnetic conductive [transition metals]. The cells must be connected electrically to one another and to the rest of the system. Externally, popular terrestrial usage photovoltaic modules use MC3 (older) or MC4 connectors to facilitate easy weatherproof connections to the rest of the system.

Application
Industrial
Commercial
Residential
Feature
Residential, grid-connected rooftop systems which have a capacity more than 10 kilowatts can meet the load of most consumers.[2] They can feed excess power to the grid where it is consumed by other users. The feedback is done through a meter to monitor power transferred. Photovoltaic wattage may be less than average consumption, in which case the consumer will continue to purchase grid energy, but a lesser amount than previously. If photovoltaic wattage substantially exceeds average consumption, the energy produced by the panels will be much in excess of the demand. In this case, the excess power can yield revenue by selling it to the grid. Depending on their agreement with their local grid energy company, the consumer only needs to pay the cost of electricity consumed less the value of electricity generated. This will be a negative number if more electricity is generated than consumed.[3] Additionally, in some cases, cash incentives are paid from the grid operator to the consumer.
Packaging
With carton and box
- Q:How do solar energy systems impact public health?
- Solar energy systems have a positive impact on public health. They reduce air pollution associated with fossil fuel combustion, leading to improved air quality and decreased respiratory diseases. Additionally, solar energy systems do not produce hazardous waste or emissions, reducing the risk of water and soil contamination. Overall, the adoption of solar energy systems promotes a healthier environment and enhances public health outcomes.
- Q:Are solar energy systems suitable for residential use?
- Yes, solar energy systems are suitable for residential use. They provide a clean and renewable source of energy, reduce electricity bills, and help homeowners become more self-sufficient. With advancements in technology and decreasing costs, solar energy systems have become increasingly popular and accessible for residential use.
- Q:Can solar energy systems be used in powering art galleries or museums?
- Art galleries and museums can definitely utilize solar energy systems to power their establishments. In fact, there are numerous benefits associated with the use of solar power in these venues. Firstly, due to their large spaces and extensive lighting systems, art galleries and museums consume a significant amount of energy. By implementing solar energy systems, these establishments can generate a substantial amount of electricity, reducing their reliance on traditional energy sources and cutting down on operating expenses. Furthermore, incorporating solar energy aligns with the environmental values often associated with art and culture. By utilizing clean and renewable energy, art galleries and museums can greatly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts in fighting climate change. Additionally, solar energy systems provide a reliable source of power, particularly during peak hours when galleries and museums experience a high influx of visitors. Moreover, the installation of solar panels on the rooftops of these establishments can serve as a visual representation of their commitment to sustainability, inspiring visitors to adopt similar practices in their own lives. However, it is important to consider that the feasibility of solar energy systems in art galleries or museums may vary depending on factors such as available roof space, geographical location, and specific energy requirements. Conducting a comprehensive assessment and feasibility study is vital to determine the optimal size and configuration of the solar energy system for each individual establishment. Overall, solar energy systems offer a clean, renewable, and cost-effective solution for powering art galleries and museums. Implementing these systems not only aligns their operations with sustainable practices but also reduces their environmental impact.
- Q:How often do solar energy systems need to be cleaned?
- Solar energy systems generally need to be cleaned at least once or twice a year. However, the frequency of cleaning can vary depending on factors such as the local climate, amount of dust or debris accumulation, and location of the solar panels.
- Q:What is the impact of lightning on solar panels?
- The impact of lightning on solar panels can be significant and potentially damaging. Lightning strikes can cause immediate damage to the solar panels themselves, leading to malfunctions or complete destruction. The intense heat generated by lightning can melt or vaporize the materials used in the solar panels, resulting in irreparable damage. Moreover, lightning strikes can also cause electrical surges that can travel through the solar panel system and damage other connected equipment, such as inverters, charge controllers, or batteries. These power surges can overload and fry the delicate electrical components within the system, rendering them inoperable. To mitigate the impact of lightning, solar panel installations often include surge protectors or lightning arrestors to redirect the high-voltage electrical currents away from the solar panels and other sensitive equipment. These protective measures help to minimize the risk of damage to the solar panel system. However, even with these precautions in place, lightning strikes can still pose a threat to solar panels. Therefore, it is advisable to have a comprehensive insurance policy that covers lightning damage for solar panel installations. Regular maintenance and inspection of the solar panel system can also help identify any potential issues caused by lightning strikes and enable timely repairs. Overall, the impact of lightning on solar panels can be detrimental, leading to immediate damage and potential long-term consequences for the entire solar panel system. Taking precautionary measures, having proper insurance coverage, and monitoring the system's condition are essential to minimize the risk and ensure the longevity of solar panel installations.
- Q:Can solar energy systems be installed in areas with heavy snowfall?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be installed in areas with heavy snowfall. However, it is important to consider the impact of snow on the system's performance and take necessary precautions during installation. Snow can temporarily reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the solar panels, which in turn reduces their energy production. However, the panels are designed to have a tilt and smooth surface, allowing snow to slide off easily. Additionally, advancements in technology have led to the development of snow-resistant solar panels that are more effective at converting sunlight into electricity even in snowy conditions. It is also worth noting that solar panels are often mounted at an angle to maximize their exposure to the sun, which helps to minimize snow accumulation. Overall, while heavy snowfall may impact the efficiency of solar energy systems, they can still be successfully installed and can contribute to renewable energy generation in areas with such climatic conditions.
- Q:How much space do I need for a solar energy system?
- The space required for a solar energy system depends on various factors such as the size of the system, the amount of energy needed, and the efficiency of the solar panels. In general, for a residential solar energy system, you would need a roof space of about 100-400 square feet per kilowatt (kW) of solar panels. However, there are alternative options like ground-mounted systems or solar canopies that can be used if roof space is limited. It is recommended to consult with a solar energy professional who can assess your specific energy needs and available space to determine the appropriate size and configuration of the system.
- Q:Are solar energy systems suitable for commercial buildings?
- Yes, solar energy systems are suitable for commercial buildings. They offer numerous benefits such as reduced energy costs, increased energy efficiency, and a positive environmental impact. Additionally, solar panels can be easily installed on rooftops or as ground-mounted systems, making them a viable option for various types of commercial buildings.
- Q:What is the difference between on-grid and off-grid solar energy systems?
- On-grid solar energy systems are connected to the main electrical grid, allowing for the excess energy produced by the solar panels to be fed back into the grid for credits or compensation. This means that on-grid systems rely on the grid for power when sunlight is unavailable. On the other hand, off-grid solar energy systems are standalone systems that are not connected to the main electrical grid. This type of system typically relies on battery storage to store excess energy produced during the day, which can then be used during the night or when sunlight is not available. In summary, the main difference between on-grid and off-grid solar energy systems lies in their connection to the electrical grid and the reliance on external sources of power.
- Q:How does solar energy impact job creation?
- Solar energy impacts job creation by creating a significant number of employment opportunities in various sectors such as manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research and development. The growth of the solar energy industry has led to the creation of numerous jobs, both in the renewable energy sector and related industries. This includes positions for engineers, technicians, project managers, salespeople, and more. Additionally, as solar energy becomes more affordable and widely adopted, it stimulates economic growth and encourages investments, further boosting job creation in local communities.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
CNBM On Grid System 9000W with Certificate UL TUV CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords