Aluminum sheet,plate with smooth surface
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 9000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
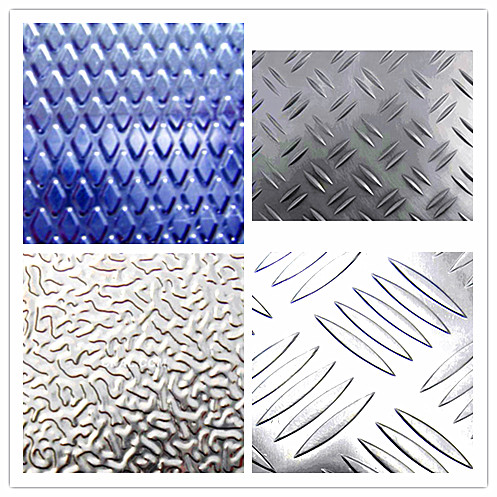
Aluminum Checkered Plate for Five-Bar :
two bar five bar Aluminum Checkered Sheet Plate
1.Alloy: 1100 1200 1050 2024 2014 2017 3003 5052 6061 6063 etc.
2. Temper: O, F, H111, H112, H12 ,H14, H16, H18, H19, H22, H24, H26, H32, H34, H36, H38, T3, T4 , T6, T7, T351 , T451, T651, T851.
3. Dimensions can be produced according to clients specifications.
4.Good plasticity, conductivity.
5. Generally used in industry and architecture industries.
Packing,
Covering with standard and package or according to your demand.

Machinability :
This alloy has relatively fair machinability. It is easier to machine in the hard temper than as annealed and the quality of finish is better if machined in the hard condition. Oil lubricants should be used for machining, except that very light cuts may .

Forming :
AL 5052 is readily formed at room temperature. Successive cold working decreases the formability.
Corrosion Resistance :
Corrosion resistance to salt water and general atmospheric conditions is good.
Heat Treatment:
AL 5052 cannot be hardened by means of heat treatment. It does harden due to cold working.
- Q:How does the surface finish of aluminum sheet affect its cleaning requirements?
- The cleaning requirements of aluminum sheet are significantly influenced by its surface finish. Various surface finishes, such as mill finish, brushed finish, or anodized finish, can impact how dirt, grime, and other contaminants adhere to the surface. Smooth and polished surface finishes like brushed or anodized are generally more resistant to dirt and stains, making them simpler to clean. These finishes have a lower surface roughness, resulting in fewer areas for dirt particles to stick to. As a result, they can be effectively cleaned using gentle cleaning solutions or even just water and a soft cloth. Conversely, aluminum sheets with a mill finish or a rougher surface may require more rigorous cleaning methods. The higher surface roughness of these finishes can create more areas for dirt and grime to become trapped, making it more difficult to remove them with basic cleaning techniques. In such cases, more aggressive cleaning solutions or abrasive cleaning tools may be necessary to eliminate stubborn stains or dirt particles. It should be noted that the specific cleaning requirements for aluminum sheet also depend on the type and severity of the contaminants present. For example, if the aluminum sheet comes into contact with harsh chemicals or corrosive substances, special cleaning methods may be needed to ensure complete removal and prevent any potential damage. In conclusion, the surface finish of aluminum sheet directly affects the cleaning requirements. Smoother and polished finishes are generally easier to clean due to their lower surface roughness, while rougher finishes may require more rigorous cleaning methods. Understanding the surface finish of aluminum sheet is crucial in determining the most suitable cleaning techniques to maintain its appearance and functionality.
- Q:A sample of aluminum and a sample of steel have superficially identical microstructures. Which would you expect to be stronger, and why?
- If you define stronger to be a higher yield strength, then it's about dislocation movement. Dislocations form as a material begins to deform. As more deformation occurs, dislocations begin to move. Since steel is iron with impurities (namely carbon), these impurities impede dislocation movement. Aluminum, in pure form, does not have anything to impede dislocation movement except for the grain boundaries of the microstructure, which the steel also has if the microstructures are identical. If you define stronger as in ultimate tensile strength, then it becomes an issue of bond strength. Basically how tightly iron atoms bond to one another versus aluminum atoms. There are some quantum mechanical considerations at this point, but I won't get into those details.
- Q:What are the different methods for perforating aluminum sheets?
- There are several different methods for perforating aluminum sheets, each with its own advantages and applications. Some of the most common methods include: 1. Punching: Punching is one of the most traditional methods for perforating aluminum sheets. It involves using a punch and die set to create holes in the material. This method is efficient and cost-effective for producing simple hole patterns and is commonly used in industries such as automotive and construction. 2. Laser cutting: Laser cutting is a precise and versatile method for perforating aluminum sheets. It uses a high-powered laser beam to vaporize or melt the metal, creating intricate and complex hole patterns. This method is highly accurate, fast, and suitable for a wide range of applications, including decorative and functional perforations. 3. Waterjet cutting: Waterjet cutting is another popular method for perforating aluminum sheets. It uses a high-pressure jet of water mixed with abrasive materials to erode the metal and create holes. Waterjet cutting is known for its ability to cut through thick aluminum sheets and produce clean and precise edges. It is commonly used in industries such as aerospace and architecture. 4. Rotary perforating: Rotary perforating involves using a rotating cylindrical tool with sharp blades or teeth to perforate aluminum sheets. This method is ideal for producing continuous perforations or creating patterns that require curved or irregular hole shapes. Rotary perforating is commonly used in applications such as filtration systems and acoustic panels. 5. Pressing: Pressing, also known as embossing or stamping, is a method that involves pressing a patterned die into an aluminum sheet to create raised or sunken areas. These areas can act as perforations, providing aesthetic appeal or functional applications such as slip resistance. Pressing can be achieved using hydraulic or mechanical presses and is commonly used in industries such as architecture and interior design. It is worth noting that the choice of perforation method depends on various factors, including the desired hole pattern, material thickness, production volume, and budget. Consulting with a perforation specialist can help determine the most suitable method for a specific application.
