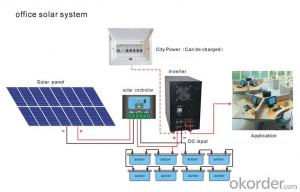
Solar System Module
Solar System Module Related Searches
Primer For Galvanized Steel H S Code For Stainless Steel Wd 40 For Stainless Steel Spray Paint For Stainless Steel Glue For Stainless Steel Step Bit For Stainless Steel Magnets For Stainless Steel Caulking For Stainless Steel Steel Vessels For Kitchen Best Solar Inverter For HomeHot Searches
Steel Mesh Panels For Sale Cheap High Tea Sets For Sale High Density Fiberboard For Sale Solar Hot Water Collectors For Sale Scaffolding For Sale In Uae Scaffolding For Sale In Ireland Scaffolding For Sale In Houston Type Of Inverter For Solar Price Of Shipping Containers For Sale Used Solar Inverter For Sale Portable Led Signs For Sale Stone Hot Water Bottles For Sale Large Led Screens For Sale 1/4 Aluminum Plate For Sale H4 Led Headlight Bulbs For Sale Flexible Solar Cells For Sale Air Pump For Aquarium Price Inverter Size For Solar System Solar Edge Inverter For Sale Aluminum Bar Stock For SaleSolar System Module Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Okorder.com is a professional Solar System Module supplier & manufacturer, offers integrated one-stop services including real-time quoting and online cargo tracking. We are funded by CNBM Group, a Fortune 500 enterprise and the largest Solar System Module firm in China.Hot Products
FAQ
- i don't know very much about it, but can you somehow take off the little solar panels off of the outdoor light things and make it so you can hook an outlet up to it and plug in to it like a phone charger for electricity.
- Little solar panels on lights are very low power. The battery in one such may be 0.5 Amp-hours and .2 V ; it may be different but it should be marked on the panel/battery/manual. An outlet in your house is designed to run on 20 V (typically in N. Am.) and they run on alternating current (AC) whereas the panel generates direct current (DC). (If you don't know the difference, do not worry to much but just understand that they are not directly compatible.) You therefore need an inverter to change DC to AC (and lose some although inverters are now very efficient). But the amount of power generated by those panels is still very small. That is why solar lights are low power (just a few watts in most cases). To make things even more irritating, phone chargers do not work off 20 V AC as you are charging the battery and need a low voltage DC -- which is what the solar panel is giving you. It is almost certain that the voltage from the panel will be less than the voltage required for the phone. The charger is mostly cable but there is a black box incorporated and it should say what the voltage and current output are (the input will be 20V). So you should be able to overcome this not by hooking up the panel to a 20V outlet and then plugging the charger in but by hooking up the panel to the phone directly if you can get enough voltage out of the solar panel (or hook up several) and if you fashion a connection device. They already make them -- solar battery chargers and I am sure you can enter that into a search engine and find loads. Typically the panel alone is much more than a solar light -- which shows the relative power requirements.
- Where can I find the info (sites) that clearly gives the anatomy of a solar panel?Likewise, I want to know where can I find (sites) the solar panel that produces 3.75 v? Thank you very much!!!
- You've probably seen calculators that have solar cells -- calculators that never need batteries, and in some cases don't even have an off button. As long as you have enough light, they seem to work forever. You may have seen larger solar panels -- on emergency road signs or call boxes, on buoys, even in parking lots to power lights. Although these larger panels aren't as common as solar powered calculators, they're out there, and not that hard to spot if you know where to look. There are solar cell arrays on satellites, where they are used to power the electrical systems. You have probably also been hearing about the solar revolution for the last 20 years -- the idea that one day we will all use free electricity from the sun. This is a seductive promise: On a bright, sunny day, the sun shines approximately ,000 watts of energy per square meter of the planet's surface, and if we could collect all of that energy we could easily power our homes and offices for free.
- Yes, there are a few risks associated with solar panel installation. These include potential damage to the roof during installation, the risk of electrical shocks or fires if the system is not properly installed or maintained, and the possibility of reduced energy production if the panels are not positioned correctly or if they become shaded over time. It is important to hire experienced and licensed professionals to minimize these risks and ensure a safe and efficient installation process.