- Q:When water continually sprays on the aluminum sheet, how to avoid corrosion of aluminum sheet and keep its water resistance?
- Don’t worry about it, after aluminum contacts water or air, a layer of oxide film will generate on its surface to separate aluminum from the water or air and protect it, so it won’t be erosive.
- Q:How do you form curves or shapes in aluminum sheets?
- There are several methods to form curves or shapes in aluminum sheets. One common technique is called bending, where the sheet is clamped and then gradually bent using a mechanical press brake or a hammer. Another method is called roll forming, which involves passing the aluminum sheet through a series of rollers to achieve the desired shape. Additionally, aluminum sheets can be molded or pressed into curves or shapes using specialized tools or dies.
- Q:Is aluminium plate the same as aluminium alloy?
- Oh, No. aluminum contains only aluminum, and there are some other metals besides aluminium.
- Q:What is the typical shear strength of aluminum sheets?
- The typical shear strength of aluminum sheets can vary depending on various factors such as the alloy, temper, thickness, and manufacturing process. However, for most common aluminum alloys, the typical shear strength falls within the range of 207 to 310 megapascals (MPa) or 30,000 to 45,000 pounds per square inch (psi). It is important to note that these values are just general guidelines and there can be variations depending on the specific application and conditions. For critical applications, it is recommended to consult the material specifications or seek professional advice to determine the precise shear strength requirements for the specific aluminum sheet being used.
- Q:My frame snapped and I want to fix it by welding it back together. In order to do that, I need to know what all is in the aluminum.
- You can NOT weld back an aluminum frame unless you have the facilities to anneal and heat treat the frame again. Rewelding without the post treatments will result in a very soft area around the new weld causing sudden catastrophic failure... this means if you are riding it could fail at any time causing injury or death. EDIT: Wait just a durn minute. The 2100 and 2300 had carbon fiber tubes bonded to aluminum lugs and stays. If your bike failed then you ABSOLUTELY should not try to weld it. The heat from welding (even if you had post treatment facilities) would destroy the bond between the CF and aluminum. Fair warning- cut the frame apart and throw it away.
- Q:Can aluminum sheets be anodized for added durability?
- Yes, aluminum sheets can be anodized for added durability. Anodizing is an electrochemical process that creates a protective oxide layer on the surface of aluminum. This layer not only enhances the appearance of the material but also increases its resistance to corrosion, wear, and scratches. Anodizing provides a hard, durable, and long-lasting finish, making it an ideal choice for various applications where durability is crucial, such as in construction, automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. Additionally, anodized aluminum sheets can be dyed in various colors, further enhancing their aesthetic appeal while maintaining their durability.
- Q:What are the different methods for cutting aluminum sheets?
- Aluminum sheets can be cut using various methods that are commonly employed. 1. Shearing: To make a straight cut through the aluminum sheet, a sharp blade is used in this method. Shearing is typically used for thinner sheets and results in clean and straight cuts. 2. Sawing: Another method for cutting aluminum sheets is sawing. It involves the use of a saw blade with small teeth to cut through the material. Sawing can be done manually or with the assistance of power tools like band saws or circular saws. 3. CNC Machining: For highly precise cutting of aluminum sheets, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is employed. This method utilizes a computer-controlled machine that follows programmed instructions to achieve the desired shape. CNC machines are capable of creating complex cuts and shapes with great accuracy. 4. Laser Cutting: A non-contact method, laser cutting, employs a high-powered laser to cut through aluminum sheets. The laser beam melts or vaporizes the aluminum, resulting in a clean and precise cut. Laser cutting is commonly used for intricate designs and offers a high level of precision. 5. Waterjet Cutting: Waterjet cutting involves the use of a high-pressure jet of water mixed with an abrasive substance to cut through aluminum sheets. This method is versatile and can be used for various materials and thicknesses. It produces clean cuts without generating heat, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials as well. 6. Plasma Cutting: Plasma cutting utilizes a high-temperature plasma arc to cut through aluminum sheets. The plasma arc melts the metal and blows away the molten material, creating the desired cut. This method is commonly used for thicker aluminum sheets and can be done manually or with the assistance of CNC machines. These different cutting methods offer varied precision levels, speeds, and suitability for different sheet thicknesses and designs. The choice of cutting method depends on factors such as the desired cut quality, aluminum sheet thickness, and specific project requirements.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Aluminum sheet,plate with smooth surface
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 9000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords





