- Hi, I am starting to get curious about the pros/cons of installing solar panels - has anyone done it and is it worth it?
- In the state of Pennsylvania in the USA, a very basic 5KW solar installation will cost you $35,000. Of that you will recover approximately $28,000 over the next five (5) years between the State and the Feds. Making your net-cost something between $7,000 and $9,000 depending on various factors. All other things being equal in a standard household with fuel-based heat and window units vs. central AC, this system will provide roughly 50% of power required with a payback of approximately eight (8) years (with electricity at $0.4/kwh). The system has an estimated forty (40) year service life. Without _all_ the subsidies, the payback is longer than the estimated system life, especially if you consider the time-value of money. The life-cycle cost of a photo-voltaic array is horrendous. By that, I mean the total cost of producing the panels, installing them, and then removing them and disposing of them in an environmentally correct manner. All that added in and there is a negative payback. So, it all depends on what one defines as worth it. Putting the cost onto taxpayers via governmental subsidy to make an otherwise wretchedly expensive process viable may give you all sorts of warm-and-fuzzy feelings about renewable resources and reducing dependence on foreign oil and so forth. But the reality is that the true cost of solar panels exceeds that of nuclear power per KW delivered. Even today when nuclear plants start in the Billions-with-a-B in any currency you would care to name.
- Does anybody know if there are any courses for solar panel installation, and/or what trades you need for this position?
- In Europe the governments offer an electrical buy back incentive of surplus solar electricity but to claim the income the solar panels must be installed by a registered installer who submits details of their skills. The skill to install requires some experience in building/roofing work for which there is no qualification and an electrician to wire up the components to the mains. Electrical engineering courses are available at local tech colleges. If you are just installing a 2/24 volt system you don't really need much experience, it is not syncing a full mains voltage in to the domestic mains! Installing thermal [water] solar uses similar building skills and requires he final fix to be performed by a heating engineer, again the course is available at tech colleges. both plumbing and electrical engineers need to be updated on changes and so there is ongoing education costs and licenses. If you can't afford college [two year +] try finding an employer who will let you work and study part time. There is a lot of demand here so few employers pay for the course but some do. go through your yellow pages and submit your cv to electricians/plumbers. Then when you get qualified learn about solar, and set up your own business. As a builder of sorts! Ive fitted systems and then found a electrician/plumber to do the final fix. You cant beat experience.
- I'm writing a post-apocalyptic story in it the main character finds a warehouse. Eventually he finds out the roof is covered with commercial solar panels. Given it's been over a year since the majority of the world died no manainence was done, do they still work?
- In my experience working with solar panels, I've found that the panels themselves are robust and can last years. How that energy is transferred from the panel to perform work (sorry for the boffinism) is where the complexity emerges, namely due to the fact solar panels produce DC current, and nearly all of our electrical appliances use AC current. In most cases, solar panels will either send energy through a DC/AC inverter directly to be used for appliances, or stored in deep cycle batteries, then converted to AC using an inverter when the user wants to use his/her appliance. Now to answer your question: the solar panels will be fine, and could conceivably be in fine working order with AC current available IF... and I cannot stress this enough (namely through years of field experience dealing with solar powered scientific instrumentation that was working well and then mysteriously not working)... IF rats and other rodents haven't eaten through the wires. This is probably the most likely reason that a set of solar panels wouldn't be working in your given scenario. Hope this helps, and good luck!!
- Solar panels are designed to be durable and withstand various weather conditions, including hail. They are made with tempered glass that is highly resistant to impact, ensuring that hailstones won't damage the panels. Additionally, the panels undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can withstand extreme weather conditions, such as strong winds and heavy snow. The frame surrounding the panels also provides stability and protection.
- Yes, solar panels can be used in areas with high levels of dust storms. However, it is important to regularly clean and maintain the panels to ensure optimal performance. Dust storms may cause a temporary decrease in energy production, but it can be mitigated by implementing proper maintenance practices such as cleaning the panels and installing protective measures like dust shields.